UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
x ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2018
o TRANSITION REPORT UNDER SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1934
FOR THE TRANSITION PERIOD FROM TO
Commission file number 001-14775
DMC Global Inc.
(Exact name of Registrant as Specified in its Charter)
|
| | |
Delaware | | 84-0608431 |
(State of Incorporation or Organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
5405 Spine Road, Boulder, Colorado 80301
(Address of principal executive offices, including zip code)
(303) 665-5700
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
| | |
Title of each class | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
Common Stock, $.05 Par Value | | The Nasdaq Global Select Market |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act from their obligations under those sections. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of the registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
| | |
Large accelerated filer o | | Accelerated filer x |
| | |
Non-accelerated filer o | | Smaller reporting company o |
| | |
| | Emerging growth company o |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 under the Act). Yes o No x
The approximate aggregate market value of the voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was $534,852,796 as of June 30, 2018.
The number of shares of Common Stock outstanding was 14,902,894 as of February 21, 2019.
Certain information required by Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 of Form 10-K is incorporated by reference into Part III hereof from the registrant’s proxy statement for its 2019 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which is expected to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) within 120 days of the close of the registrant’s fiscal year ended December 31, 2018.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PART I
ITEM 1. Business
References made in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to “we”, “our”, “us”, “DMC” and the “Company” refer to DMC Global Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries. Unless stated otherwise, all dollar figures in this report are presented in thousands (000s).
Overview
DMC Global Inc. operates two technical product and process business segments, DynaEnergetics and NobelClad, which collectively serve the energy, industrial and infrastructure markets. DynaEnergetics designs, manufactures and distributes products utilized by the global oil and gas industry principally for the perforation of oil and gas wells. NobelClad is a global leader in the production of explosion-welded clad metal plates for use in the construction of corrosion resistant industrial processing equipment and specialized transition joints. Both DynaEnergetics and NobelClad operate globally through an international network of manufacturing, distribution and sales facilities. See Note 6 within Item 8 — Financial Statements and Supplementary Data for net sales, operating income, and total assets for each of our segments.
Our Strategy
Our diversified segments each provide a suite of unique technical products to niche sectors of the global energy, industrial and infrastructure markets, and each has established a strong position in the markets in which it participates. With an underlying focus on generating free cash flow, our objective is to sustain and grow the market share of our businesses through increased market penetration, development of new applications, and research and development of new and adjacent products that can be sold across our global sales and distribution network. We routinely explore acquisitions of related businesses that could strengthen or add to our existing product portfolios, or expand our geographic footprint and market presence. We also seek acquisition opportunities outside our current markets that would complement our existing businesses, diversify our end markets and revenue streams, and enable us to build a stronger company.
Business Segments
DynaEnergetics
DynaEnergetics designs, manufactures, markets and sells perforating systems and associated hardware for the international oil and gas industry. The oil and gas industry uses perforating products to punch holes in the casing or liner of wells and create a flow path in the formation, thereby connecting the well to the surrounding reservoir. During the drilling process, steel casing and cement are inserted into the well to isolate and support the wellbore. As part of the well completion process, the perforating guns, which contain a series of specialized shaped charges, are lowered into the well to the desired area of the targeted formation. When initiated, the shaped charges shoot a plasma jet through the casing and cement and into the formation. The resulting channels in the formation allow hydrocarbons to flow into the wellbore.
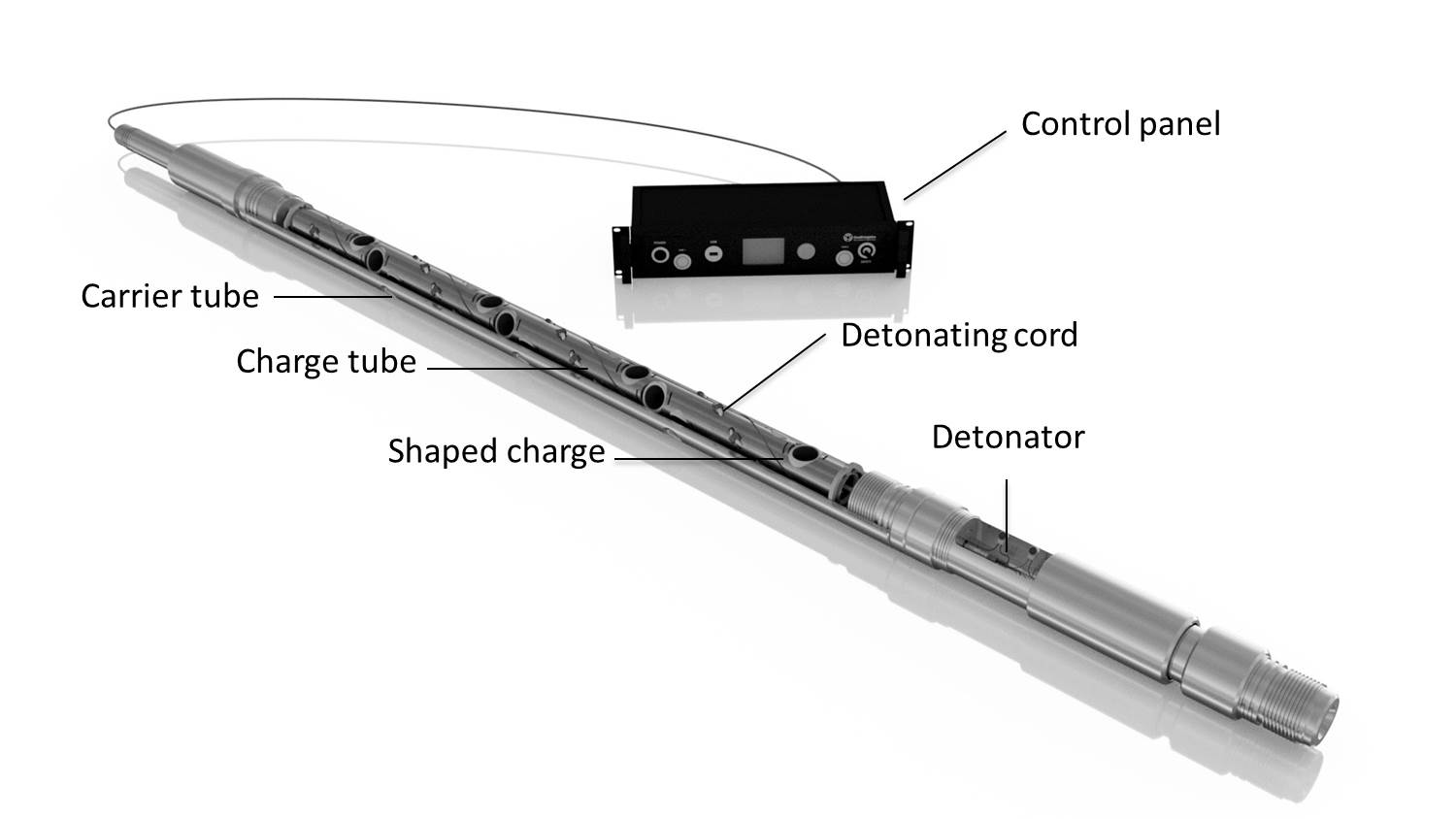
DynaEnergetics designs, manufactures and sells all five primary components of a perforating system, which are: 1) carrier tubes and charge tubes, 2) shaped charges, 3) detonating cord, 4) detonators and initiating systems, and 5) control panels. In addition, DynaEnergetics has leveraged its broad product portfolio and detonator technology to create a unique factory-assembled, performance-assured well perforating system known as DynaStage® The DynaStage system arrives fully assembled at the well, thereby reducing the customers’ need for field assembly crews and associated infrastructure.
PRIMARY COMPONENTS OF A PERFORATING SYSTEM
The types of perforating products manufactured by DynaEnergetics are essential to oil and gas recovery. These products are sold to oilfield service companies around the world. DynaEnergetics also promotes its technologies and systems directly with end-user exploration and production companies. The level of market activity for perforating products, which are used during the well completion process, generally corresponds with the level of oil and gas exploration and production ("E&P") activity. Modern E&P activity has led to increasingly complex well completion operations, which in turn have increased the demand for high quality and technically advanced perforating products.
Operations
The DynaEnergetics segment seeks to build on its products and technologies, as well as its sales, supply chain and distribution network. During the three years ended December 31, 2018, 2017 and 2016, the DynaEnergetics segment represented approximately 73%, 63% and 42% of our consolidated net sales, respectively.
DynaEnergetics has been producing detonating cord and detonators and selling these along with seismic explosives systems for decades. Since 1994, the business has placed significant emphasis on enhancing its offering by improving existing products and adding new products through research and development as well as acquisitions. Today, DynaEnergetics offers a comprehensive portfolio of detonating cord, detonators, bi-directional boosters, shaped charges, and corresponding gun systems.
In recent years, DynaEnergetics has increased its development efforts and introduced several new products specifically designed for safe and selective perforating, particularly in North America’s growing onshore, unconventional oil and gas industry. Included among these products is the DynaSelectTM family of "intrinsically safe," integrated switch-detonators. DynaSelect detonators require a specific electronic code for firing and are immune from induced currents and voltages, static electricity and high-frequency irradiation. These safety features substantially reduce the risk of unintentional detonation and
enable concurrent perforating and hydraulic fracturing operations at drilling sites with multiple wellbores, improving operating efficiencies for customers.
Our DynaSelect products integrate our earlier Selectronic Switches with our "intrinsically safe" detonator technologies in a unique one-piece system for improved well site efficiency, reliability, simplicity and service quality. The fully integrated design incorporates advanced software controls and reduces the size of the detonator and switch assembly. DynaSelect reduces by 40% the number of electrical connections required within each perforating gun versus traditional selective initiation systems. This reduces set-up times and significantly increases reliability. The DynaSelect detonator is controlled by our Multitronic IV and V Firing Panels. These systems enable safe and reliable firing of up to 20 guns and setting a plug in a single run and incorporates a shot detection function resulting in significant time and cost savings.
Our DynaStage factory-assembled perforating system combines all our advanced technologies into a preassembled perforating gun that can be armed at the well site with the wireless DynaStage detonator, which incorporates all of the features of the intrinsically safe DynaSelect detonator. The DynaStage system is operated using Multitronic IV and our latest Multitronic V Firing Panel, and can be tested before going down hole using our Surface Tester, reducing the risk of lost time, mishaps, misruns and misfires due to a system fault. The Multitronic V Firing Panel is highly intuitive and allows the gun string to be safely tested and monitored throughout the pump-down operation. The Multitronic V panel introduces several new features designed to ease the use and the reliability of the system, including “shoot-on-the-fly” operation through an instant-fire capability. The patented plug-n-go design of the DynaStage wireless detonator reduces the potential for errors by eliminating the need for wiring and crimping.
Our DynaSlotTM perforating system is designed for well abandonment operations. During abandonment, the wellbore is encased and permanently sealed so that layers of sedimentary rock, and in particular freshwater aquifers, are pressure isolated from each other and the wellbore. The DynaSlot perforating system facilitates this process by creating access to a full 360-degree area between the rock formations and the tubing and casing. Customers use the unique, helical perforation pattern created by DynaSlot to perform cement squeeze operations that seal off the wellbore.
DynaEnergetics develops and sells a wide range of shaped charges for use in its perforating systems. These include the family of HaloFrac™ charges, which incorporate advancements in liner materials and shaped charge geometry designed to improve hydraulic fracturing performance through lower and more consistent breakdown pressures, uniform proppant placement, uniform frac clusters and higher well productivity ratios. Another line, FracTune™, delivers uniform hole diameter in the well casing independent of shot phasing and gun positioning within the well bore. DynaEnergetics also sells the DPEX™ family of charges, which feature energetic liners. All three lines can be used with the DynaStage perforating system as well as conventional perforating gun systems across a range of gun diameters.
DynaEnergetics Tubing Conveyed Perforating ("TCP") systems are customized for individual customer needs and well applications. TCP enables perforating of more complex highly deviated and horizontal wells. These types of wells are increasingly being drilled by the off-shore industry. TCP tools also perforate long intervals in a single trip, which significantly improves rig efficiency. Our TCP tool range includes mechanical and hydraulic firing systems, gun releases, redundant firing heads, under-balancing devices and auxiliary components. Our tools are designed to withstand downhole temperatures of up to 260 degrees Celsius (500 degrees Fahrenheit), for safe and quick assembly at the well site, and to allow unrestricted total system length.
DynaEnergetics’ manufacturing facilities are located in Germany, the United States and Russia. During the first half of 2018, DynaEnergetics added a second automated DynaSelect detonator line at its facility in Troisdorf, Germany, and plans to add two additional detonator lines there by the end of the second quarter of 2019. In the fourth quarter of 2018, DynaEnergetics completed construction of 74,000 square feet of new manufacturing, assembly and administrative space on its existing site in Blum, Texas, which substantially increased DynaEnergetics' component manufacturing and DynaStage assembly capacity. In early 2019, the business commissioned a second automated shaped charge manufacturing line at Blum and plans to finish the installation of an additional automated shaped-charge line there in the second quarter of 2019, which will more than triple its shaped charge production capacity in the U.S. We refer to the new construction and manufacturing lines collectively as the “Blum expansion”. These investments expanded our global capacity for shaped charge and perforating gun production and improved our delivery and customer service capabilities in our key markets.
Suppliers and Raw Materials
DynaEnergetics' product offering consists of complex components that require numerous high-end inputs. DynaEnergetics utilizes a variety of raw materials for the production of oilfield perforating and seismic products, including high-quality steel tubes, steel and copper, explosives, granulates, plastics and ancillary plastic product
components. DynaEnergetics obtains its raw materials primarily from a number of different producers in Germany, other European countries, and the U.S. but also purchases materials from other international suppliers.
Competition
DynaEnergetics faces competition from independent manufacturers of perforating products and from the industry's three largest oil and gas service companies, which produce most of their own shaped charges but also buy other perforating components and specialty products from independent suppliers such as DynaEnergetics. DynaEnergetics competes for sales primarily on customer service, product quality, reliability, safety, performance, price and, in North America, its ability to provide customers with a factory-assembled perforating system, versus a series of components that must be assembled at a well site or nearby staging facility.
Customer Profile
DynaEnergetics' perforating and seismic products are purchased by international and regional oilfield service companies of all sizes working in both onshore and offshore oil and gas fields. Our customers select perforating products based on their leading performance, system compatibility and ability to address a broad spectrum of factors, including pressures and temperatures in the borehole and geological characteristics of the targeted formation.
The customers for our oilfield products can be divided into five broad categories: purchasing centers of large service companies, international service companies, independent international and North America-based service companies (often referred to as “wireline” companies), oil companies with and without their own service companies, and local resellers.
Marketing, Sales, Distribution
DynaEnergetics’ worldwide marketing and sales efforts for its oilfield and seismic products are located in Troisdorf, Germany; Houston, Texas; and Tyumen, Siberia. DynaEnergetics’ sales strategy focuses on direct selling, distribution through licensed distributors and independent sales representatives, educating current and prospective service-company customers about our products and technologies, and educating E&Ps about the benefits of our products and technologies in an effort to generate pull-through demand. Currently, DynaEnergetics sells its oilfield and seismic products through wholly-owned affiliates in Germany, the U.S., Canada, and Russia and through independent sales agents in other parts of the world. DynaEnergetics serves the Americas region through its network of sales and distributions centers in the United States and Canada.
DynaEnergetics also designs and manufactures customized perforating products for third-party customers according to their designs and requirements.
Research and Development
DynaEnergetics devotes substantial resources to its research and development (R&D) programs. Based predominantly in Troisdorf, Germany, the R&D team works closely with sales, product management, and operations management teams to establish priorities and effectively manage individual projects. Through its ongoing involvement in oil and gas industry trade shows and conferences, DynaEnergetics has increased its profile in the oil and gas industry. In addition to its existing shaped charge test facility, which can simulate downhole, wellbore, and reservoir pressure conditions to develop and test high performance perforating charges for both oil companies and service providers, the R&D group has a purpose-built pressure vessel which can reach 30,000 psi test pressures and be heated to up to 200 degrees Celsius (392 degrees F). This enables the R&D group to support the oil and gas industry with test methods for new products that realistically simulate potentially difficult downhole conditions. An R&D plan, which focuses on new technology, products, process support and contracted projects, is prepared and reviewed at least quarterly. R&D costs are included in our cost of products sold and were $5,932, $4,335, and $3,990 for the years ended December 31, 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
NobelClad
Clad metal plates are typically used in the construction of heavy, corrosion resistant pressure vessels and heat exchangers. Clad metal plates consist of a thin layer of an expensive, corrosion-resistant cladder metal, such as titanium or nickel alloy, which is metallurgically welded to a less expensive structural backing metal, such as carbon steel. For heavy equipment, clad plates generally provide an economical alternative to building the equipment solely of a corrosion-resistant alloy. While a significant portion of the demand for our clad metal products is driven by maintenance and retrofit projects at existing chemical processing, petrochemical processing, oil refining, and aluminum smelting facilities, new plant construction
and large plant expansion projects also account for a significant portion of total demand. These industries tend to be cyclical in nature, and timing of new order inflow remains difficult to predict.
There are three major industrial clad plate manufacturing technologies: explosion welding, hot roll bonding and weld overlay. Detaclad®, NobelClad’s process-controlled explosion clad, uses explosion welding, the most versatile of the clad plate manufacturing methods. Created using a robust cold-welding technology, explosion-welded clad products exhibit high bond strength and combine the corrosion resistance of the cladder material with the mechanical properties and structural strength of the lower cost backer material. The explosion welding process is suitable for joining virtually any combination of common engineered metals. This represents a competitive advantage versus the hot roll bonding and weld overlay processes, which generally can only clad compatible metals such as nickel alloys and stainless steel.
Explosion-welded clad metal is produced as flat plates or concentric cylinders, which can be further formed and fabricated into a broad range of industrial processing equipment or specialized transition joints. When fabricated properly, the two metals will not come apart, as the bond zone is generally stronger than the parent metals. The dimensional capabilities of the process are broad: cladding metal layers can range from a few thousandths of an inch to several inches in thickness and base metal thickness and lateral dimensions are primarily limited only by the capabilities of the world’s metal production mills. Explosion welding is used to clad to steel to a broad range of metals, including aluminum, titanium, zirconium, nickel alloys and stainless steels.
Clad Metal End-Use Markets
Explosion-welded clad metal is primarily used in the construction of large industrial processing equipment that is subject to high pressures and temperatures and/or corrosive processes. Explosion-welded clad plates also can be cut into transition joints, which are used to facilitate conventional welding of dissimilar metals. The eight broad industrial sectors discussed below comprise the bulk of demand for NobelClad’s products, with oil and gas and chemical and petrochemical constituting approximately two-thirds of NobelClad sales in 2018. This demand is driven by the underlying need for both new equipment and facility maintenance in these primary market sectors.
Oil and Gas: Oil and gas end use markets include both oil and gas production and petroleum refining. Oil and gas production covers a broad scope of operations related to recovering oil and/or gas for subsequent processing in refineries. Clad metal is used in separators, glycol contractors, pipelines, heat exchangers and other related equipment. Increased oil and gas production from deep, hot, and more corrosive fields also has increased the demand for clad equipment. The primary clad metals for the oil and gas production market are stainless steel and nickel alloys clad to steel, with some use of reactive metals, such as titanium.
Petroleum refining processes frequently are corrosive and operate at high temperatures and pressures. Clad metal is extensively used in a broad range of equipment including desulfurization hydrotreaters, coke drums, distillation columns, separators and heat exchangers. Reliance upon low-quality, high-sulfur crude drives additional demand for new corrosion resistant equipment. Worldwide trends in regulatory control of sulfur emissions in gas, diesel and jet fuel are also increasing the need for clad equipment. Like the upstream oil and gas sector, the clad metals are primarily stainless steel and nickel alloys.
Chemical and Petrochemical: Many common products, ranging from plastics to prescription drugs to electronic materials, are produced by chemical processes. Because the production of these items often involves corrosive agents and is conducted under high pressures or temperatures, corrosion resistant equipment is needed. One of the larger applications for clad equipment is in the manufacture of purified terephthalic acid (PTA), a precursor product for polyester, which is used in products as diverse as carpets and plastic bottles. The chemical market requires extensive use of stainless steel and nickel alloys, but also uses titanium, zirconium and tantalum.
Alternative Energy: Some alternative energy technologies involve conditions that necessitate clad metals. Solar panels predominantly incorporate high purity polysilicon. Processes for manufacturing high purity silicon utilize a broad range of highly corrosion-resistant clad alloys. Many geothermal fields are corrosive, requiring high alloy clad separators to handle the hot steam. Some ethanol technologies may require corrosion resistant metals at thicknesses where clad is an attractive alternative.
Hydrometallurgy: The processes for production of nickel, gold, and copper involve acids, high pressures, and high temperatures, and titanium-clad plates are used extensively for construction of associated leaching and peripheral equipment.
Aluminum Production: Aluminum is reduced from its oxide in large electric smelters called potlines. The electric current is carried via aluminum conductors. The electricity must be transmitted into steel components for the high temperature smelting
operations. Aluminum cannot be welded to steel conventionally. Explosion-welded aluminum-steel transition joints provide an energy efficient and highly durable solution for making these connections. Modern potlines use a large number of transition joints, which are typically replaced after approximately five years in service. Although aluminum production is the major electrochemical application for NobelClad products, there are a number of other electrochemical applications including production of zinc, magnesium, chlorine and chlorate.
Shipbuilding: The combined problems of corrosion and top-side weight drive demand for our aluminum-steel transition joints, which serve as the juncture between a ship's upper and lower structures. Top-side weight is often a significant problem with tall ships, including cruise ships, naval vessels, ferries and yachts. Use of aluminum in the upper structure and steel in the lower structure provides stability. Since aluminum cannot be welded directly to steel using conventional welding processes, and since bolted joints between aluminum and steel corrode quickly in seawater, explosion-welded transition joints are a common solution. NobelClad's transition joints have been used in the construction of many well-known ships, including the Queen Elizabeth II and modern U.S. Navy aircraft carriers.
Power Generation: Fossil fuel and nuclear power generation plants require extensive use of heat exchangers, many of which require corrosion resistant alloys to handle low quality cooling water. Our clad plates are used extensively for heat exchanger tubesheets. The largest clad tubesheets are used in the final low-pressure condensers. For most coastal and brackish water-cooled plants, titanium is the metal of choice, and titanium-clad tubesheets are the low-cost solution for power plant condensers.
Industrial Refrigeration: Heat exchangers are a core component of refrigeration systems. When the cooling fluid is seawater, brackish, or even slightly polluted, corrosion-resistant metals are necessary. Metal selection can range from stainless steel to copper alloy to titanium. Explosion-welded clad metal is often the low-cost solution for making the tubesheets. Applications range from refrigeration chillers on fishing boats to massive air conditioning units for skyscrapers, airports, and deep underground mines.
Operations
The NobelClad segment seeks to build on its leadership position in its markets. During the three years ended December 31, 2018, 2017 and 2016, the NobelClad segment represented approximately 27%, 37% and 58% of our consolidated net sales, respectively. Our manufacturing plants and their respective shooting sites in Pennsylvania and Germany provide the production capacity to address projects for NobelClad’s global customer base.
In December 2017, DMC approved a plan to consolidate NobelClad's European production facilities and it completed the process in the fourth quarter of 2018. NobelClad's state-of-the-art manufacturing center in Liebenscheid, Germany, purchased in November 2014, now performs all of NobelClad’s European explosion cladding, although the business maintains its sales and administrative office in France.
The principal product of metal cladding, regardless of the process used, is a metal plate composed of two or more dissimilar metals, usually a corrosion resistant metal (the "cladder") bonded to a steel backing plate. Prior to the explosion-welding process, the materials are inspected, the mating surfaces are ground, and the metal plates are assembled for cladding. The process involves placing a sheet of the cladder over a parallel plate of backer material and then covering the cladder with a layer of specifically formulated explosive powder. A small gap or “standoff space” is maintained between the cladder and backer using small spacers. The explosion is then initiated on one side of the cladder and travels across the surface of the cladder forcing it onto the backer. The explosion happens in approximately one-thousandth of a second. The collision conditions cause a thin layer of the mating surfaces, as well as the spacers, to be spalled away in a jet. This action removes oxides and surface contaminants immediately ahead of the collision point. The extreme pressures force the two metal components together, creating a metallurgical bond between them. The explosion welding process produces a strong, ductile, continuous metallurgical weld over the clad surface. After the explosion is completed, the resulting clad plates are flattened and cut, and then undergo testing and inspection to assure conformance with product specifications.
EXPLOSION-WELDING PROCESS
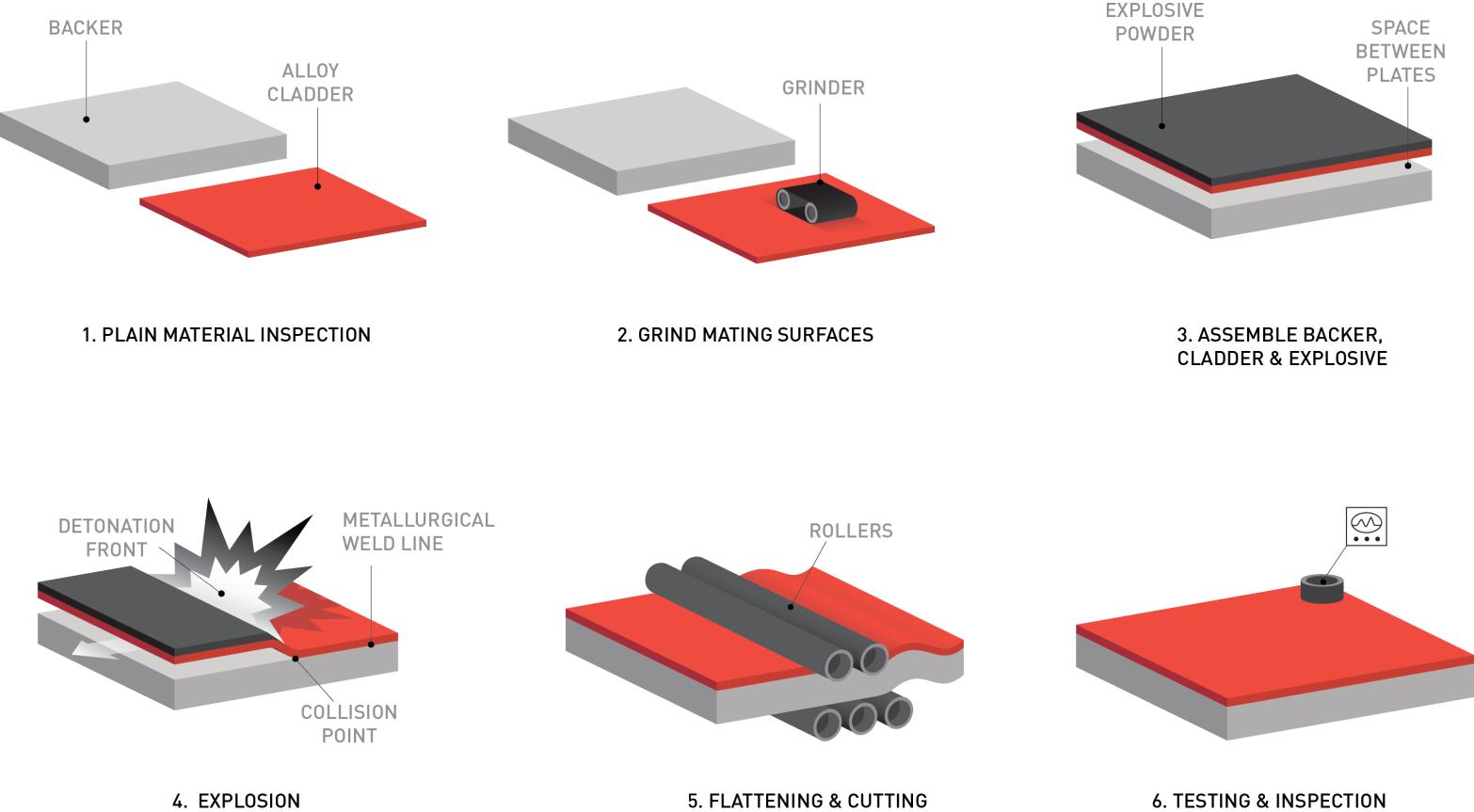
Explosion-welded cladding technology is a method for welding metals that cannot be joined using conventional welding processes, such as titanium-steel, aluminum-steel, and aluminum-copper. Explosion welding also can be used to weld compatible metals, such as stainless steels and nickel alloys to steel. The cladding metals are typically titanium, stainless steel, aluminum, copper alloys, nickel alloys, tantalum, and zirconium. The base metals are typically carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel and aluminum. Although the patents for the basic explosion-welded cladding process have expired, NobelClad has developed a proprietary knowledge of process control that distinguishes it from its competitors by maintaining high quality and low re-work costs. The entire explosion-welding process involves significant precision in all stages, and any errors can be extremely costly as they often result in the discarding of the expensive raw material metals. NobelClad’s technological expertise is a significant advantage in preventing costly waste.
NobelClad’s metal products are primarily produced for custom projects and conform to requirements set forth in customers’ purchase orders. Upon receipt of an order, NobelClad obtains the component materials from a variety of sources based on quality, availability and cost and then produces the order in one of its manufacturing plants. Final products are processed to meet contract specific requirements for product configuration and quality/inspection level.
Suppliers and Raw Materials
NobelClad's operations involve a range of alloys, steels and other materials, such as stainless steel, copper alloys, nickel alloys, titanium, zirconium, tantalum, aluminum and other metals. NobelClad sources its raw materials from a number of different producers and suppliers. It holds a limited metal inventory and purchases its raw materials based on contract specifications. Under most contracts, any raw material price increases are passed on to NobelClad’s customers. NobelClad closely monitors the quality of its supplies and inspects the type, dimensions, markings, and certification of all incoming metals to ensure that the materials will satisfy applicable construction codes. NobelClad also manufactures a majority of its own explosives from standard raw materials, and we believe that this allows us to achieve higher quality and lower cost.
Competition
Metal Cladding. NobelClad faces competition from two primary alternative cladding technologies: hot roll bonding and weld overlay. Usually the three processes do not compete directly, as each has its own preferential domain of application relating to metal used and thicknesses required. However, due to specific project considerations such as technical specifications, price and delivery time, explosion-welding may have the opportunity to compete against these technologies. Roll bond is only produced by a few steel mills in the world. In this process, the clad metal and base metal are
bonded during the hot rolling operation in which the metal slab is converted to plate. Being a high temperature process that yields the formation of detrimental intermetallics, hot roll bond is limited to joining similar metals, such as stainless steel and nickel alloys to steel. Roll bond’s niche is production of large quantities of light to medium gauge clad plates. Roll bond products are generally suitable for most pressure vessel applications but have lower bond shear strength and may have inferior corrosion resistance.
The weld overlay process, which is used by the many vessel fabricators that are often also NobelClad customers, is a slow and labor-intensive process that requires a large amount of floor space for the equipment. In weld overlay cladding, the clad metal layer is deposited on the base metal using arc-welding type processes. Weld overlay is a cost-effective technology for complicated shapes, for field service jobs, and for production of some very heavy-wall pressure vessel reactors. During overlay welding, the cladding metal and base metal are melted together at their interface. The resulting dilution of the cladding metal chemistry may compromise corrosion performance and limit use in certain applications. Weld metal shrinkage during cooling potentially causes distortion when the base layer is thin. As with rollbond, weld overlay is limited to metallurgically similar metals, primarily stainless steels and nickel alloys joined to steel. Weld overlay is typically performed in conventional metal fabrication shops.
Explosion-Welded Metal Cladding. Competition in the explosion-welded clad metal business is fragmented. NobelClad holds a strong market position in the clad metal industry. It is the leading producer of explosion-welded clad products in North America, and has a strong position in Europe against smaller competitors. NobelClad has mixed competition in Asia ranging from competitors with competitive technology and strong brand names to other producers which are technically limited and offer minimal exports outside of their domestic markets. To remain competitive, NobelClad intends to continue developing and providing technologically advanced manufacturing services, maintaining quality levels, offering flexible delivery schedules, delivering finished products on a reliable basis and competing favorably on the basis of price.
Customer Profile
NobelClad’s products are used in critical applications in a variety of industries, including upstream oil and gas, oil refining, chemical and petrochemical, hydrometallurgy, aluminum production, shipbuilding, power generation, industrial refrigeration and other similar industries. NobelClad’s customers in these industries require metal products that can withstand exposure to corrosive materials, high temperatures and high pressures. NobelClad’s customers can be divided into three tiers: the product end users (e.g., operators of chemical processing plants), the engineering contractors that design and construct plants for end users, and the metal fabricators that manufacture the products or equipment that utilize NobelClad’s metal products. It is typically the fabricator that places the purchase order with NobelClad and pays the corresponding invoice. NobelClad has developed strong relationships over the years with the engineering contractors, process licensors, and equipment operating companies that frequently act as buying agents for fabricators.
Marketing, Sales, Distribution
NobelClad conducts its selling efforts by marketing its services to potential customers' senior management, direct sales personnel, program managers, and independent sales representatives. Prospective customers in specific industries are identified through networking in the industry, cooperative relationships with suppliers, public relations, customer references, inquiries from technical articles and seminars and trade shows. NobelClad’s sales office in the United States covers the Americas and Asia. Its sales offices in Europe cover the full European continent, Africa, the Middle East, India, Asia, and Russia. NobelClad also has sales offices in South Korea and China to address these markets and uses contract agents to cover various other countries. Contract agents typically work under multi-year agreements which are subject to sales performance targets as well as compliance with NobelClad quality and customer service expectations. Members of the global sales team may be called to work on projects located outside their usual territory. By maintaining relationships with its existing customers, developing new relationships with prospective customers, and educating all its customers as to the technical benefits of NobelClad’s products, NobelClad endeavors to assist in setting standard specifications, both by our customers and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers and ASTM, to ensure that the highest quality and reliability are achieved.
NobelClad’s products are generally shipped from its manufacturing locations in the United States and Germany. Any shipping costs or duties for which NobelClad is responsible typically will be included in the price paid by the customer. Regardless of where the sale is booked, NobelClad will produce it, capacity permitting, at the location closest to the delivery place. In the event that there is a short-term capacity issue at one facility, NobelClad can produce the order at its other production site, prioritizing timing. The two production sites allow NobelClad to meet customer production needs in a timely manner.
Research and Development
We prepare a formal research and development plan annually. It is implemented at our cladding sites and is supervised by a technical committee that reviews progress quarterly and meets once a year to establish the plan for the following 12 months. The research and development projects concern process support, new products, new applications, and special customer-paid projects.
Corporate History and Recent Developments
The genesis of the Company was an unincorporated business called “Explosive Fabricators,” which was formed in Colorado in 1965. The business was incorporated in Colorado in 1971 under the name “E. F. Industries, Inc.,” which was later changed to “Explosive Fabricators, Inc.” The Company became publicly traded in 1976. In 1994, it changed its name to “Dynamic Materials Corporation.” The Company reincorporated in Delaware in 1997.
In 1976, the Company became a licensee of Detaclad, the explosion-welded clad process developed by DuPont in 1959. In 1996, the Company purchased the Detaclad operating business from DuPont.
In 1998, the Company acquired AMK Technical Services ("AMK"), a specialty welding business.
In 2001, the Company acquired substantially all of the stock of NobelClad Europe SA, a French company (“NobelClad Europe”). Early in its history, NobelClad Europe was a licensee of the Detaclad technology. The acquisition of NobelClad Europe expanded the Company’s explosive metalworking operations to Europe.
In 2007, the Company acquired the German company DynaEnergetics GmbH and Co. KG (“DynaEnergetics”) and certain affiliates. DynaEnergetics was comprised of two primary businesses: explosive metalworking and oilfield products. This acquisition expanded the Company’s explosive metalworking operations in Europe and added a complementary oilfield products business.
Over the next several years the Company further grew the DynaEnergetics business by acquiring additional related sales and manufacturing companies in Canada and the United States and purchasing minority interests in certain Russian joint ventures.
In 2013, the Company branded its explosive metalworking operations under the single name NobelClad. The NobelClad segment is comprised of the Company’s U.S. clad operations as well as the explosion metalworking assets and operations purchased in the NobelClad Europe and DynaEnergetics acquisitions. In 2014, the Company re-branded the oilfield products segment as DynaEnergetics, which is comprised entirely of DynaEnergetics (other than its explosion metalworking operations), its subsidiaries and sister companies.
In 2014, the Company sold AMK. Also in 2014, the Company acquired a modern manufacturing and office complex in Liebenscheid, Germany. The facility enhances NobelClad's manufacturing capabilities and serves as a state-of-the-art production and administrative resource for NobelClad's European operations and also serves as a production resource for DynaEnergetics.
In 2016, the Company changed its name to DMC Global Inc. to reflect that we are a diversified portfolio of technical product and process businesses serving niche markets around the world.
In 2018, NobelClad completed the consolidation of its European explosion-welding operations into its manufacturing facility in Liebenscheid, Germany. DynaEnergetics expanded its North American operations, adding 74,000 square feet of manufacturing, assembly and administrative space on its Blum, Texas campus.
Employees
As of December 31, 2018, we had 665 permanent and part-time employees (400 U.S. and 265 non-U.S.), the majority of whom are engaged in manufacturing operations, with the remainder primarily in sales, marketing and administrative functions. Most of our manufacturing employees are not unionized. In addition, we use a number of temporary workers at any given time, depending on the workload. We currently believe that employee relations are good.
Insurance
Our operations expose us to potential liabilities for personal injury or death as a result of the failure of a component that has been designed, manufactured, serviced, processed, or distributed by us. We maintain liability insurance that we believe adequately protects us from potential product liability claims.
Intellectual Property
We hold a variety of intellectual property through our DynaEnergetics business including but not limited to patents, patent applications, registered and unregistered trademarks, trade secrets, proprietary information and know-how. We have followed a policy of seeking patent and trademark protection in countries and regions throughout the world for products and methods that appear to have commercial significance. DynaEnergetics seeks and holds numerous patents covering various products and processes, including but not limited to perforating guns and their various components, shaped charges, packaging of explosive materials, detonating cord, initiating systems and electronics.
We hold a variety of intellectual property through our NobelClad business, including but not limited to patent applications, proprietary information and know-how, trade secrets, and registered and unregistered trademarks. Much of our proprietary manufacturing expertise lies in the knowledge of the factors that affect the quality of the finished clad product, including the types of metals to be explosion-welded, the setting of the explosion, the composition of the explosive, and the preparation of the plates to be bonded. We have developed this specialized knowledge over our 40 years of experience in the explosive metalworking business.
No single patent or trademark is considered to be critical to either DynaEnergetics' or NobelClad's businesses.
We are careful in protecting our proprietary know-how and manufacturing expertise in both DynaEnergetics and NobelClad, and we have implemented measures and procedures designed to ensure that the information remains confidential.
Foreign and Domestic Operations and Export Sales
All of our sales are shipped from our manufacturing facilities and distribution centers located in the United States, Germany, France, Canada, and Russia. The following chart represents our net sales based on the geographic location to where we shipped the product, regardless of the country of the actual end user. NobelClad products are usually shipped to the fabricator before being passed on to the end user.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| | For the years ended December 31, |
| | 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
United States | | $ | 221,847 |
| | $ | 116,083 |
| | $ | 78,999 |
|
Canada | | 30,126 |
| | 23,377 |
| | 16,021 |
|
United Arab Emirates | | 4,093 |
| | 1,768 |
| | 7,449 |
|
France | | 4,581 |
| | 3,032 |
| | 3,744 |
|
South Korea | | 2,263 |
| | 1,173 |
| | 1,690 |
|
Germany | | 4,067 |
| | 5,397 |
| | 5,979 |
|
Russia | | 4,117 |
| | 4,504 |
| | 3,731 |
|
India | | 4,291 |
| | 2,927 |
| | 5,066 |
|
Egypt | | 2,419 |
| | 2,721 |
| | 1,942 |
|
Spain | | 1,083 |
| | 1,126 |
| | 1,500 |
|
Iraq | | 314 |
| | 77 |
| | 13 |
|
China | | 12,503 |
| | 3,673 |
| | 7,012 |
|
Italy | | 1,730 |
| | 1,582 |
| | 2,577 |
|
Hong Kong | | 496 |
| | 255 |
| | 699 |
|
Sweden | | 2,339 |
| | 2,009 |
| | 2,124 |
|
Rest of the world | | 30,160 |
| | 23,099 |
| | 20,029 |
|
| | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 326,429 |
| | $ | 192,803 |
| | $ | 158,575 |
|
Company Information
We are subject to the informational requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"). We therefore file periodic reports, proxy statements and other information with the Securities Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). The SEC maintains an Internet site at www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding issuers that file electronically.
Our Internet address is www.dmcglobal.com. Information contained on our website does not constitute part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our annual report on SEC Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Forms 10-Q, current reports on Forms 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act are available free of charge on our website as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with or furnish it to the SEC. We also regularly post information about our Company on our website under the "Investors" tab.
ITEM 1A. Risk Factors
Risk Factors Related to DynaEnergetics
Demand for DynaEnergetics’ products is substantially dependent on the levels of expenditures by the oil and gas industry. Decreased oil and gas prices and reduced expenditures in the oil and gas industry could have a material adverse impact on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Demand for the majority of our products depends substantially on the level of expenditures by the oil and gas industry for the exploration, development and production of oil and natural gas reserves. These expenditures are generally dependent on the industry’s view of future oil and natural gas prices and are sensitive to the industry’s view of future economic growth and the resulting impact on demand for oil and natural gas. From 2014 through mid-2017, oil and gas prices declined significantly, resulting in lower expenditures by the oil and gas industry during this period. As a result, many of our customers reduced or delayed their oil and gas exploration and production spending, reducing the demand for our products and causing downward pressure on the prices that we charged and the revenues and profits we earned during this period. This resulted in DynaEnergetics’ revenues declined 12.5% in 2016 compared with 2015 and declined 27.0% in 2015 compared with 2014. Although we experienced increased exploration and production spending in 2017 and 2018, including improved revenues and profitability in DynaEnergetics over the past two years, there is no assurance such conditions will continue, particularly because oil prices again declined substantially in late 2018.
There can be no assurance that the demand or pricing for oil and natural gas will continue at current levels or follow historic patterns. A decline in oil and gas prices could cause reductions in cash flows for our customers, which could have material adverse effects on the financial condition of our customers. This could result in project modifications, delays or cancellations, general business disruptions, and delays in payment of, or nonpayment of, amounts that are owed to us. These effects could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
The prices for oil and natural gas have historically been volatile and can be affected by a variety of factors, including:
• demand for hydrocarbons, which is affected by general economic, business and regulatory conditions;
• the ability or willingness of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (“OPEC”) to set and maintain production levels for oil;
• oil and gas production levels by non-OPEC countries;
• the level of excess production capacity;
• political and economic uncertainty and geopolitical unrest;
• the level of worldwide oil and gas exploration and production activity;
• access to potential resources;
• governmental policies and subsidies;
• the costs of exploring for, producing and delivering oil and gas;
• technological advances affecting energy consumption; and
• weather conditions.
Constraints in the supply of, prices for, and availability of transportation of raw materials could have a material adverse effect on our business and consolidated results of operations.
Our business requires a continuous supply of raw materials, such as explosives, steel, metal powder, and electronics, which normally are readily available. However, shortages of raw materials or long-lead times in receiving such materials, as a result of high levels of demand or loss of suppliers during market challenges, could trigger constraints in the supply chain of
those raw materials, particularly, where we have a relationship with a single supplier for a particular resource. An increase in military activity in certain parts of the world could impact the availability of explosives as capacity could potentially be diverted to supply military requirements. These delays and constraints could have a material adverse effect on our business and consolidated results of operations. In addition, price increases imposed by our vendors for raw materials used in our business and the inability to pass these increases on to our customers could have a material adverse effect on our business and consolidated results of operations.
Failure to adjust our manufacturing and supply chain to accurately meet customers demand could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We make significant decisions, including determining the levels of business that we will seek and accept, production schedules, levels of reliance on contract manufacturing and outsourcing, internal fabrication utilization and other resource requirements, based on our estimates of customer requirements. Factors that can impact our ability to accurately estimate future customer requirements include the short-term nature of many customers’ commitments, our customers’ ability to reschedule, cancel and modify orders with little or no notice and without significant penalty, the accuracy of our customers’ forecasts, and seasonal or cyclical trends in customers' industries.
To ensure availability of our products, particularly for our largest customers, we may start manufacturing our relevant products based on our customers’ forecasts, which are not binding. As a result, we incur inventory and manufacturing costs in advance of anticipated sales that may never materialize or which may be substantially lower than expected. If actual demand for our products is lower than forecast, we may also experience higher inventory carrying and operating costs and product obsolescence. Because certain of our sales, research and development, and internal manufacturing overhead expenses are relatively fixed, a reduction in customer demand may also decrease our gross margin and operating income.
Conversely, customers often require rapid increases in production on short notice. We may be unable to secure sufficient materials or contract manufacturing capacity to meet such increases in demand. This could damage our customer relationships, reduce revenue growth and margins, subject us to additional liabilities, harm our reputation, and prevent us from taking advantage of opportunities.
Failure to manage periods of growth or contraction may seriously harm our business.
Our industry frequently sees periods of expansion and contraction to adjust to customers’ needs and market demands. We regularly contend with these issues and must carefully manage our business to meet customer and market requirements. If we fail to manage these growth and contraction decisions effectively, we may find ourselves with either excess or insufficient resources and our business and our profitability could suffer as a result.
Expansions, including the transfer of operations to other facilities or the construction of new manufacturing facilities, such as the recently completed Blum expansion, include the risk of additional costs and start-up inefficiencies. If we are unable to effectively manage our expansion projects or related anticipated net sales are not realized, our operating results could be materially adversely affected. Risks of the Blum expansion project and future expansions include:
| |
• | increased costs associated with opening new facilities, including the ability to meet budget constraints on construction projects; |
| |
• | difficulties in the timing of expansions, including delays in the implementation of construction and manufacturing plans; |
| |
• | the inability to successfully integrate additional facilities or incremental capacity and to realize anticipated efficiencies, economies of scale or other value; |
| |
• | challenges faced as a result of transitioning programs; |
| |
• | additional fixed or other costs, or selling, general and administrative ("SG&A") expenses, which may not be fully absorbed by the new business; |
| |
• | a reduction of our return on invested capital, including as a result of excess inventory or excess capacity at new facilities; |
| |
• | diversion of management’s attention from other business areas during the planning and implementation of expansions; |
| |
• | increased debt levels and borrowing costs; |
| |
• | strain placed on our operational, financial and other systems and resources; and |
| |
• | inability to locate sufficient employees or management talent to support the expansion. |
Periods of contraction or reduced net sales, or other factors affecting particular sites, create other challenges. We must determine whether facilities remain viable, whether staffing levels need to be reduced, and how to respond to changing levels
of customer demand. While maintaining excess capacity or higher levels of employment entails short-term costs, reductions in capacity or employment could impair our ability to respond to new opportunities and programs, market improvements or to maintain customer relationships. Our decisions to reduce costs and capacity can affect our short-term and long-term results and result in restructuring charges.
If we are not able to design, develop, and produce commercially competitive products in a timely manner in response to changes in the market, customer requirements, competitive pressures, and technology trends, our business and consolidated results of operations and the value of our intellectual property could be materially and adversely affected.
The market for our products is characterized by continual technological developments to provide better and more reliable performance. If we are not able to design, develop, and produce commercially competitive products in a timely manner in response to changes in the market, customer requirements, competitive pressures, and technology trends, our business and consolidated results of operations and the value of our intellectual property could be materially and adversely affected. Likewise, if our proprietary technologies, equipment, facilities, or work processes become obsolete, we may no longer be competitive, and our business and consolidated results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
The manufacturing of explosives subjects DynaEnergetics to various environmental, health and safety laws and any accidents or injuries could subject us to significant liabilities.
The use of explosives is inherently dangerous. DynaEnergetics is subject to a number of environmental, health, and safety laws and regulations covering all aspects of the business including general operating licenses, transportation domestically and internationally, storage requirements, waste disposal, manufacturing regulations, employee training and certification requirements, and labor regulations. Violation of these laws and regulations could result in significant penalties or in interruption of our business activities. DynaEnergetics’ success depends on continued compliance with applicable laws and regulations. In addition, new environmental, health and safety laws and regulations could be passed that could create costly compliance issues. While DynaEnergetics endeavors to comply with all applicable laws and regulations, compliance with future laws and regulations may not be economically feasible or even possible. Even with compliance with applicable health and safety laws, it is possible that accidents may occur, potentially resulting in injury to our employees, equipment, facilities, and customers. Any accident could result in significant manufacturing delays, disruption of operations or legal claims for damages resulting from death or injuries, which could result in decreased sales and increased expenses.
We may not be able to continue to compete successfully against other perforating companies.
DynaEnergetics competes principally with perforating companies based in North America, South America, and Russia, which produce and market perforating services and products. DynaEnergetics also competes with oil and gas service companies that are able to satisfy a portion of their perforating needs through in-house production. To remain competitive, DynaEnergetics must continue to provide innovative products and maintain an excellent reputation for safety, quality, on-time delivery, and value. There can be no assurances that we will continue to compete successfully against these companies.
Risk Factors Related to NobelClad
NobelClad’s business is dependent on sales to a limited number of customers in cyclical markets and our results are affected by the price of metals.
NobelClad revenues are affected both by the demand for NobelClad’s explosion-welded cladding services and the base price of metal used in explosion-welded cladding operations. The explosion-welded cladding market is dependent upon sales of products for use by customers in a limited number of heavy industries, including oil and gas, chemicals and petrochemicals, alternative energy, hydrometallurgy, aluminum production, shipbuilding, rail car manufacturing, power generation, and industrial refrigeration. These industries tend to be cyclical in nature and an economic slowdown in one or all of these industries-whether due to traditional cyclicality, general economic conditions or other factors-could impact capital expenditures within that industry. In addition, metals prices affect the demand for cladded products and our margins. Higher metal prices increase demand by making it more economical for customers to use cladding on less-expensive metal than using solid metal plates. Higher metal prices also lead to higher sales (in terms of dollars rather than square meters of cladding) and generally higher margins for NobelClad. We have experienced a significant decline in the demand for clad products in recent years due in part to a low-metals price environment. If demand or metals prices do not increase or decline further, our sales would be adversely affected, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Our backlog figures may not accurately predict future sales.
We use backlog to predict our anticipated future sales. Our year-end backlog was $29.9 million, $37.5 million, and $31.6 million at the end of fiscal years 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively. We define “backlog” at any given point in time to consist of all firm, unfulfilled purchase orders and commitments at that time. We expect to fill most items of backlog within the following 12 months. However, since orders may be rescheduled or canceled and a significant portion of our net sales is derived from a small number of customers, backlog is not necessarily indicative of future sales levels. Moreover, we cannot be sure of when during the future 12-month period we will be able to recognize revenue corresponding to our backlog nor can we be certain that revenues corresponding to our backlog will not fall into periods beyond the 12-month horizon.
There is a limited availability of sites suitable for cladding operations.
Our cladding process involves the detonation of large amounts of explosives. As a result, the sites where we perform cladding must meet certain criteria, including adequate distance from densely populated areas, specific geological characteristics, and the ability to comply with local noise and vibration abatement regulations in conducting the process. Our shooting sites in Pennsylvania and in Dillenburg, Germany are located in mines. We terminated the lease to our secondary shooting site in Tautavel, France in late 2018 associated with the closure of manufacturing operations in France, and we moved all European shooting operations to Dillenburg. This will increase the demands on the Dillenburg mine. Access to our Dillenburg mine is subject to a lease that expires in 2022, and if we are unable to negotiate a suitable extension of the lease, this could impact our operations. If a mine were seriously damaged, we might not be able to locate a suitable replacement site in a timely manner to continue our operations. In addition, our primary U.S. shooting site is subleased under an arrangement pursuant to which we provide certain contractual services to the sub-landlord. The efforts to identify alternative suitable sites and obtain permits for using the sites from local government agencies can be time-consuming and may not be successful. In addition, we could experience difficulty in obtaining or renewing permits because of resistance from residents in the vicinity of existing or proposed sites. The failure to obtain required governmental approvals or permits could limit our ability to expand our cladding business in the future, and the failure to maintain such permits or satisfy other conditions to use the sites would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
There is no assurance that we will continue to compete successfully against other manufacturers of competitive products.
Our explosion-welded clad products compete with explosion-welded clad products made by other manufacturers in the clad metal business located throughout the world and with clad products manufactured using other technologies. Our combined North American and European operations typically supply explosion-welded clad to the worldwide market. There is one other well-known explosion-welded clad supplier worldwide - a division of Asahi-Kasei Corporation of Japan. There are also a number of smaller companies worldwide with explosion-welded clad manufacturing capability, including several companies in China and India that appear to be growing significantly in their domestic markets. Explosion-welded clad products also compete with those manufactured by rollbond and weld overlay cladding processes. The technical and commercial niches of each cladding process are well understood within the industry and vary from one world market location to another. We focus on reliability, product quality, on-time delivery performance, and low-cost manufacturing to minimize the potential of future competitive threats. However, there is no guarantee we will be able to maintain our competitive position.
We do not maintain a reserve fund for warranty or defective products claims. Our costs could substantially increase if we experience a large claim or a significant number of warranty claims.
Our product warranties against technical defects of our clad products vary depending on our purchase orders with customers. The warranties require us to repair or replace defective products and may require the payment of a certain percentage of the purchase price as liquidated damages for our failure to meet the specified product specifications and delivery requirements. In addition, our clad products are often used as part of larger projects or are used in potentially hazardous applications that can cause injury or loss of life and damage to property or equipment. In the event of a product defect, we may be named as a defendant in product liability or other lawsuits asserting potentially large claims. We cannot guarantee that insurance will be available or adequate to cover any or all liabilities incurred. We have not established any reserve funds for potential warranty claims since historically we have experienced few warranty claims for our products so that the costs associated with our warranty claims have been low. If we experience an increase in warranty claims or if our repair and replacement costs associated with warranty claims increase significantly, it could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
The use of explosives subjects us to additional regulation, and any accidents or injuries could subject us to significant liabilities.
Our operations involve the detonation of large amounts of explosives. The use of explosives is an inherently dangerous activity. As a result, we are required to use specific safety precautions under U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration guidelines and guidelines of similar entities in Germany. These include precautions which must be taken to protect employees from exposure to sound and ground vibration or falling debris associated with the detonation of explosives. There is a risk that an accident or death could occur in one of our facilities.
Explosions, even if occurring as intended, can lead to damage to the shooting site or manufacturing facility or to equipment used at the facility or injury or death to persons at the facility. Any accident could result in significant manufacturing delays, disruption of operations or claims for damages resulting from death or injuries, which could result in decreased sales and increased expenses. To date, we have not incurred any significant delays, disruptions or claims resulting from accidents at our facilities. If an accident occurred, we might be required to suspend our operations for a period of time while an investigation is undertaken or repairs are made. Such a delay might impact our ability to meet the demand for our products.
The Company’s customers use some of its products in potentially hazardous applications that can cause injury or loss of life and damage to property or equipment. The Company cannot be certain that its products will be completely free from defects. The Company may be named as a defendant in product liability or other lawsuits asserting potentially large claims. In addition, the Company cannot guarantee that insurance will be available or adequate to cover any or all liabilities incurred.
Customers have the right to change orders until products are completed.
Customers have the right to change orders after they have been placed. If orders are changed, the extra expenses associated with the change usually will be passed on to the customer. However, because a change in an order may delay completion of the project, recognition of income for the project may also be delayed. Additionally, any errors or changes as to specifications or significant changes in pricing or availability of materials may cause cost overruns and delays in completion of projects. If we fail to meet delivery schedules, we may be required to pay damages or may risk loss of an order, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Risk Factors Related to our Businesses Generally
Our operating results fluctuate from quarter to quarter.
We have experienced, and expect to continue to experience, fluctuations in annual and quarterly operating results caused by various factors at both NobelClad and DynaEnergetics. At NobelClad, quarterly sales and operating results depend on the volume and timing of the orders in our backlog as well as bookings during the quarter. At DynaEnergetics, the level of demand from our customers is impacted by oil and gas prices as well as a variety of other factors and can vary significantly from quarter to quarter. Significant portions of our operating expenses are fixed, and planned expenditures are based primarily on sales forecasts and product development programs. If sales do not meet our expectations in any given period, the adverse impact on operating results may be magnified by our inability to adjust operating expenses sufficiently or quickly enough to compensate for such a shortfall. Results of operations in any period should not be considered indicative of the results for any future period. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” Fluctuations in operating results may also result in fluctuations in the price of our common stock.
We are exposed to potentially volatile fluctuations of the U.S. dollar (our reporting currency) against the currencies of many of our operating subsidiaries.
Many of our operating subsidiaries conduct business in euros, Canadian dollars, Russian rubles or other foreign currencies. Sales made in currencies other than U.S. dollars accounted for 21%, 28%, and 23% of total sales for the years ended 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Any increase (decrease) in the value of the U.S. dollar against any foreign currency that is the functional currency of any of our operating subsidiaries will cause us to experience foreign currency translation (gains) losses with respect to amounts already invested in such foreign currencies. In addition, our company and our operating subsidiaries are exposed to foreign currency risk to the extent that we or they enter into transactions denominated in currencies other than our or their respective functional currencies. For example, DynaEnergetics KG’s functional currency is euros, but its sales often occur in U.S. dollars. Changes in exchange rates with respect to these items will result in unrealized (based upon period-end exchange rates) or realized foreign currency transaction gains and losses upon settlement of the transactions. In addition, we are exposed to foreign exchange rate fluctuations related to our operating subsidiaries’ assets and liabilities and to the financial results of foreign subsidiaries and affiliates when their respective financial statements are translated into U.S. dollars for inclusion in our Consolidated Financial Statements. Cumulative translation adjustments are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) as a separate component of equity. Our primary exposure to foreign currency risk is the euro, due to the percentage of our U.S. dollar revenue that is derived from countries where the euro is the functional
currency, and the Russian ruble due to our operations in Tyumen, Siberia. During the third quarter of 2017, we began using foreign currency forward contracts, generally with maturities of one month, to offset foreign exchange rate fluctuations on certain foreign currency denominated asset and liability account balances. These hedge transactions relate to our operating entities with significant economic exposure to transactions denominated in currencies other than their functional currency. Our primary economic exposures include the U.S. dollar to the euro, the U.S. dollar to the Canadian dollar, the euro to the U.S. Dollar and the euro to the Russian ruble. Since the underlying balance sheet account balances being hedged can fluctuate significantly throughout our monthly hedge periods, our hedging program cannot fully protect against foreign currency fluctuations.
The terms of our indebtedness contain a number of restrictive covenants, the breach of any of which could result in acceleration of payment of our credit facilities.
As of December 31, 2018, we had an outstanding balance of approximately $42.1 million on our syndicated credit agreement. This agreement includes various covenants and restrictions and certain of these relate to the incurrence of additional indebtedness and the mortgaging, pledging or disposing of major assets. We are also required to maintain certain financial ratios on a quarterly basis. A breach of any of these covenants could impair our ability to borrow and could result in acceleration of our obligations to repay our debt, if we are unable to obtain a waiver or amendment from our lenders. As of December 31, 2018, we were in compliance with all financial covenants and other provisions of the credit agreement and our other loan agreements. Any failure to remain in compliance with any material provision or covenant of our credit agreement could result in a default, which would, absent a waiver or amendment, require immediate repayment of outstanding indebtedness under our credit facilities.
We are dependent on a relatively small number of large projects and customers for a significant portion of our net sales.
A significant portion of our net sales is derived from a relatively small number of projects and customers; therefore, the failure to complete existing contracts on a timely basis, to receive payment for such services in a timely manner, or to enter into future contracts at projected volumes and profitability levels could adversely affect our ability to meet cash requirements exclusively through operating activities. We attempt to minimize the risk of losing customers or specific contracts by continually improving commercial execution, product quality, delivering product on time and competing aggressively on the basis of price. We expect to continue to depend upon our principal customers for a significant portion of our sales, although our principal customers may not continue to purchase products and services from us at current levels, if at all. The loss of one or more major customers or a change in their buying patterns could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We are susceptible to the cyclicality of the steel industry.
Steel plate and steel pipe are key materials used our NobelClad and DynaEnergetics’ businesses. The steel industry is very cyclical and is affected significantly by supply and demand factors, general economic conditions and other factors such as worldwide production capacity, fluctuations in steel imports/exports, tariffs and quotas. The downturn in the U.S. economy in fiscal 2010 and the continued low metals prices since that time have had an adverse effect on the U.S. steel industry and on our NobelClad business and any future economic downturn or a prolonged period of stagnation in the economy could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Tariffs imposed by the U.S. government and related counter tariffs have increased our costs, limited the availability of metals and may lead to further trade conflicts.
In 2018, the U.S. announced tariffs of 25 percent on steel and 10 percent on aluminum imported from countries where we typically source metals. These tariffs were met with retaliatory tariffs from certain countries and increased, broader tariffs were levied by the U.S. on targeted countries, including China. The tariffs impacted the cost of the importation of steel, which we utilize in our steel plate and steel pipe, a key material in our NobelClad and DynaEnergetics’ businesses. Though in many cases we have been able to source metals from domestic suppliers, some materials are only available from sources subject to tariffs. The cost of domestic steel and aluminum has also increased, along with the price of delivery, and the availability of certain materials has been limited. These increased costs have increased the price of our products to our customers and, in some instances, our ability to be competitive. For our NobelClad business, this impacts our ability to compete on international projects and negatively impacts U.S. fabricators, which are strong consumers of NobelClad products. Additionally, there is a risk that the U.S. tariffs on imports and retaliatory tariffs on U.S.-produced exports will trigger a broader global trade conflict. The risk of a broader global trade conflict or the prolonged duration of tariffs could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
If our customers delay paying or fail to pay a significant amount of our outstanding receivables, it could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, consolidated results of operations, and consolidated financial condition.
We depend on a limited number of significant customers, and the loss of one or more significant customers could have a material adverse effect on our business and our consolidated results of operations.
In most cases, we bill our customers for our services in arrears and are, therefore, subject to the risk that our customers will delay payment of or fail to pay our invoices. In weak economic environments, we may experience increased delays and failures due to, among other reasons, a reduction in our customers’ cash flow from operations and their access to the credit markets and rising interest rates. If our customers delay paying or fail to pay us a significant amount of our outstanding receivables, it could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, consolidated results of operations, and consolidated financial condition.
Failure to attract and retain key personnel could adversely affect our current operations.
Our continued success depends to a large extent upon the efforts and abilities of key managerial and technical employees. The loss of services of certain of these key personnel could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, and financial condition. There can be no assurance that we will be able to attract and retain such individuals on acceptable terms, if at all, and the failure to do so could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We are subject to extensive government regulation and failure to comply could subject us to future liabilities and could adversely affect our ability to conduct or to expand our business.
We are subject to extensive government regulation in the United States, Germany, Canada and Russia, including guidelines and regulations for the purchase, manufacture, handling, transport, storage and use of explosives issued by the U.S. Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms; the Federal Motor Carrier Safety regulations set forth by the U.S. Department of Transportation; the Safety Library Publications of the Institute of Makers of Explosive; and similar guidelines of their European counterparts. In Germany, the transport, storage and use of explosives is governed by a permit issued under the Explosives Act (Sprengstoffgesetz). Our shooting sites located in Pennsylvania and in Dillenburg, Germany are located in mines, which subject us to certain regulations and oversight of governmental agencies that oversee mines.
We are also subject to extensive environmental, health and safety regulation, as described below under “Liabilities for natural resource damages, cleanup costs, and other damages under environmental, health and safety laws could result in restrictions or prohibitions on our facilities, substantial civil or criminal liabilities and could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations, and consolidated financial condition.” and above under “The use of explosives subjects us to additional regulation, and any accidents or injuries could subject us to significant liabilities.”
In addition, the shipment of goods, services, and technology across international borders subjects us to extensive trade laws and regulations. Our import activities are governed by the unique customs laws and regulations in each of the countries where we operate. Moreover, many countries, including the United States, control the export and re-export of certain goods, services and technology and impose related export recordkeeping and reporting obligations. Governments may also impose economic sanctions against certain countries, persons, and entities that may restrict or prohibit transactions involving such countries, persons and entities, which may limit or prevent our conduct of business in certain jurisdictions.
The laws and regulations concerning import activity, export recordkeeping and reporting, export control, and economic sanctions are complex and constantly changing. Changes in these laws and regulations or in related banking compliance programs and practices can cause delays in shipments or require us to cancel orders or restrict our ability to receive payments on certain orders. Moreover, any failure to comply with applicable legal and regulatory trading obligations could result in criminal and civil penalties and sanctions, such as fines, imprisonment, debarment from governmental contracts, seizure of shipments and loss of import and export privileges.
Any failure to comply with current and future regulations in the countries where we operate could subject us to future liabilities. In addition, such regulations could restrict our ability to expand our facilities, construct new facilities, or compete in certain markets or could require us to incur significant expenses in order to maintain compliance. Accordingly, our business, results of operations or financial condition could be adversely affected by our non-compliance with applicable regulations, by any significant limitations on our business as a result of our inability to comply with applicable regulations, or by any requirement that we spend substantial amounts of capital to comply with such regulations.
Demand for our products and services could be reduced by existing and future legislation or regulations.
Environmental advocacy groups and regulatory agencies in the United States and other countries have been focusing considerable attention on the emissions of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases and their potential role in climate change. Existing or future legislation and regulations related to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, as well as government initiatives to conserve energy or promote the use of alternative energy sources, may significantly curtail demand for and production of fossil fuels such as oil and gas and, thus, adversely affect future demand for our products. This may, in turn, adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Some international, national, state and local governments and agencies have also adopted laws and regulations or are evaluating proposed legislation and regulations that are focused on the extraction of shale gas or oil using hydraulic fracturing. Hydraulic fracturing is a stimulation treatment routinely performed on oil and gas wells in low-permeability reservoirs. Specially engineered fluids are pumped at high pressure and rate into the reservoir interval to be treated, causing cracks in the target formation. Proppant, such as sand of a particular size, is mixed with the treatment fluid to keep the cracks open when the treatment is complete. Future hydraulic fracturing-related legislation or regulations could limit or ban hydraulic fracturing, or lead to operational delays and increased costs, and therefore reduce demand for our products. If such additional international, national, state or local legislation or regulations are enacted, it could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
In November 2018, voters in Colorado defeated a "setback" initiative, Proposition 112. Proposition 112 would have amended the Oil and Gas Conservation Act and prohibited the Colorado Oil and Gas Conservation Commission from permitting new oil and gas development closer than 2,500 feet from occupied structures or other areas such as playgrounds, parks, public open space and certain bodies of water. If Proposition 112 had passed, it would have significantly impacted the oil and gas industry in Colorado. Although Proposition 112 was defeated, similar legislation may be introduced in Colorado and other states to address public concerns about oil and gas development, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our operations are subject to political and economic instability and risk of government actions that could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations, and consolidated financial condition.
We are exposed to risks inherent in doing business in each of the countries in which we operate. Our operations are subject to various risks unique to each country that could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations, and consolidated financial condition. With respect to any particular country, these risks may include:
| |
• | political and economic instability, including: |
| |
◦ | civil unrest, acts of terrorism, force majeure, war, other armed conflict, and sanctions; |
| |
◦ | currency fluctuations, devaluations, conversion, or repatriation restrictions; and |
| |
• | governmental actions that may: |
| |
◦ | result in expropriation and nationalization of our assets in that country; |
| |
◦ | result in confiscatory taxation or other adverse tax policies; |
| |
◦ | limit extraction of shale gas or oil using hydraulic fracturing; |
| |
◦ | limit or disrupt markets or our operations, restrict payments, or limit the movement of funds; |
| |
◦ | result in increased tariffs; |
| |
◦ | impose trade and economic sanctions or other restrictions; |
| |
◦ | increase borrowing costs; |
| |
◦ | result in the deprivation of contract rights; and |
| |
◦ | result in the inability to obtain or retain licenses required for operation. |
Liabilities for natural resource damages, cleanup costs, and other damages under environmental, health and safety laws could result in restrictions or prohibitions on our facilities, substantial civil or criminal liabilities and could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations, and consolidated financial condition.
We are subject to extensive environmental, health and safety regulation in the United States and the other countries where our manufacturing facilities are located including those covering hazardous materials. We and all of our activities in the United States are subject noise abatement and air emissions regulations, the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act of 1980, regulations issued and laws enforced by the labor and employment departments of the U.S. and the states in which we conduct business, the U.S. Department of Commerce, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. In Germany, we and all our activities are subject to various safety and environmental regulations of the federal state which are enforced by the local authorities, including the Federal Act on Emission Control (Bundes-
Immissionsschutzgesetz). The Federal Act on Emission Control permits are held by companies jointly owned by DynaEnergetics and the other companies that are located at the Troisdorf manufacturing site and are for an indefinite period of time. The Dillenburg, Germany facility is operated based on a specific permit granted by the local mountain authority and must be renewed every three years. Any failure to comply with current and future environmental and safety regulations could subject us to significant liabilities. Any actual or alleged violations of environmental, health or safety laws could result in restrictions or prohibitions on our facilities or substantial civil or criminal sanctions. In addition, under certain environmental laws, we could be held responsible for all of the costs relating to any contamination at our facilities and at third party waste disposal sites, even when such contamination was caused by a predecessor and even when the actions resulting in the contamination were lawful at the time. We could also be held liable for any and all consequences arising out of human exposure to hazardous substances or other environmental damage. Accordingly, environmental, health or safety matters may result in significant unanticipated costs or liabilities, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results and financial condition.
Our failure to comply with Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”) and other laws could have a negative impact on our ongoing operations.
We are subject to complex U.S. and foreign laws and regulations, such as the FCPA and the U.K. Bribery Act, and various other anti-bribery and anticorruption laws. The internal controls, policies and procedures, and employee training and compliance programs we have implemented to deter prohibited practices may not be effective in preventing employees, contractors or agents from violating or circumventing such internal policies and violating applicable laws and regulations. Any determination that we have violated or are responsible for violations of anti-bribery or anti-corruption laws could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition. Violations of international and U.S. laws and regulations may result in fines and penalties, criminal sanctions, administrative remedies, and restrictions on business conduct and could have a material adverse effect on our reputation and our business, operating results and financial condition.
Changes in or interpretation of tax law and currency/repatriation control could impact the determination of our income tax liabilities for a tax year.
We have worldwide operations. Consequently, we are subject to the jurisdiction of a significant number of taxing authorities. The income earned in these various jurisdictions is taxed on differing bases, including net income actually earned, net income deemed earned, and revenue-based tax withholding. The final determination of our income tax liabilities involves the interpretation of local tax laws, tax treaties, and related authorities in each jurisdiction, as well as the use of estimates and assumptions regarding the scope of future operations and results achieved and the timing and nature of income earned and expenditures incurred. Changes in the operating environment, including changes in or interpretation of tax law and currency/repatriation controls, could impact the determination of our income tax liabilities for a tax year in a manner that is adverse to us.
The enactment of legislation implementing changes in taxation of international business activities, the adoption of other corporate tax reform policies, or changes in tax legislation or policies could materially impact our financial position and results of operations.
Corporate tax reform, base-erosion prevention efforts and tax transparency continue to be high priorities in many tax jurisdictions where we have business operations. As a result, policies regarding corporate income and other taxes in numerous jurisdictions are under heightened scrutiny and tax reform legislation is being proposed or enacted in a number of jurisdictions. For example, the 2017 Tax Reform Act, among other things, reduced the U.S. corporate income tax rate and imposed base-erosion prevention measures on non-U.S. earnings of U.S. entities as well as a one-time mandatory deemed repatriation tax on accumulated non-U.S. earnings of U.S. entities. The 2017 Tax Reform Act will affect the tax position reflected on our Consolidated Balance Sheets and our obligations for cash taxes of our U.S. entities and has had a corresponding impact on our consolidated financial results starting in the first quarter of our fiscal year 2018.
In addition, many countries are beginning to implement legislation and other guidance to align their international tax rules with the Organisation for Economic Co-operation’s Base Erosion and Profit Shifting recommendations and action plan that aim to standardize and modernize global corporate tax policy, including through changes to cross-border tax, transfer-pricing documentation rules, and nexus-based tax incentive practices. As a result of the heightened scrutiny of corporate taxation policies, prior decisions by tax authorities regarding treatments and positions of corporate income taxes could be subject to enforcement activities, and legislative investigation and inquiry, which could also result in changes to tax policies or prior tax rulings. Any such changes in policies or rulings may also result in the taxes we previously paid being subject to change.
Due to the large scale of our international business activities any substantial changes in international corporate tax policies, enforcement activities or legislative initiatives may materially and adversely affect our business, the amount of taxes we are required to pay and our financial condition and results of operations generally.
Work stoppages and other labor relations matters may make it substantially more difficult or expensive for us to produce our products, which could result in decreased sales or increased costs, either of which would negatively impact our financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to the risk of work stoppages and other labor relations matters, particularly in Germany and France, where some of our employees are unionized. The employees at our U.S. manufacturing facilities are not unionized. Any prolonged work stoppage or strike at any one of our principal facilities could have a negative impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
We are subject to litigation and may be subject to additional litigation in the future.
We are currently, and may in the future become, subject to litigation, arbitration or other legal proceedings with other parties. Managing or defending such legal proceedings may result in substantial legal fees, expenses and costs and diversion of management resources. If decided adversely to DMC, these legal proceedings, or others that could be brought against us in the future, could have a material adverse effect on our financial position or prospects. For a more detailed discussion of pending litigation, see Note 8 to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
In the event of a dispute arising at our foreign operations, we may be subject to the exclusive jurisdiction of foreign courts or arbitral panels, or may not be successful in subjecting foreign persons to the jurisdiction of courts or arbitral panels in the United States. Our inability to enforce our rights and the enforcement of rights on a prejudicial basis by foreign courts or arbitral panels could have an adverse effect on our results of operations and financial position.
Our failure to protect our proprietary information and any successful intellectual property challenges or infringement proceedings against us could materially and adversely affect our competitive position.
We rely on a variety of intellectual property rights that we use in our products and services. We may not be able to successfully preserve these intellectual property rights in the future, and these rights could be invalidated, circumvented, or challenged. In addition, the laws of some foreign countries in which our products and services may be sold do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States. Our failure to protect our proprietary information could materially and adversely affect our competitive position. In addition, our competitors may be able to develop technology independently that is similar to ours without infringing on our patents or gaining access to our trade secrets, and this could have a similar effect on our competitive position.
We may be subject to litigation if another party claims that we have infringed upon its intellectual property rights.
Moreover, the tools, techniques, methodologies, programs and components we use to provide our services may infringe upon the intellectual property rights of others. We have an active "freedom to operate" review process for our technology, but there is no assurance that future infringement claims will not be asserted. Infringement claims, such as those raised in the recent GEODynamics litigation, generally result in significant legal and other costs and may distract management from running our core business even if we are ultimately successful. In the event of any adverse ruling in any intellectual property litigation, we could be required to pay substantial damages, cease the manufacturing, use and sale of infringing products, discontinue the use of certain processes or obtain a license from the third party claiming infringement with royalty payment obligations by us. We also have certain indemnification obligations to customers with respect to the infringement of third party intellectual property rights by our products, which may increase our costs.
A failure in our information technology systems or those of third parties, including those caused by security breaches, cyber-attacks or data protection failures, could disrupt our business, damage our reputation and cause losses.
We are dependent upon information technology systems in the conduct of our operations. Our information technology systems are subject to disruption, damage or failure from a variety of sources, including, without limitation, computer viruses, security breaches, cyber-attacks, natural disasters and defects in design. Cybersecurity incidents in particular are evolving and include, but are not limited to, malicious software, attempts to gain unauthorized access to data and other electronic security breaches that could lead to disruptions in systems, unauthorized release of confidential or otherwise protected information and the corruption of data. Various measures have been implemented to manage our risks related to information technology systems and network disruptions. However, given the unpredictability of the timing, nature and scope of information technology
disruptions, we could potentially be subject to production downtimes, operational delays, the compromising of confidential or otherwise protected information, destruction or corruption of data, security breaches, theft, other manipulation or improper use of our systems and networks or financial losses from remedial actions, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our cash flows, competitive position, financial condition or results of operations.
We outsource certain technology and business process functions to third parties and may increasingly do so in the future. If we do not effectively develop, implement and monitor our outsourcing strategy, third party providers do not perform as anticipated or we experience technological or other problems with a transition, we may not realize productivity improvements or cost efficiencies and may experience operational difficulties, increased costs and loss of business. Our outsourcing of certain technology and business processes functions to third parties may expose us to enhanced risks related to data security, which could result in monetary and reputational damages. In addition, our ability to receive services from third party providers may be impacted by cultural differences, political instability, and unanticipated regulatory requirements or policies. As a result, our ability to conduct our business may be adversely affected.
The regulatory environment surrounding information security and privacy is increasingly demanding. We are subject to numerous U.S. federal and state laws and non-U.S. laws and regulations governing the protection of personal and confidential information of our customers and employees. In particular, the European Union (“E.U.”) has adopted the General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, which contains numerous requirements that must be complied with when handling the personal data of E.U.-based data subjects. We are subject to the GDPR with respect to our E.U. operations and employees. The GDPR and similar laws and regulations are increasing in complexity and number, change frequently and sometimes conflict. In particular, as the E.U. states reframe their national legislation to harmonize with the GDPR, we will need to monitor compliance with all relevant E.U. member states' laws and regulations, including where permitted derogations from the GDPR are introduced. In addition, the states of California and Colorado have recently enacted data privacy laws, and such laws may be enacted in other states or at the U.S. federal level.
The GDPR, any resultant changes in E.U. member states' national laws and regulations, and existing or new U.S. state or federal data privacy laws and regulations may increase our compliance obligations and may necessitate the review and implementation of policies and processes relating to our collection and use of data. This increase in compliance obligations could also lead to an increase in compliance costs which may have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations. If any person, including any of our employees or those with whom we share such information, negligently disregards or intentionally breaches our established controls with respect to our client or employee data, or otherwise mismanages or misappropriates that data, we could be subject to significant monetary damages, regulatory enforcement actions, fines and/or criminal prosecution in one or more jurisdictions. For example, under the GDPR there are significant new punishments for noncompliance which could result in a penalty of up to the greater of €20 million or 4% of a firm's global annual revenue. In addition, a data breach could result in negative publicity which could damage our reputation and have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
To the extent that we seek to expand our business through acquisitions, we may experience issues in executing acquisitions or integrating acquired operations.
From time to time, we examine opportunities to make selective acquisitions in order to increase shareholder return by increasing our total available markets, expanding our existing operations and, potentially, generating synergies. The success of any acquisition depends on a number of factors, including, but not limited to:
| |
• | identifying suitable candidates for acquisition and negotiating acceptable terms; |
| |
• | obtaining approval from regulatory authorities and potentially DMC’s shareholders; |
| |
• | maintaining our financial and strategic focus and avoiding distraction of management during the process of integrating the acquired business; |
| |
• | implementing our standards, controls, procedures and policies at the acquired business and addressing any pre-existing liabilities or claims involving the acquired business; and |
| |
• | to the extent the acquired operations are in a country in which we have not operated historically, understanding the regulations and challenges of operating in that new jurisdiction. |
There can be no assurance that we will be able to conclude any acquisitions successfully or that any acquisition will achieve the anticipated synergies or other positive results. Any material problems that we encounter in connection with such an acquisition could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial position.
If we fail to establish and maintain adequate internal controls over financial reporting, we may not be able to report our financial results in a timely and reliable manner, which could harm our business and impact the value of our securities.
We depend on our ability to produce accurate and timely financial statements in order to run our business. If we fail to do so, our business could be negatively affected and our independent registered public accounting firm may be unable to attest to the fair presentation of our Consolidated Financial Statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting, as required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. Effective internal controls are necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports and to effectively prevent fraud. If we cannot provide reliable financial reports and effectively prevent fraud, our reputation and operating results could be harmed. Even effective internal controls have inherent limitations including the possibility of human error, the circumvention or overriding of controls, or fraud. Therefore, even effective internal controls can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements. In addition, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting in future periods are subject to the risk that the control may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or a deterioration in the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures.
If we fail to maintain adequate internal controls, including any failure to implement new or improved controls, or if we experience difficulties in their execution, we could fail to meet our reporting obligations, and there could be a material adverse effect on our business and financial results. In the event that our current control practices deteriorate, we may be unable to accurately report our financial results or prevent fraud, and investor confidence and the market price of our stock may be adversely affected.
Risk Factors Related to Our Common Stock
The price of our common stock may be volatile, which may make it difficult for you to resell the common stock when you want or at prices you find attractive.
The market price and volume of our common stock may be subject to significant fluctuations due to general stock market conditions and/or a change in sentiment in the market regarding our operations, business prospects or liquidity. Among the factors that could affect the price of our common stock are:
| |
• | changes in the oil and gas, industrial, or infrastructure markets; |
| |
• | operating and financial performance that vary from the expectations of management, securities analysts or investors; |
| |
• | developments in our business or in our business sectors generally; |
| |
• | regulatory changes affecting our industry generally or our business and operations; |
| |
• | the operating and stock price performance of companies that investors consider to be comparable to us; |
| |
• | announcements of strategic developments, acquisitions and other material events by us or our competitors; |
| |
• | our ability to integrate and operate the companies and the businesses that we acquire; and |
| |
• | changes in global financial markets and global economies and general market conditions, including volatility in foreign exchange rates, tariffs and stock, commodity, credit or asset valuations, and federal government actions or shutdowns. |
The stock markets in general have experienced extreme volatility that has at times been unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. These broad market fluctuations may adversely affect the trading price of our common stock.
Holders of our common stock may not receive dividends.
Holders of our common stock are entitled to receive only such dividends as our Board of Directors may declare out of funds legally available for such payments. We are incorporated in Delaware and governed by the Delaware General Corporation Law. Delaware law allows a corporation to pay dividends only out of surplus, as determined under Delaware law or, if there is no surplus, out of net profits for the fiscal year in which the dividend was declared and for the preceding fiscal year. Under Delaware law, however, we cannot pay dividends out of net profits if, after we pay the dividend, our capital would be impaired. Our ability to pay dividends will be subject to our future earnings, capital requirements and financial condition, as well as our compliance with covenants and financial ratios related to existing or future indebtedness. Although we have historically declared cash dividends on our common stock, we are not required to do so and our Board of Directors may modify the dividend policy or reduce, defer or eliminate our common stock dividend in the future.
ITEM 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
ITEM 2. Properties
Corporate Headquarters
Our corporate headquarters currently are located in Boulder, Colorado. During the third quarter of 2018, we signed a lease for new office space for our corporate headquarters and for NobelClad’s U.S. administrative offices. We expect to move into the new offices during the second quarter of 2019.
|
| | | | | | | | |
Location | | Property Type | | Property Size | | Owned/Leased | | Expiration Date of Lease (if applicable) |
Boulder, Colorado (a) | | Corporate and Sales Office | | 14,630 sq. ft. | | Leased | | November 30, 2022 |
Broomfield, Colorado | | Corporate and Sales Office | | 18,284 sq. ft. | | Leased | | September 1, 2029 |
(a) The Boulder, Colorado office has an early termination provision that would accelerate the lease expiration date to November 30, 2019.
DynaEnergetics
DynaEnergetics leases a manufacturing site and sales office in Troisdorf, Germany. The leases for these properties expire on December 31, 2020. In the U.S., DynaEnergetics owns manufacturing and assembly sites in Texas and assembly operations in Pennsylvania and leases storage bunkers and office and warehouse space in various cities throughout Texas, Oklahoma, and Louisiana. DynaEnergetics also leases office and warehouse space and bunkers for storage of its explosives in various cities throughout Alberta, Canada. DynaEnergetics owns the land for its manufacturing site and sales office site in Tyumen, Siberia.
The tables below summarize our properties by segment, including their location, type, size, whether owned or leased and expiration terms, if applicable.
|
| | | | | | | | |
Location | | Property Type | | Property Size | | Owned/Leased | | Expiration Date of Lease (if applicable) |
Troisdorf, Germany | | Manufacturing and administration office | | Manufacturing: 263,201 sq. ft. Office: 2,033 sq. ft. | | Leased | | December 31, 2020, with renewal option for 5 years |
Troisdorf, Germany | | Office, Sieglarer Strasse | | 9,203 sq. ft. | | Leased | | February 29, 2020 with yearly renewal options |
Liebenscheid, Germany | | Manufacturing and office | | 91, 493 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
Edmonton, Alberta (a) | | Sales office and warehouse | | 24,000 sq. ft. | | Leased | | January 31, 2019 |
Grande Prairie, Alberta | | Sales office and warehouse | | 3,504 sq. ft. | | Leased | | December 31, 2021 |
Grande Prairie, Alberta | | Storage magazines | | 144 sq. ft. | | Leased | | Month to month agreement |
Red Deer, Alberta (b) | | Sales office and warehouse | | 12,500 sq. ft. | | Leased | | March 31, 2020 |
Red Deer, Alberta | | Storage magazines | | 1,000 sq. ft. | | Leased | | Lease is continuous until either party gives 120 days notice |
Bonnyville, Alberta (a) | | Sales office and warehouse | | 5,355 sq. ft. | | Leased | | October 31, 2019 |
Bonnyville, Alberta | | Storage magazines | | 95 sq. ft. | | Leased | | Month to month agreement |
Andrews, Texas | | Office and warehouse | | 4,000 sq. ft. | | Leased | | Month to month agreement |
Andrews, Texas | | Land for magazines | | 600 sq. ft. | | Leased | | Month to month agreement |
Houston, Texas | | Office | | 4,572 sq. ft. | | Leased | | April 30, 2023 |
Blum, Texas | | Office, warehouse, and manufacturing | | 83,000 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
Blum, Texas (c) | | Warehouse | | 10,000 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
Blum, Texas | | Land for office, warehouse, and manufacturing | | 284 acres | | Owned | | |
Victoria, Texas | | Office and warehouse | | 4,000 sq. ft. | | Leased | | Month to month agreement |
Victoria, Texas | | Storage magazine | | 8,000 sq. ft. | | Leased | | Month to month agreement |
Whitney, Texas | | Office, warehouse, and manufacturing | | 36,000 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Location | | Property Type | | Property Size | | Owned/Leased | | Expiration Date of Lease (if applicable) |
Lafayette, Louisiana | | Office and warehouse | | 6,800 sq. ft. | | Leased | | Month to month agreement |
Beaux Bridge, Louisiana | | Storage magazine | | 600 sq. ft. | | Leased | | Month to month agreement |
Dunbar, Pennsylvania | | Storage magazines | | 400 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
Mt. Braddock, Pennsylvania | | Office and warehouse | | 661 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
Oklahoma City, OK | | Office and Warehouse | | 5,900 sq ft. | | Leased | | Month to month agreement |
Oklahoma City, OK | | Storage Magazines | | 24 sq ft. | | Leased | | March 31, 2022 |
Russia, Nizhnetavdinskiy District | | Land | | 59.7 acres | | Owned | | |
| | | | 1.6 acres | | Owned | | |
Russia, Nizhnetavdinskiy District | | Office | | 9,860 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
Russia, Nizhnetavdinskiy District | | Manufacturing | | 58,216 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
Urengoy, Russia | | Warehouse | | 900 sq. ft. | | Leased | | December 31, 2019 |
Sheremetyevo, Russia (Mezdunarodnoye Shosse 9) | | Warehouse | | Any shipped quantity of goods | | Leased | | Not limited |
(a) The Edmonton, Alberta sales office and warehouse and a portion of the Bonnyville, Alberta sales office and warehouse have been subleased for the duration of their remaining leases.
(b) The Red Deer, Alberta sales office has been vacant since December 31, 2016.
(c ) The Blum, Texas warehouse is separate from the main Blum manufacturing campus.
NobelClad
We own our principal domestic manufacturing site, which is located in Mount Braddock, Pennsylvania. We currently lease our primary domestic shooting site, which is located in Dunbar, Pennsylvania, and we also have license and risk allocation agreements relating to the use of a secondary shooting site, Coolspring, that is located within a few miles of the Mount Braddock facility. The shooting site in Dunbar and the nearby secondary shooting site support our Mount Braddock facility. The lease for the Dunbar property will expire on December 15, 2020, but we have options to renew the lease which would then extend through December 15, 2029. The license and risk allocation agreements will expire on March 31, 2023.
NobelClad owns a manufacturing site in Liebenscheid, Germany as well as a mine used as a shooting site in Dillenburg, Germany. We lease buildings and land around the mine to ensure access to the shooting site. The leases associated with the Dillenburg shooting site expire August 31, 2021. NobelClad owns the building housing its sales and administrative office in Rivesaltes, France.
|
| | | | | | | | |
Location | | Property Type | | Property Size | | Owned/Leased | | Expiration Date of Lease (if applicable) |
Mt. Braddock, Pennsylvania (a) | | Clad plate manufacturing and administration office | | Land: 14 acres Buildings: 101,300 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
Dunbar, Pennsylvania | | Clad plate shooting site | | Land: 322 acres Buildings: 15,960 sq. ft. | | Leased | | December 15, 2020, with renewal options through December 15, 2029 |
Cool Spring, Pennsylvania | | Clad plate shooting site | | 1,200,000 sq. ft. | | Leased | | March 31, 2023, with renewal options through December 31, 2028 |
Rivesaltes, France (b) | | Clad plate manufacturing, sales and administration office | | Land: 6.6 acres Buildings: 49,643 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
Tautavel, France (c) | | Clad shooting site | | 109 acres | | Owned | | |
Dillenburg, Germany | | Clad plate shooting site | | 11.4 acres | | Owned | | |
| | | | 31,345 sq. ft. | | Leased | | August 31, 2021 |
Würgendorf, Germany (d) | | Manufacturing | | Land: 24.6 acres | | Owned | | |
| | | | Storehouse 174 and 265: 2,756 sq. ft. | | Leased | | December 31, 2020 with renewal options through December 31, 2025 |
| | | | Building: 34,251 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
Liebenscheid, Germany | | Manufacturing | | Land: 10.47 acres Buildings: 125,394 sq. ft. | | Owned | | |
(a) The Mt. Braddock, Pennsylvania location is also used as a manufacturing and distribution center for our DynaEnergetics business segment.
(b) NobelClad has entered into a sales agreement with a buyer for the Rivesaltes, France manufacturing plant, and the sale is expected to close during the first quarter of 2019.
(c) Though NobelClad is no longer performing manufacturing activities in France, it owns this land in order to have access to a redundant shooting site.
(d) In connection with the purchase of the manufacturing facility in Liebenscheid, Germany, NobelClad ceased use of the manufacturing facility in Würgendorf, Germany in the first quarter of 2015.
ITEM 3. Legal Proceedings
Anti-dumping and Countervailing Duties
In June 2015, U.S. Customs and Border Protection (“U.S. Customs”) sent us a Notice of Action that proposed to classify certain of our imports as subject to anti-dumping duties pursuant to a 2010 anti-dumping duty (“AD”) order on Oil Country Tubular Goods (“OCTG”) from China. A companion countervailing duty (“CVD”) order on the same product is in effect as well. The Notice of Action covered one entry of certain raw material steel mechanical tubing made in China and imported into the U.S. from Canada by our DynaEnergetics segment during 2015 for use in manufacturing perforating guns.
In July 2015, we sent a response to U.S. Customs outlining the reasons for our position that our mechanical tubing imports do not fall within the scope of the AD order on OCTG from China and should not be subject to anti-dumping duties. U.S. Customs proposed to take similar action with respect to other entries of this product and requested an approximately $1,100 cash deposit or bond for AD/CVD duties.
In August 2015, we posted bonds of approximately $1,100 to U.S. Customs. Subsequently, U.S. Customs declined to conclude that the mechanical tubing the Company had been importing was not within the scope of the AD order on OCTG from China. As a result, on September 25, 2015 the Company filed a request for a scope ruling with the U.S. Department of Commerce ("Commerce Department").
On February 15, 2016, the Company received the Commerce Department’s scope ruling, which determined certain imports, primarily used for gun carrier tubing, are included in the scope of the AD/CVD orders on OCTG from China and thus are subject to AD/CVD. On March 11, 2016, the Company filed an appeal with the U.S. Court of International Trade (“CIT”) related to the Commerce Department’s scope ruling. On February 7, 2017, the CIT remanded the scope ruling to the Commerce Department to reconsider its determination. The Commerce Department filed its remand determination with the CIT on June 7, 2017, continuing to find that the Company’s imports at issue are within the scope of the AD/CVD orders on OCTG from China. On March 16, 2018, the CIT issued its decision on the appeal and sustained the Commerce Department’s scope ruling. The Company did not appeal this ruling, and during the quarter ended September 30, 2018, the Company paid the remaining accrued AD/CVD and interest of $3,461 to U.S. Customs.
On December 27, 2016, we received notice from U.S. Customs that it may pursue penalties against us related to the AD/CVD issue and demanding tender of alleged loss of AD/CVD in an amount of $3,049, which had previously been accrued for in our financial statements. We filed a response to the notice on February 6, 2017. On February 16, 2017, we received notice that U.S. Customs was seeking penalties in the amount of $14,783. U.S. Customs also reasserted its demand for tender of alleged loss of AD/CVD in the amount of $3,049. We tendered $3,049 in AD amounts on March 6, 2017 into a suspense account pending ultimate resolution of the AD/CVD case. We submitted a petition for relief and mitigation of penalties on May 17, 2017.
On March 27, 2018, we received notice from U.S. Customs Headquarters that it intended to move forward with its pursuit of penalties. The Company engaged in discussions with U.S. Customs Headquarters regarding the scope of penalties asserted and the arguments set forth in the Company’s petition for relief and mitigation of penalties. Based on these discussions and the Company’s assessment of the probable ultimate penalty rate, the Company accrued $3,103 in the first quarter of 2018.
On October 11, 2018, we received a decision from U.S. Customs Headquarters in which a mitigated amount of $8,000 in penalties was asserted. In its financial statements for the quarter ended September 30, 2018, the Company accrued an additional $4,897 of penalties. On December 7, 2018, we submitted a supplemental petition requesting a waiver of the penalty under the Small Business Regulatory Enforcement Act in lieu of tendering the penalty amount. We expect to receive a response to this waiver request by the end of the first quarter of 2019.
Patent and Trademark Infringement
On April 28, 2017, GEODynamics, Inc., a U.S.-based oil and gas perforating equipment manufacturer based in Fort Worth, Texas (“GEODynamics”) filed a patent infringement action against DynaEnergetics US, Inc. (“DynaEnergetics”) in the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Texas (“District Court”) alleging infringement of U.S. Patent No. 8,220,394 (the “394 patent”), based on DynaEnergetics’ U.S. sales of its DPEX® and HaloFrac® shaped charges. The 394 patent case went to trial in early October 2018, and on October 10, 2018, the jury found in favor of DynaEnergetics on all counts.
On August 21, 2017, GEODynamics filed a patent infringement action against DynaEnergetics and DynaEnergetics Beteiligungs GmbH, both wholly owned subsidiaries of DMC (collectively, “DynaEnergetics EU”), in the Regional Court of Düsseldorf, Germany, alleging infringement of the German part DE 60 2004 033 297 of European patent EP 1 671 013 B1 granted on June 29, 2011, a patent related to the 394 patent (the “EP 013 patent”). DynaEnergetics EU filed its defense at the Regional Court of Düsseldorf and a nullity action against EP 013 at the German Federal Patent Court on February 14, 2018.
On September 27, 2017, DynaEnergetics filed a revocation action in the Patents Court, Shorter Trials Scheme in the UK against GEODynamics, asserting that the EP 013 patent, as maintained in the UK, is invalid. GEODynamics filed its defense in November 2017.
On November 9, 2018, DynaEnergetics entered into a global settlement agreement with GEODynamics, which resolves all outstanding claims and legal disputes concerning reactive shaped charge technology. All actions in the UK and Germany and other related actions have been dismissed. The settlement had no negative financial impact on DynaEnergetics.
ITEM 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Our Coolspring property is subject to regulation by the Federal Mine Safety and Health Administration ("MSHA") under the Federal Mine Safety and Health Act of 1977 (the "Mine Act"). Pursuant to Section 1503(a) of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the "Dodd-Frank Act"), issuers that are operators, or that have a subsidiary that is an operator, of a coal or other mine in the United States are required to disclose in their periodic reports filed with the SEC information regarding specified health and safety violations, orders and citations, related assessments and legal actions, and mining-related fatalities. During the year ended December 31, 2018, we had no such specified health and safety violations, orders or citations, related assessments or legal actions, mining-related fatalities, or similar events in relation to our United States operations requiring disclosure pursuant to Section 1503(a) of the Dodd-Frank Act.
PART II
ITEM 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Our common stock is publicly traded on The Nasdaq Global Select Market (“Nasdaq”) under the symbol “BOOM.” As of February 20, 2019, there were 246 holders of record of our common stock (does not include beneficial holders of shares held in “street name”).
Equity Compensation Plan
Refer to “Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters” for information regarding securities authorized for issuance under our equity compensation plans, which is incorporated in this Item by this reference.
Stock Performance Graph
The following graph compares the performance of our common stock with the Nasdaq Non-Financial Stocks Index and the Nasdaq Composite (U.S.) Index. The comparison of total return (change in year-end stock price plus reinvested dividends) for each of the years assumes that $100 was invested on December 31, 2013, in each of the Company, the Nasdaq Non-Financial Stocks Index and the Nasdaq Composite (U.S.) Index with investment weighted on the basis of market capitalization. The comparisons in the graph below are based upon historical data and are not indicative of, or intended to forecast, future performance of our common stock.
|
| | | | | | |
Total Return Analysis | 12/31/13 | 12/31/14 | 12/31/15 | 12/31/16 | 12/31/17 | 12/31/18 |
DMC Global Inc. | $100.00 | $73.69 | $32.15 | $72.91 | $115.23 | $161.55 |
Nasdaq Non-Financial Stocks | $100.00 | $119.40 | $131.05 | $140.58 | $186.96 | $187.03 |
Nasdaq Composite (U.S.) | $100.00 | $112.46 | $113.00 | $127.70 | $155.01 | $146.57 |
ITEM 6. Selected Financial Data
The following selected financial data should be read in conjunction with the Consolidated Financial Statements, including the related Notes, and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” In October 2014, we completed the sale of AMK, and the 2014 information reflects the classification of AMK into discontinued operations.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (Dollars in Thousands, Except Per Share Data) |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
Statement of Operations | | 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 | | 2015 | | 2014 |
Net sales | | $ | 326,429 |
| | $ | 192,803 |
| | $ | 158,575 |
| | $ | 166,918 |
| | $ | 202,561 |
|
Gross profit | | 110,695 |
| | 59,391 |
| | 38,680 |
| | 35,624 |
| | 61,419 |
|
Costs and expenses | | 64,157 |
| | 49,784 |
| | 42,752 |
| | 43,776 |
| | 47,973 |
|
Restructuring expenses | | 1,114 |
| | 4,283 |
| | 1,202 |
| | 4,063 |
| | 6,781 |
|
Anti-dumping duty penalty | | 8,000 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Goodwill impairment | | — |
| | 17,584 |
| | — |
| | 11,464 |
| | — |
|
Income (loss) from operations | | 37,424 |
| | (12,260 | ) | | (5,274 | ) | | (23,679 | ) | | 6,665 |
|
Other expense, net | | (2,817 | ) | | (3,024 | ) | | (434 | ) | | (2,410 | ) | | (826 | ) |
Income (loss) before income taxes and discontinued operations | | 34,607 |
| | (15,284 | ) | | (5,708 | ) | | (26,089 | ) | | 5,839 |
|
Income tax provision (benefit) | | 4,134 |
| | 3,569 |
| | 797 |
| | (2,118 | ) | | 3,913 |
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations | | 30,473 |
| | (18,853 | ) | | (6,505 | ) | | (23,971 | ) | | 1,926 |
|
Income from discontinued operations | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 641 |
|
Net income (loss) | | $ | 30,473 |
| | $ | (18,853 | ) | | $ | (6,505 | ) | | $ | (23,971 | ) | | $ | 2,567 |
|
Net income (loss) per share - Basic: | | |
| | |
| | |
| | | | |
|
Continuing operations | | $ | 2.05 |
| | $ | (1.31 | ) | | $ | (0.46 | ) | | $ | (1.72 | ) | | $ | 0.13 |
|
Discontinued operations | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 0.05 |
|
Net income (loss) | | $ | 2.05 |
| | $ | (1.31 | ) | | $ | (0.46 | ) | | $ | (1.72 | ) | | $ | 0.18 |
|
Net income (loss) per share - Diluted: | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | $ | 2.04 |
| | $ | (1.31 | ) | | $ | (0.46 | ) | | $ | (1.72 | ) | | $ | 0.13 |
|
Discontinued operations | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 0.05 |
|
Net income (loss) | | $ | 2.04 |
| | $ | (1.31 | ) | | $ | (0.46 | ) | | $ | (1.72 | ) | | $ | 0.18 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Dividends Declared per Common Share | | $ | 0.08 |
| | $ | 0.08 |
| | $ | 0.08 |
| | $ | 0.14 |
| | $ | 0.16 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Financial Position | | |
| | |
| | |
| | | | |
|
Total assets | | $ | 240,418 |
| | $ | 173,083 |
| | $ | 162,555 |
| | $ | 182,192 |
| | $ | 219,329 |
|
Long-term debt, including current portion | | $ | 41,355 |
| | $ | 17,984 |
| | $ | 15,732 |
| | $ | 26,826 |
| | $ | 22,782 |
|
ITEM 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with our historical Consolidated Financial Statements and notes, as well as the selected historical consolidated financial data included elsewhere in this annual report.
Unless stated otherwise, all dollar figures in this report are presented in thousands (000s). N/M indicates that the change in dollars or percentage was not meaningful.
Overview
General
DMC operates a diversified family of technical product and process businesses serving the energy, industrial and infrastructure markets. Our businesses operate through a global network of manufacturing, distribution and sales facilities. Our business is organized into two segments: NobelClad and DynaEnergetics.
Our diversified segments each provide a suite of unique technical products to niche sectors of the global energy, industrial and infrastructure markets, and each has established a strong or leading position in the markets in which it participates. With an underlying focus on generating free cash flow, our objective is to sustain and grow the market share of our businesses through increased market penetration, development of new applications, and research and development of new and adjacent products that can be sold across our global network of sales and distribution facilities. We routinely explore acquisitions of related businesses that could strengthen or add to our existing product portfolios, or expand our geographic footprint and market presence. We also seek acquisition opportunities outside our current markets that would complement our existing businesses and enable us to build a stronger and more diverse company.
NobelClad
NobelClad is a global leader in the production of explosion-welded clad metal plates for use in the construction of corrosion resistant industrial processing equipment and specialized transition joints. While a significant portion of the demand for our clad metal products is driven by maintenance and retrofit projects at existing chemical processing, petrochemical processing, oil refining, and aluminum smelting facilities, new plant construction and large plant expansion projects also account for a significant portion of total demand. These industries tend to be cyclical in nature and timing of new order inflow remains difficult to predict. We use backlog as a primary means to measure the immediate outlook for our NobelClad business. We define “backlog” at any given point in time as all firm, unfulfilled purchase orders and commitments at that time. Most firm purchase orders and commitments are realized, and we expect to fill most backlog orders within the following 12 months. NobelClad's backlog decreased to $29,879 at December 31, 2018 from $37,529 at December 31, 2017.
DynaEnergetics
DynaEnergetics designs, manufactures and distributes products utilized by the global oil and gas industry principally for the perforation of oil and gas wells. These products are sold to oilfield service companies in the U.S., Europe, Canada, South America, Africa, the Middle East, Russia, and Asia. DynaEnergetics also sells directly to end-users. The market for perforating products, which are used during the well completion process, generally corresponds with oil and gas exploration and production activity. Well completion operations are increasingly complex, which in turn, has increased the demand for intrinsically-safe, reliable and technically advanced perforating systems.
Cost of products sold for DynaEnergetics includes the cost of metals, explosives and other raw materials used to manufacture shaped charges, detonating products and perforating guns as well as employee compensation and benefits, depreciation of manufacturing facilities and equipment, manufacturing supplies and other manufacturing overhead expenses.
Factors Affecting Results
The following items impacted the comparability of the company's results for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017:
| |
• | DynaEnergetics' sales of $237,448 in 2018 increased 96% compared with 2017 due to increased activity levels in the North American unconventional well-completions sector and growth in demand from operators and service companies for DynaEnergetics’ advanced perforating systems. |
| |
• | NobelClad’s sales of $88,981 in 2018 increased 24% compared with 2017 primarily due to shipping three large capital equipment projects in 2018 coupled with higher volume in core repair and maintenance projects. |
| |
• | Consolidated gross profit of 34% in 2018 increased from 31% in 2017 due to a higher proportion of DynaEnergetics sales relative to NobelClad sales, higher average selling prices in DynaEnergetics and the favorable impact of higher volume on fixed manufacturing overhead expenses in both segments. |
| |
• | Restructuring expenses of $1,114 in 2018 were related to the closure of NobelClad's manufacturing operations in France. Restructuring expenses of $4,283 in 2017 related to the planned closure of NobelClad's manufacturing operations in France and the closure of DynaEnergetics' sales and distribution facility in Kazakhstan. |
| |
• | A goodwill impairment charge of $17,584 related to the NobelClad reporting unit was recorded in the third quarter of 2017 to reflect the decline in activity levels in NobelClad’s primary end markets during the second half of 2017. |
| |
• | Consolidated selling, general, and administrative expenses were $61,213 in 2018 compared with $45,724 in 2017. The increase primarily was due to an increase of $3,700 in legal costs over 2017 related to the successful defense of patent infringement lawsuits in DynaEnergetics, increased salaries and wages from headcount additions and higher variable incentive compensation expense. |
| |
• | Net debt of $27,980 (comprised of $41,355 of total debt net of $13,375 in cash) increased from $9,001 at December 31, 2017. Net debt, a non-GAAP measure, is calculated as amounts borrowed under our syndicated credit facility less cash and cash equivalents. |
Business Outlook
| |
• | During the fourth quarter of 2018, DynaEnergetics completed its new manufacturing, assembly and administrative facility in Blum, Texas. Concurrently, NobelClad concluded a multi-year consolidation of its European manufacturing operations. |
| |
• | In 2019, our businesses will continue to focus on technology, product and application development. In the first quarter of 2019, DynaEnergetics completed successful field trials on its new DS TrinityTM system - a key addition to the DynaStage family. The three shaped charges in DS Trinity are aligned on a single plane, and at 8-inches in length, the system is up to 3.5 times shorter than conventional perforating guns. DynaEnergetics intends to release a 4-inch diameter version of DS Trinity in the second quarter of 2019, and a 3 ½-inch diameter version shortly thereafter. |
| |
• | We expect to invest $25,000 to $30,000 in capital expenditures during 2019 to further expand the capacity and capabilities at our manufacturing facilities, primarily in Blum, Texas. Investments are also planned to further the development of front-end digital apps and technology that improve our customers’ experience, and upgrades to the enterprise resource planning systems in both of our businesses. |
| |
• | Management continues to explore strategic alternatives for its Russia-based perforating manufacturing and sales operations, which contributed less than 2% to the Company’s sales in 2018. |
Use of Non-GAAP Financial Measures
Adjusted EBITDA is a non-GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) measure that we believe provides an important indicator of our ongoing operating performance and that we use in operational and financial decision-making. We define EBITDA as net income or loss plus or minus net interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization. Adjusted EBITDA excludes from EBITDA stock-based compensation, restructuring and impairment charges and, when appropriate, other items that management does not utilize in assessing DMC’s operating performance (as further described in the tables below). As a result, internal management reports used during monthly operating reviews feature Adjusted EBITDA and certain management incentive awards are based, in part, on the amount of Adjusted EBITDA achieved during the year.
Net Debt is a non-GAAP measure we use to supplement information in our Consolidated Financial Statements. We define net debt as total debt less cash and cash equivalents. In addition to conventional measures prepared in accordance with GAAP, the Company uses this information to evaluate its performance, and we believe that certain investors may do the same.
The presence of non-GAAP financial measures in this report is not intended to suggest that such measures be considered in isolation or as a substitute for, or as superior to, DMC’s GAAP information, and investors are cautioned that the non-GAAP financial measures are limited in their usefulness. Because not all companies use identical calculations, DMC’s presentation of non-GAAP financial measures may not be comparable to other similarly titled measures of other companies.
Forward-Looking Statements
This annual report and the documents incorporated by reference into it contain certain forward-looking statements within the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigations Reform Act of 1995. Words such as “anticipates,” “expects,”
“intends,” “plans,” “believes,” “seeks,” “estimates,” “may,” “will,” “continue,” “project,” “forecast,” and similar expressions, as well as statements in the future tense, identify forward-looking statements. Such statements include projections, guidance and other statements regarding our future expected financial position and operating results, our growth and business strategy, our expectations regarding the oil and gas industry, expected product developments in DynaEnergetics, planned capital expenditures in 2019, impacts of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, our financing plans, our future liquidity position and factors impacting such position, and the outcome of the pending anti-dumping penalty matters.
These forward-looking statements are not guarantees of our future performance and are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results contemplated by the forward-looking statements. These risks and uncertainties include those relating to:
| |
• | Changes in global economic conditions; |
| |
• | The ability to obtain new contracts at attractive prices; |
| |
• | The size and timing of customer orders and shipments; |
| |
• | Product pricing and margins; |
| |
• | Our ability to realize sales from our backlog and our ability to adjust our manufacturing and supply chain; |
| |
• | Fluctuations in customer demand; |
| |
• | Our ability to manage periods of growth and contraction effectively; |
| |
• | General economic conditions, both domestic and foreign, impacting our business and the business of the end-market users we serve; |
| |
• | The timely completion of contracts; |
| |
• | The timing and size of expenditures; |
| |
• | The timely receipt of government approvals and permits; |
| |
• | The price and availability of metal and other raw material; |
| |
• | The adequacy of local labor supplies at our facilities; |
| |
• | Current or future limits on manufacturing capacity at our various operations; |
| |
• | Our ability to successfully integrate acquired businesses; |
| |
• | The ability to remain an innovative leader in our fields of business; |
| |
• | The impacts of pending or future litigation or regulatory matters; |
| |
• | The application of governmental regulation and oversight of our operations and products and the industries in which our customers operate; |
| |
• | The impacts of trade and economic sanctions or other restrictions imposed by the European Union, the United States or other countries; |
| |
• | Exposure under the United States Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”) or similar legislation; |
| |
• | The availability and cost of funds; and |
| |
• | Fluctuations in foreign currencies. |
The effects of these factors are difficult to predict. New factors emerge from time to time and we cannot assess the potential impact of any such factor on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statement. All forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this annual report, and we do not undertake any obligation to update any forward-looking statement to reflect
events or circumstances after the date of such statement or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. In addition, see “Risk Factors” for a discussion of these and other factors that could materially affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Consolidated Results of Operations
Year ended December 31, 2018 compared to Year Ended December 31, 2017
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 | | $ change | | % change |
Net sales | | $ | 326,429 |
| | $ | 192,803 |
| | $ | 133,626 |
| | 69 | % |
Gross profit | | 110,695 |
| | 59,391 |
| | 51,304 |
| | 86 | % |
Gross profit percentage | | 33.9 | % | | 30.8 | % | | | | |
COSTS AND EXPENSES: | | | | | | | | |
General and administrative expenses | | 38,452 |
| | 27,135 |
| | 11,317 |
| | 42 | % |
% of net sales | | 11.8 | % | | 14.1 | % | |
| | |
Selling and distribution expenses | | 22,761 |
| | 18,589 |
| | 4,172 |
| | 22 | % |
% of net sales | | 7.0 | % | | 9.6 | % | | | | |
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 2,944 |
| | 4,060 |
| | (1,116 | ) | | (27 | )% |
% of net sales | | 0.9 | % | | 2.1 | % | | | | |
Restructuring expenses | | 1,114 |
| | 4,283 |
| | (3,169 | ) | | (74 | )% |
Anti-dumping duty penalties | | 8,000 |
| | — |
| | 8,000 |
| | |
|
Goodwill impairment charge | | — |
| | 17,584 |
| | (17,584 | ) | | (100 | )% |
Operating income (loss) | | 37,424 |
| | (12,260 | ) | | 49,684 |
| | 405 | % |
Other expense, net | | (1,202 | ) | | (1,376 | ) | | 174 |
| | 13 | % |
Interest expense, net | | (1,615 | ) | | (1,648 | ) | | 33 |
| | 2 | % |
Income tax provision | | 4,134 |
| | 3,569 |
| | 565 |
| | 16 | % |
Net income (loss) | | 30,473 |
| | (18,853 | ) | | 49,326 |
| | 262 | % |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 59,638 |
| | $ | 23,148 |
| | $ | 36,490 |
| | 158 | % |
Net sales increased compared with 2017 primarily due to higher activity levels in the North American unconventional onshore oil and gas well completions sector and growth in customer demand for DynaEnergetics' advanced perforating systems combined with higher project volume in NobelClad.
Gross profit percentage increased compared with 2017 primarily due to a higher proportion of net sales in DynaEnergetics relative to NobelClad, higher average selling prices and better product mix and the favorable impact of higher sales on fixed manufacturing overhead expenses.
General and administrative expenses increased compared with 2017 principally due to the legal costs related to the successful defense of patent infringement lawsuits in DynaEnergetics, higher outside service expenses, increased salaries and wages from headcount additions, merit-based pay increases and higher variable incentive compensation and stock-based compensation expense.
Selling and distribution expenses increased compared with 2017 primarily due to headcount additions, merit-based pay increases and variable sales commissions, distribution costs and incentive compensation expense.
Amortization of purchased intangible assets decreased compared with 2017 primarily due to fully amortizing certain trademarks in DynaEnergetics as of December 31, 2017.
Restructuring expenses in 2018 related to equipment moving expenses, legal fees and severance costs associated with the closure of NobelClad’s manufacturing operations in France. Expenses in 2017 related to severance costs and asset impairments associated with the planned closure of NobelClad's manufacturing facility in France in addition to costs related to the closure of DynaEnergetics' sales and distribution operations in Kazakhstan.
Anti-dumping duty penalties represent an accrual for a mitigated amount of penalties related to the AD/CVD matter that was formally asserted by U.S. Customs Headquarters and recorded by the DynaEnergetics segment.
Goodwill impairment charge relates to fully impairing NobelClad's goodwill balance in the third quarter of 2017.
Operating income in 2018 compared with an operating loss in 2017 primarily was due to improved earnings in DynaEnergetics and NobelClad in 2018 as well as the non-recurring impact of the goodwill impairment charge recorded in 2017. Improvements in 2018 partially were offset by higher corporate unallocated and stock-based compensation expenses.
Other expense, net in 2018 and 2017 related to realized and unrealized foreign currency losses. Our subsidiaries frequently enter into inter-company and third party transactions that are denominated in currencies other than their functional currency. Changes in exchange rates with respect to these transactions will result in unrealized gains or losses if unsettled at the end of the reporting period or realized gains or losses at settlement of the transaction. During the third quarter of 2017, we began using foreign currency forward contracts, generally with maturities of one month, to offset foreign exchange rate fluctuations on certain foreign currency-denominated asset and liability positions. None of these contracts are designated as accounting hedges, and all changes in the fair value of the forward contracts are recognized immediately in "Other income (expense), net" within our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Interest expense, net decreased compared with last year. During 2018 we capitalized interest of approximately $423 incurred in relation to DynaEnergetics’ new manufacturing, assembly and administrative facility in Blum, Texas. Additionally, we amortized $314 of deferred debt issuance costs in 2018 versus $390 in 2017. These decreases partially were offset by interest incurred on a higher average outstanding debt balance in 2018 versus 2017.
Income tax provision of $4,134 for 2018 compared with an income tax provision of $3,569 for 2017. The current-year income tax provision included a benefit of $604 related to Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) 118 measurement period adjustment to the provisional amount that was recorded in 2017 for the transition tax under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act ("TCJA"). The 2017 provision included expense of $946 related to the transition tax. The transition tax is a tax on previously untaxed accumulated and current earnings and profits (“E&P”) of certain of our foreign subsidiaries.
The current-year effective tax rate was favorably impacted by changes in the valuation allowance of $8,860, which included a benefit of $5,818 related to the release of valuation allowances in certain jurisdictions and the remainder due to movements in the underlying deferred tax assets due to current year income or losses. As of each reporting date, the Company considers new evidence, both positive and negative, that could impact its view with regard to future realization of deferred tax assets. As of December 31, 2018, in part because the Company was no longer in a consolidated three-year cumulative loss position, we determined that sufficient positive evidence exists to conclude that it is more likely than not that these deferred tax assets are realizable, and therefore, reduced the valuation allowance accordingly. However, we currently are unable to recognize tax benefits associated with losses incurred in certain jurisdictions due to valuation allowances recorded against deferred tax assets in those jurisdictions.
Net income in 2018 versus a net loss in 2017 primarily was a result of improved sales and gross margin in DynaEnergetics and NobelClad as well as the non-recurring impact of the goodwill impairment charge recorded in 2017. Net income in 2018 was $30,473, or $2.04 per diluted share, compared with a net loss of $18,853, or $1.31 per diluted share in 2017.
Adjusted EBITDA increased compared with 2017 due to the factors discussed above. See "Overview" above for the explanation of the use of Adjusted EBITDA. The following is a reconciliation of the most directly comparable GAAP measure to Adjusted EBITDA.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 |
Net income (loss) | | $ | 30,473 |
| | $ | (18,853 | ) |
Interest expense, net | | 1,615 |
| | 1,648 |
|
Provision for income taxes | | 4,134 |
| | 3,569 |
|
Depreciation | | 6,576 |
| | 6,506 |
|
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 2,944 |
| | 4,060 |
|
EBITDA | | 45,742 |
| | (3,070 | ) |
Restructuring expenses | | 1,114 |
| | 4,283 |
|
Goodwill impairment charge | | — |
| | 17,584 |
|
Anti-dumping duty penalties | | 8,000 |
| | — |
|
Stock-based compensation | | 3,580 |
| | 2,975 |
|
Other (income) expense, net | | 1,202 |
| | 1,376 |
|
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 59,638 |
| | $ | 23,148 |
|
Year ended December 31, 2017 compared to Year Ended December 31, 2016
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2017 | | 2016 | | $ change | | % change |
Net sales | | $ | 192,803 |
| | $ | 158,575 |
| | $ | 34,228 |
| | 22 | % |
Gross profit | | 59,391 |
| | 38,680 |
| | 20,711 |
| | 54 | % |
Gross profit percentage | | 30.8 | % | | 24.4 | % | | | | |
COSTS AND EXPENSES: | | | | | | | | |
General and administrative expenses | | 27,135 |
| | 22,115 |
| | 5,020 |
| | 23 | % |
% of net sales | | 14.1 | % | | 13.9 | % | | | | |
Selling and distribution expenses | | 18,589 |
| | 16,626 |
| | 1,963 |
| | 12 | % |
% of net sales | | 9.6 | % | | 10.5 | % | | | | |
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 4,060 |
| | 4,011 |
| | 49 |
| | 1 | % |
% of net sales | | 2.1 | % |
| 2.5 | % | | | | |
Restructuring expenses | | 4,283 |
| | 1,202 |
| | 3,081 |
| | 256 | % |
Goodwill impairment charge | | 17,584 |
| | — |
| | 17,584 |
| | 100 | % |
Operating loss | | (12,260 | ) | | (5,274 | ) | | (6,986 | ) | | (132 | )% |
Other income (expense), net | | (1,376 | ) | | 633 |
| | (2,009 | ) | | (317 | )% |
Interest expense, net | | (1,648 | ) | | (1,067 | ) | | (581 | ) | | (54 | )% |
Income tax provision | | 3,569 |
| | 797 |
| | 2,772 |
| | 348 | % |
Net loss | | (18,853 | ) | | (6,505 | ) | | (12,348 | ) | | (190 | )% |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 23,148 |
| | $ | 9,021 |
| | $ | 14,127 |
| | 157 | % |
Net sales increased compared with 2016 due to an 80% increase in DynaEnergetics' net sales driven by a recovery in the North American unconventional well-completions sector and reflected increased well-stage counts; higher completion intensity and longer laterals; and increased market penetration of DynaEnergetics’ perforating products and systems. The increase in DynaEnergetics’ net sales partially was offset by a 22% decline in NobelClad's net sales as weak capital spending in NobelClad's industrial infrastructure and energy markets resulted in a decline in core repair and maintenance work and the absence of large projects.
Gross profit percentage increased compared with 2016 primarily due to higher average selling prices and improved product mix in DynaEnergetics and better project mix in NobelClad.
General and administrative expenses increased compared with 2016 primarily due to higher outside legal expenses related to patent infringement defense costs in DynaEnergetics, higher salaries and wages from headcount additions and increased variable incentive compensation, and higher stock-based compensation expense.
Selling and distribution expenses increased compared with 2016 principally due to higher salaries and benefits and increased outside professional services partially offset by a reduction in bad debt expense.
Restructuring expenses in 2017 related to the announced closures of NobelClad's manufacturing facility in France and DynaEnergetics' sales and distribution operations in Kazakhstan. In 2016, restructuring expenses related to severance for headcount reductions at DynaEnergetics' Troisdorf, Germany and Austin, Texas locations, lease termination costs to exit administrative offices in Austin, Texas, costs related to the relocation of perforating gun manufacturing operations in Germany, and the accelerated vesting of stock awards in connection with the elimination of certain positions.
Goodwill impairment charge was recorded in 2017 to fully impair NobelClad's goodwill balance.
Operating loss increased compared with 2016 due to the goodwill impairment charge and restructuring expenses combined with higher corporate unallocated and stock-based compensation expenses. The one-time impairment and restructuring charges and increased operating expenses partially were offset by increased sales volume, higher average selling prices, and favorable product mix in DynaEnergetics. Corporate unallocated and stock-based compensation expenses are not allocated to our business segments.
Other income (expense), net in 2017 primarily was made up of realized and unrealized foreign currency losses. In 2016, other income (expense), net principally consisted of realized and unrealized foreign currency gains. Our subsidiaries frequently enter into inter-company and third party transactions that are denominated in currencies other than their functional currency. Changes in exchange rates with respect to these transactions will result in unrealized gains or losses if unsettled at the end of the reporting period or realized gains or losses at settlement of the transaction. During the third quarter of 2017, we began using foreign currency forward contracts, generally with maturities of one month, to offset foreign exchange rate fluctuations on certain foreign currency-denominated asset and liability positions. None of these contracts are designated as accounting hedges, and all changes in the fair value of the forward contracts are recognized immediately in "Other income (expense), net" within our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Interest expense, net increased compared with 2016 primarily due to expensing $261 of deferred debt issuance costs in conjunction with amending our credit facility in March 2017 combined with higher interest rates on a higher average outstanding long-term debt balance.
Income tax provision of $3,569 for 2017 compared to an income tax benefit of $797 for 2016. The 2017 income tax provision included $946 of which was a transition tax related to the TCJA. The transition tax is a tax on previously untaxed accumulated and current earnings and profits (“E&P”) of certain of our foreign subsidiaries. To determine the amount of the transition tax, we had to determine, among other things, the amount of post-1986 E&P of the relevant subsidiaries, as well as the amount of non-U.S. income taxes paid on such earnings. We made a reasonable estimate of the transition tax and recorded a provisional transition tax obligation of $946, of which $871 was recorded in other long-term liabilities in our Consolidated Balance Sheets. The TCJA’s transition tax is payable over eight years beginning in 2018. Additionally, we were unable to recognize tax benefits associated with losses incurred in certain jurisdictions due to valuation allowances recorded against deferred tax assets in those jurisdictions.
Net loss in 2017 primarily was a result of the non-cash goodwill impairment charge and restructuring expenses and the other factors discussed above. Net loss in 2017 was $18,853, or $1.31 per diluted share, compared with a net loss of $6,505, or $0.46 per diluted share, in 2016.
Adjusted EBITDA increased compared with 2016 primarily due to the factors discussed above. See "Overview" above for the explanation of the use of Adjusted EBITDA. The following is a reconciliation of the most directly comparable GAAP measure to Adjusted EBITDA.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2017 | | 2016 |
| | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (18,853 | ) | | $ | (6,505 | ) |
Interest expense, net | | 1,648 |
| | 1,067 |
|
Provision for income taxes | | 3,569 |
| | 797 |
|
Depreciation | | 6,506 |
| | 6,756 |
|
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 4,060 |
| | 4,011 |
|
EBITDA | | (3,070 | ) | | 6,126 |
|
Restructuring charges | | 4,283 |
| | 1,202 |
|
Goodwill impairment charge | | 17,584 |
| | — |
|
Stock-based compensation | | 2,975 |
| | 2,326 |
|
Other (income) expense, net | | 1,376 |
| | (633 | ) |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 23,148 |
| | $ | 9,021 |
|
Business Segment Financial Information
We primarily evaluate performance and allocate resources based on segment revenues, operating income and Adjusted EBITDA as well as projected future performance. Segment operating income (loss) is defined as revenues less expenses identifiable to the segment. DMC operating income (loss) and Adjusted EBITDA include unallocated corporate expenses and stock-based compensation expense, which are not allocated to our business segments. Segment operating income will reconcile to consolidated income (loss) before income taxes by deducting unallocated corporate expenses, including stock-based compensation, net other expense, net interest expense, and income tax provision (benefit).
Net sales, segment operating income or loss, and Adjusted EBITDA for each segment were as follows for years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 |
| | DynaEnergetics | | NobelClad | | DMC Global Inc. |
Net Sales | | $ | 237,448 |
| | $ | 88,981 |
| | $ | 326,429 |
|
% of Consolidated | | 73 | % | | 27 | % | | |
| | | | | | |
Operating income | | 44,476 |
| | 6,499 |
| | 37,424 |
|
| | | | | | |
Adjusted EBITDA | | 58,784 |
| | 10,825 |
| | 59,638 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2017 |
| | DynaEnergetics | | NobelClad | | DMC Global Inc. |
Net Sales | | $ | 121,253 |
| | $ | 71,550 |
| | $ | 192,803 |
|
% of Consolidated | | 63 | % | | 37 | % | | |
| | | | | | |
Operating income (loss) | | 15,470 |
| | (17,360 | ) | | (12,260 | ) |
| | | | | | |
Adjusted EBITDA | | 22,807 |
| | 7,736 |
| | 23,148 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2016 |
| | DynaEnergetics | | NobelClad | | DMC Global Inc. |
Net Sales | | $ | 67,290 |
| | $ | 91,285 |
| | $ | 158,575 |
|
% of Consolidated | | 42 | % | | 58 | % | | |
| | | | | | |
Operating income (loss) | | (5,381 | ) | | 8,878 |
| | (5,274 | ) |
| | | | | | |
Adjusted EBITDA | | 2,515 |
| | 12,877 |
| | 9,021 |
|
DynaEnergetics
Year ended December 31, 2018 compared to Year Ended December 31, 2017
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 | | $ change | | % change |
Net sales | | $ | 237,448 |
| | $ | 121,253 |
| | $ | 116,195 |
| | 96 | % |
Gross profit | | 90,623 |
| | 44,029 |
| | 46,594 |
| | 106 | % |
Gross profit percentage | | 38.2 | % | | 36.3 | % | | | | |
COSTS AND EXPENSES: | | | | | | | | |
General and administrative expenses | | 21,097 |
| | 13,373 |
| | 7,724 |
| | 58 | % |
Selling and distribution expenses | | 14,509 |
| | 11,054 |
| | 3,455 |
| | 31 | % |
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 2,541 |
| | 3,674 |
| | (1,133 | ) | | (31 | )% |
Restructuring expenses | | — |
| | 458 |
| | (458 | ) | | (100 | )% |
Anti-dumping duty penalties | | 8,000 |
| | — |
| | 8,000 |
| | N/M |
|
Operating income | | 44,476 |
|
| 15,470 |
| | 29,006 |
| | 187 | % |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 58,784 |
| | $ | 22,807 |
| | $ | 35,977 |
| | 158 | % |
Net sales increased compared with 2017 primarily due to higher activity levels in North America’s unconventional onshore oil and gas well completions sector, increased customer demand for DynaEnergetics' advanced perforating systems and higher average selling prices.
Gross profit percentage increased compared with 2017 due to higher average selling prices and the favorable impact of higher volume on fixed overhead expenses.
General and administrative expenses increased compared with 2017 primarily due to expenses associated with the successful defense of patent lawsuits, increased salaries and wages due to headcount additions, merit-based pay increases and higher variable incentive compensation expense.
Selling and distribution expenses increased compared with 2017 primarily due to headcount additions, merit-based pay increases and higher variable distribution expenses, sales commissions and incentive compensation expense.
Amortization of purchased intangibles decreased compared with 2017 primarily due to fully amortizing certain trademarks as of December 31, 2017.
Restructuring expense in 2017 related to the closure of DynaEnergetics operations in Kazakhstan.
Anti-dumping duty penalties represent an accrual for a mitigated amount of penalties on AD/CVD that was formally asserted by U.S. Customs Headquarters.
Operating income increased compared with 2017 due to higher unit volume and higher average selling prices, partially offset by accrued penalties on AD/CVD as well as increased general and administrative expenses and selling and distribution expenses.
Adjusted EBITDA increased compared with 2017 primarily due to the factors discussed above. See "Overview" above for the explanation of the use of Adjusted EBITDA. The following is a reconciliation of the most directly comparable GAAP measure to Adjusted EBITDA.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 |
Operating income | | $ | 44,476 |
| | $ | 15,470 |
|
Adjustments: | | | | |
Restructuring expenses | | — |
| | 458 |
|
Anti-dumping duty penalties | | 8,000 |
| | — |
|
Depreciation | | 3,767 |
| | 3,205 |
|
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 2,541 |
| | 3,674 |
|
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 58,784 |
|
| $ | 22,807 |
|
Year ended December 31, 2017 compared to Year Ended December 31, 2016
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2017 | | 2016 | | $ change | | % change |
Net sales | | $ | 121,253 |
| | $ | 67,290 |
| | $ | 53,963 |
| | 80 | % |
Gross profit | | 44,029 |
| | 19,811 |
| | 24,218 |
| | 122 | % |
Gross profit percentage | | 36.3 | % | | 29.4 | % | | | | |
COSTS AND EXPENSES: | | | | | | | | |
General and administrative expenses | | 13,373 |
| | 9,964 |
| | 3,409 |
| | 34 | % |
Selling and distribution expenses | | 11,054 |
| | 10,467 |
| | 587 |
| | 6 | % |
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 3,674 |
| | 3,633 |
| | 41 |
| | 1 | % |
Restructuring expenses | | 458 |
| | 1,128 |
| | (670 | ) | | (59 | )% |
Operating income (loss) | | 15,470 |
|
| (5,381 | ) | | 20,851 |
| | 387 | % |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 22,807 |
| | $ | 2,515 |
| | $ | 20,292 |
| | 807 | % |
Net sales increased compared with 2016 primarily due to a recovery in North America’s onshore unconventional drilling and completion market and increased market penetration of DynaEnergetics' initiating systems and DynaStage perforating system.
Gross profit percentage increased compared with 2016 primarily due to higher average selling prices, improved product mix and the favorable impact of higher volume on fixed overhead expenses.
General and administrative expenses increased compared with 2016 primarily due to higher outside legal expenses related to patent infringement defense costs and higher salaries and wages from headcount additions and variable incentive compensation expense.
Selling and distribution expenses increased compared with 2016 primarily due to higher salaries and wages and higher outside service costs, partially offset by lower bad debt expense.
Restructuring expense in 2017 related to the closure of operations in Kazakhstan. Restructuring activity in 2016 related to severance for headcount reductions in Troisdorf, Germany and Austin, Texas and the accelerated vesting of stock awards in connection with the elimination of certain positions.
Operating income was $15,470 in 2017 compared to an operating loss of $5,381 in 2016 due to higher unit volume, favorable product mix and higher average selling prices, partially offset by increased general and administrative expenses.
Adjusted EBITDA increased compared with 2016 due to the factors discussed above. See "Overview" above for the explanation of the use of Adjusted EBITDA. The following is a reconciliation of the most directly comparable GAAP measure to Adjusted EBITDA.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2017 | | 2016 |
Operating income (loss) | | $ | 15,470 |
| | $ | (5,381 | ) |
Adjustments: | | | | |
Restructuring expenses | | 458 |
| | 1,128 |
|
Depreciation | | 3,205 |
| | 3,135 |
|
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 3,674 |
| | 3,633 |
|
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 22,807 |
|
| $ | 2,515 |
|
NobelClad
Year ended December 31, 2018 compared to Year Ended December 31, 2017
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 | | $ change | | % change |
Net sales | | $ | 88,981 |
| | $ | 71,550 |
| | $ | 17,431 |
| | 24 | % |
Gross profit | | 20,414 |
| | 15,644 |
| | 4,770 |
| | 30 | % |
Gross profit percentage | | 22.9 | % | | 21.9 | % | | | | |
COSTS AND EXPENSES: | | | | | | | | |
General and administrative expenses | | 4,522 |
| | 4,031 |
| | 491 |
| | 12 | % |
Selling and distribution expenses | | 7,876 |
| | 7,178 |
| | 698 |
| | 10 | % |
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 403 |
| | 386 |
| | 17 |
| | 4 | % |
Restructuring expenses | | 1,114 |
| | 3,825 |
| | (2,711 | ) | | -71 | % |
Goodwill impairment charge | | — |
| | 17,584 |
| | (17,584 | ) | | -100 | % |
Operating income (loss) | | 6,499 |
|
| (17,360 | ) | | 23,859 |
| | 137 | % |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 10,825 |
| | $ | 7,736 |
| | $ | 3,089 |
| | 40 | % |
Net sales increased compared with 2017 principally due to shipping three large capital equipment projects in 2018 coupled with higher volume in core repair and maintenance projects.
Gross profit percentage increased compared with 2017 primarily due to favorable impact of higher sales on fixed manufacturing overhead as well as better margins on the mix of projects in the current year.
General and administrative expenses increased compared with 2017 primarily due to headcount additions, merit-based pay increases, higher variable incentive compensation expense, and increased outside services costs.
Selling and distribution expenses increased compared with 2017 primarily due to headcount additions, increased sales commissions and higher outside service costs.
Restructuring expense related to the closure of manufacturing operations in France. Costs in 2018 primarily related to equipment moving expenses, legal fees and severance costs, while expenses in 2017 primarily related to severance costs and asset impairments.
Goodwill impairment charge in 2017 related to fully impairing NobelClad's goodwill balance.
Operating income in 2018 compared with operating loss in 2017 was primarily due to the non-recurring goodwill impairment charge in 2017 combined with increased sales volumes in 2018 partially offset by higher selling, general and administrative expenses.
Adjusted EBITDA increased due to the factors discussed above. See "Overview" above for the explanation of the use of Adjusted EBITDA. The following is a reconciliation of the most directly comparable GAAP measure to Adjusted EBITDA.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 |
Operating income (loss) | | $ | 6,499 |
| | $ | (17,360 | ) |
Adjustments: | | | | |
Restructuring expenses | | 1,114 |
| | 3,825 |
|
Goodwill impairment charge | | — |
| | 17,584 |
|
Depreciation | | 2,809 |
| | 3,301 |
|
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 403 |
| | 386 |
|
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 10,825 |
|
| $ | 7,736 |
|
Year ended December 31, 2017 compared to Year Ended December 31, 2016
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2017 | | 2016 | | $ change | | % change |
Net sales | | $ | 71,550 |
| | $ | 91,285 |
| | $ | (19,735 | ) | | -22 | % |
Gross profit | | 15,644 |
| | 19,103 |
| | (3,459 | ) | | -18 | % |
Gross profit percentage | | 21.9 | % | | 20.9 | % | | | | |
COSTS AND EXPENSES: | | | | | | | | |
General and administrative expenses | | 4,031 |
| | 4,024 |
| | 7 |
| | — | % |
Selling and distribution expenses | | 7,178 |
| | 5,823 |
| | 1,355 |
| | 23 | % |
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 386 |
| | 378 |
| | 8 |
| | 2 | % |
Restructuring expenses | | 3,825 |
| | — |
| | 3,825 |
| | 100 | % |
Goodwill impairment charge | | 17,584 |
| | — |
| | 17,584 |
| | 100 | % |
Operating income (loss) | | (17,360 | ) |
| 8,878 |
| | (26,238 | ) | | -296 | % |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 7,736 |
| | $ | 12,877 |
| | $ | (5,141 | ) | | -40 | % |
Net sales decreased compared with 2016 due to a decline in core repair and maintenance orders from the downstream energy industry and absence of large-project bookings in 2017. Additionally, during the second quarter of 2016, NobelClad shipped a large project related to specialized explosion clad plates used in the fabrication of equipment for a semiconductor material production facility in East Asia.
Gross profit percentage increased compared with 2016 primarily due to better margins on the mix of projects in the current year.
Selling and distribution expenses increased compared with 2016 primarily from higher salaries and benefits due to increased investment in business growth resources and higher outside services expenses.
Restructuring expenses in 2017 related to the announced closure of NobelClad's manufacturing facility in France.
Goodwill impairment charge in 2017 related to fully impairing NobelClad's goodwill balance.
Operating loss was primarily due to the goodwill impairment charge and the restructuring expenses combined with lower project volume and higher selling and distribution expenses.
Adjusted EBITDA declined due to the factors discussed above. See "Overview" above for the explanation of the use of Adjusted EBITDA. The following is a reconciliation of the most directly comparable GAAP measure to Adjusted EBITDA.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2017 | | 2016 |
Operating income (loss) | | $ | (17,360 | ) | | $ | 8,878 |
|
Adjustments: | | | | |
Restructuring expenses | | 3,825 |
| | — |
|
Goodwill impairment charge | | 17,584 |
| | — |
|
Depreciation | | 3,301 |
| | 3,621 |
|
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | | 386 |
| | 378 |
|
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 7,736 |
|
| $ | 12,877 |
|
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We have historically financed our operations from a combination of internally generated cash flow, revolving credit borrowings, and various long-term debt arrangements. We believe that cash flow from operations and funds available under our current credit facilities and any future replacement thereof will be sufficient to fund the working capital, debt service, dividends and other capital requirements of our current business operations for the foreseeable future. Nevertheless, our ability to generate sufficient cash flows from operations will depend upon our success in executing our strategies. If we are unable to (i) realize sales from our backlog; (ii) secure new customer orders; (iii) continue selling products at attractive margins; and (iv) continue to implement cost-effective internal processes, our ability to meet cash requirements through operating activities could be impacted. Furthermore, any restriction on the availability of borrowings under our credit facilities could negatively affect our ability to meet future cash requirements. In March 2017, we filed a shelf registration statement on Form S-3 with the Securities and Exchange Commission, which has been declared effective, and on which we registered for sale up to $150 million of certain of our securities from time to time and on terms that we may determine in the future. Our ability to access this capital may be limited by market conditions at the time of any future potential offering. There can be no assurance that any such capital will be available on acceptable terms or at all.
We declared and paid quarterly dividends aggregating $0.08 per share in 2018 and $0.08 per share in 2017. We may pay quarterly dividends subject to capital availability and periodic determinations that cash dividends are in the best interests of our stockholders. Future dividends may be affected by, among other items, our views on potential future capital requirements, future business prospects, debt covenant compliance considerations, changes in income tax laws, and any other factors that our Board of Directors deems relevant. Any determination to pay cash dividends will be at the discretion of the Board of Directors.
Debt facilities
On March 8, 2018, we entered into a five-year $75,000 syndicated credit agreement (“credit facility”) which replaced in its entirety our prior syndicated credit facility entered into on February 23, 2015. The new credit facility allows for revolving loans of up to $50,000 with a $20,000 US dollar equivalent sublimit for alternative currency loans. In addition, the new agreement provides for a $25,000 Capital Expenditure Facility (“Capex Facility") which has been used to assist in financing our DynaEnergetics manufacturing expansion project in Blum, Texas. The Capex Facility allowed for advances to fund capital expenditures of the Blum expansion project during year one of the credit facility. At the end of year one, the Capex Facility will convert to a term loan which will be amortizable at 12.5% of principal per year with a balloon payment for the outstanding balance upon the credit facility maturity date in year five. The credit facility has a $100,000 accordion feature to increase the commitments under the revolving loan class and/or by adding a term loan subject to approval by applicable lenders. We entered into the credit facility with a syndicate of three banks, with KeyBank, N.A. acting as administrative agent. The syndicated credit facility is secured by the assets of DMC including accounts receivable, inventory, and fixed assets, as well as guarantees and share pledges by DMC and its subsidiaries.
Borrowings under the $50,000 revolving loan limit can be in the form of one, two, three, or six month London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) loans. Additionally, US dollar borrowings on the revolving loan can be in the form of Base Rate loans (Base Rate borrowings are based on the greater of the administrative agent’s Prime rate, an adjusted Federal Funds rate or an adjusted LIBOR rate). LIBOR loans bear interest at the applicable LIBOR rate plus an applicable margin (varying from 1.50% to 3.00%). Base Rate loans bear interest at the defined Base rate plus an applicable margin (varying from 0.50% to 2.00%).
Borrowings under a $20,000 alternate currency sublimit can be in euros, Canadian dollars, pounds sterling, or in any other currency acceptable to the administrative agent. Alternative currency borrowings denominated in euros, pounds sterling, and any other currency that is dealt with on the London Interbank Deposit Market shall be comprised of LIBOR loans and bear interest at the LIBOR rate plus an applicable margin (varying from 1.50% to 3.00%).
As of December 31, 2018, U.S. dollar revolving loans of $17,128 and borrowings of $25,000 on the Capital Expenditure facility were outstanding under our credit facility and our available borrowing capacity was $32,872.
The credit facility includes various covenants and restrictions, certain of which relate to the payment of dividends or other distributions to stockholders; redemption of capital stock; incurrence of additional indebtedness; mortgaging, pledging or disposition of major assets; and maintenance of specified ratios.
The leverage ratio is defined in the credit facility as the ratio of Consolidated Funded Indebtedness (as defined in the agreement) on the last day of any trailing four quarter period to the Consolidated Pro Forma EBITDA for such period. The maximum leverage ratio permitted by our credit facility is 3.0 to 1.0. The actual leverage ratio as of December 31, 2018, calculated in accordance with the 2015 syndicated credit facility, as amended, was 0.7 to 1.0.
The debt service coverage ratio, as defined in the credit facility, means, for any period, the ratio of Consolidated Pro Forma EBITDA less the sum of cash dividends, cash income taxes and Consolidated Unfunded Capital Expenditures (as defined in the agreement) to Debt Service Charges (as defined in the agreement). Under our credit facility, the minimum debt service coverage ratio permitted is 1.35 to 1.0. The actual debt service coverage ratio for the trailing twelve months ended December 31, 2018, was 27.8 to 1.0.
As of December 31, 2018, we were in compliance with all financial covenants and other provisions of our credit facilities.
We also maintain a line of credit with a German bank for certain European operations. This line of credit provides a borrowing capacity of €4,000.
Other contractual obligations and commitments
The table below presents principal cash flows by expected maturity dates for our debt obligations and other contractual obligations and commitments as of December 31, 2018:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Payment Due by Period |
| | As of December 31, 2018 |
| | Less than | | | | | | More than | | |
Other Contractual Obligations | | 1 Year | | 1-3 Years | | 3-5 Years | | 5 Years | | Total |
Credit facility (1) | | $ | 3,125 |
| | $ | 9,375 |
| | $ | 29,628 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 42,128 |
|
Operating lease obligations (2) | | 2,234 |
| | 2,693 |
| | 899 |
| | 210 |
| | 6,036 |
|
License agreement obligations (3) | | 300 |
| | 600 |
| | 600 |
| | 1,275 |
| | 2,775 |
|
Purchase obligations (4) | | 42,688 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 42,688 |
|
Accrued anti-dumping penalties (5) | | 8,000 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | $ | — |
| | 8,000 |
|
Total | | $ | 56,347 |
| | $ | 12,668 |
| | $ | 31,127 |
| | $ | 1,485 |
| | $ | 101,627 |
|
(1) Represents outstanding borrowings under our credit facility. For more information about our debt obligations, see Note 3 "Debt" to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
(2) The operating lease obligations presented reflect future minimum lease payments due under non-cancelable portions of our leases as of December 31, 2018. Our operating lease obligations are described in Note 8 "Commitments and Contingencies" of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
(3) The license agreement obligations presented reflect future minimum payments due under non-cancelable portions of our agreements as of December 31, 2018. Our license agreement obligations are described in Note 8 "Commitments and Contingencies" of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
(4) Amounts represent commitments to purchase goods or services to be utilized in the normal course of business. These amounts are not reflected in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets.
(5) On December 7, 2018, we submitted a supplemental petition requesting a waiver of the penalty under the Small Business Regulatory Enforcement Act in lieu of tendering the penalty amount. We expect to receive a response to this waiver request by the end of the first quarter of 2019. The anti-dumping duties and penalties are described in Note 8 "Commitments and Contingencies" of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Cash flows from operating activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was $27,638 in 2018 compared with $6,747 for 2017. The change primarily was due to net income in 2018 compared to a net loss in 2017 partially offset by increased net working capital from higher sales during 2018.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $6,747 in 2017 compared to $18,198 in 2016. The decline primarily was due to increased net working capital requirements from higher sales and tendering $3,049 in AD/CVD amounts to U.S. Customs in March 2017.
Cash flows used in investing activities
Net cash flows used in investing activities in 2018 totaled $45,095 and primarily consisted of acquisition of property, plant and equipment of $41,041 for DynaEnergetics and $2,281 for NobelClad. The increase in capital expenditures in 2018 versus 2017 principally related to the expansion of DynaEnergetics’ manufacturing, administrative and sales office in Blum, Texas.
Net cash flows used in investing activities in 2017 totaled $6,184 and primarily consisted of acquisition of property, plant and equipment of $4,025 for DynaEnergetics and $1,584 for NobelClad.
Net cash flows used in investing activities in 2016 totaled $5,702 and consisted of acquisition of property, plant and equipment of $4,448 for DynaEnergetics and $1,217 for NobelClad.
Cash flows from financing activities
Net cash flows provided by financing activities for 2018 totaled $21,858, which included borrowings on the Capex Facility of $25,000 offset by net repayment of revolving loans of $1,628 and payment of quarterly dividends of $1,189.
Net cash flows provided by financing activities for 2017 totaled $647, which included net borrowings on revolving loans of $2,000 partially offset by payment of quarterly dividends of $1,174.
Net cash flows used in financing activities for 2016 totaled $12,107, which included net repayments on revolving loans of $11,250 and payment of quarterly dividends of $1,150.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our historical Consolidated Financial Statements and notes to our historical Consolidated Financial Statements contain information that is pertinent to our management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations. Preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires that our management make estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. However, the accounting principles used by us generally do not change our reported cash flows or liquidity. Existing rules must be interpreted and judgments made on how the specifics of a given rule apply to us.
In management’s opinion, the more significant reporting areas impacted by management’s judgments and estimates are revenue recognition, asset impairments, goodwill and other intangible assets, and income taxes. Management’s judgments and estimates in these areas are based on information available from both internal and external sources, and actual results could differ from the estimates as additional information becomes known. We believe the following to be our most critical accounting policies.
Revenue Recognition
On January 1, 2018, the Company adopted a new accounting standard, as amended, regarding revenue from contracts with customers using the modified retrospective approach, which was applied to all contracts with customers. Under the new
standard, an entity is required to recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods.
There was no cumulative financial statement effect of initially applying the new revenue standard because an analysis of our contracts supported the recognition of revenue consistent with our historical approach. In accordance with the modified retrospective approach, the comparative information has not been restated and continues to be reported under the accounting standards in effect for those periods. The Company does not expect the adoption of the new revenue standard to have a material impact on the Company’s revenues or net income on an ongoing basis.
The Company’s revenues are primarily derived from consideration paid by customers for tangible goods. The Company analyzes its different goods by segment to determine the appropriate basis for revenue recognition, as described below. Revenue is not generated from sources other than contracts with customers and revenue is recognized net of any taxes collected from customers, which are subsequently remitted to governmental authorities. There are no material upfront costs for operations that are incurred from contracts with customers. On occasion, NobelClad and DynaEnergetics may require customers to make advance payments prior to the shipment of goods. We record such payments as contract liabilities in our Consolidated Balance Sheet.
Our rights to payments for goods transferred to customers are conditional only on the passage of time and not on any other criteria. Payment terms and conditions vary by contract, although terms generally include a requirement of payment within 30 to 60 days. In instances when we require customers to make advance payments prior to the shipment of their orders, we record a contract liability. We have determined that our contract liabilities do not include a significant financing component given the short duration between order initiation and order fulfillment within each of our segments.
NobelClad
Customers agree to terms and conditions at the time of initiating an order. The significant majority of transactions contain a single performance obligation - the delivery of a clad metal product. In instances where multiple products are included within an order, each product represents a separate performance obligation given that: (1) the customer can benefit from each product on a standalone basis and (2) each product is distinct within the context of the contract.
The transaction price is readily determinable and fixed at the time the transaction is entered into with the customer. NobelClad is entitled to each product’s transaction price upon the customer obtaining control of the item. Such control occurs as of a point in time, which is generally based upon relevant International Commercial Terms (“Incoterms”) as it relates to product ownership and legal title being transferred. Upon fulfillment of applicable Incoterms, NobelClad has performed its contractual requirements such that it has a present right to payment, and the customer from that point forward bears all risks and rewards of ownership. In addition, at this date, the customer has the ability to direct the use of, or restrict access to, the asset. No payment discounts, rebates, refunds, or any other forms of variable consideration are included within its contracts. NobelClad also does not provide service-type warranties either via written agreement or customary business practice, nor does it allow customer returns.
For contracts that contain only one performance obligation, the total transaction price is allocated to the sole performance obligation. For less frequent contracts which contain multiple distinct performance obligations, judgment is required to determine the standalone selling price (“SSP”) for each performance obligation. NobelClad uses the expected cost plus margin approach in order to estimate SSP, whereby an entity forecasts its expected costs of satisfying a performance obligation and then adds an appropriate margin for that good. The required judgment described herein largely is mitigated given the short duration between order initiation and complete order fulfillment.
DynaEnergetics
Customers agree to terms and conditions at the time of initiating an order. Transactions contain standard products, which may include perforating system components, such as detonating cord, or systems and associated hardware, including factory-assembled DynaStage® perforating systems and DynaSelect® detonators. In instances where multiple products are included within an order, each product represents a separate performance obligation given that: (1) the customer can benefit from each product on a standalone basis and (2) each product is distinct within the context of the contract.
The transaction price is readily determinable and fixed at the time the transaction is entered into with the customer. DynaEnergetics is entitled to each product’s transaction price upon the customer obtaining control of the item. Such control occurs as of a point in time, which is generally based upon relevant Incoterms as it relates to product ownership and legal title being transferred. Upon fulfillment of applicable Incoterms, DynaEnergetics has performed its contractual requirements such
that it has a present right to payment, and the customer from that point forward bears all risks and rewards of ownership. In addition, at this date, the customer has the ability to direct the use of, or restrict access to, the asset. No payment discounts, rebates, refunds, or any other forms of variable consideration are included within contracts. DynaEnergetics also does not provide service-type warranties either via written agreement or customary business practice, nor does it allow customer returns without its prior approval.
For orders that contain only one performance obligation, the total transaction price is allocated to the sole performance obligation. For orders that contain multiple products being purchased by the customer, judgment is required to determine SSP for each distinct performance obligation. However, such judgment largely is mitigated given that products purchased are generally shipped at the same time. In instances where products purchased are not shipped at the same time, DynaEnergetics uses the contractually stated price to determine SSP as this price approximates the price of each good as sold separately.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower-of-cost (first-in, first-out) or net realizable value. Significant cost elements included in inventory are material, labor, freight, subcontract costs, and manufacturing overhead. As necessary, we adjust inventory to its net realizable value by recording provisions for excess, slow moving and obsolete inventory. To determine provision amounts, we regularly review inventory quantities on hand and values, and compare them to estimates of future product demand, market conditions, production requirements and technological developments.
Asset impairments
Finite-lived assets are tested for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying value may not be recoverable. We compare the expected undiscounted future operating cash flows associated with these finite-lived assets to their respective carrying values to determine if they are fully recoverable when indicators of impairment are present. If the expected future operating cash flows of an asset are not sufficient to recover the carrying value, we estimate the fair value of the asset. Impairment is recognized when the carrying amount of the asset is not recoverable and when carrying value exceeds fair value. Long-lived assets to be disposed of, if any, are reported at the lower of carrying amount or fair value less cost to sell.
In association with the 2017 goodwill impairments, we tested finite-lived assets for impairment, and found that the carrying amounts of assets at the lowest level of identifiable cash flows, in this case our reporting units, are fully recoverable. There were no indicators of impairment for finite-lived assets for 2016 or 2018.
Business Combinations
We account for our business acquisitions using the purchase method of accounting. We allocate the total cost of the acquisition to the underlying net assets based on their respective estimated fair values. As part of this allocation process, we identify and attribute values and estimated lives to the intangible assets acquired. These determinations involve significant estimates and assumptions regarding multiple, highly subjective variables, including those with respect to future cash flows, discount rates, asset lives, and the use of different valuation models, and therefore require considerable judgment. Our estimates and assumptions are based, in part, on the availability of listed market prices or other transparent market data. These determinations affect the amount of amortization expense recognized in future periods. We base our fair value estimates on assumptions we believe to be reasonable but are inherently uncertain.
Goodwill
During 2017, we determined that the estimated fair value of the NobelClad reporting unit was less than its carrying value primarily due to the factors described above and their related impact on expected future cash flows. During the third quarter of 2017, we adopted FASB accounting standards update ("ASU") 2017-04, which amends and simplifies how an entity measures a goodwill impairment loss by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test. As the carrying value of the NobelClad reporting unit exceeded the fair value by more than the book value of goodwill, we recorded an impairment charge of $17,584 to fully impair all goodwill related to this reporting unit as of September 30, 2017.
Income taxes
We recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future income tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities. Any effects of changes in income tax rates or tax laws are included in the provision for income taxes in the period of enactment. The deferred income tax impact of tax
credits are recognized as an immediate adjustment to income tax expense. We recognize deferred tax assets for the expected future effects of all deductible temporary differences to the extent we believe these assets will more likely than not be realized. We record a valuation allowance when, based on current circumstances, it is more likely than not that all or a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. In making such determination, we consider all available positive and negative evidence, including future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies, recent financial operations and their associated valuation allowances, if any.
We recognize the tax benefits from uncertain tax positions only when it is more likely than not, based on the technical merits of the position, the tax position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of any related appeals or litigation. The tax benefits recognized in the Consolidated Financial Statements from such a position are measured as the largest benefit that is more likely than not to be realized upon ultimate resolution. We recognize interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions in operating expense.
Leases
In February 2016, the FASB issued a new accounting pronouncement that requires lessees to record assets and liabilities on the balance sheet for lease-related rights and obligations and disclose key information about certain leasing arrangements. This new standard establishes a right-of-use (“ROU”) model that requires a lessee to recognize a ROU asset and lease liability on the balance sheet for all leases with a term longer than 12 months.
Leases will be classified as financing or operating, with classification affecting the pattern of expense recognition in the Statement of Operations. The Company will adopt the new standard, including the related amendments, effective January 1,
2019 using the modified retrospective approach, applying the provisions of the new standard on its effective date.
Management has substantially completed its analysis and determined that the significant majority of its leasing arrangements will be classified as operating. Additionally, management has implemented new systems to facilitate the requirements of the new standard and estimates the ROU asset to be less than 5% of total assets on January 1, 2019.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
At December 31, 2018, we had no off-balance sheet arrangements, as defined by SEC rules, that have or are reasonably likely to have a material current or future effect on our financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital resources.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Please refer to Note 2 "Significant Accounting Policies" to our Consolidated Financial Statements in this annual report for a discussion of recent accounting pronouncements and their anticipated effect on our business.
ITEM 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Foreign Currency Risk
Our Consolidated Financial Statements are expressed in U.S. dollars, but a portion of our business is conducted in currencies other than U.S. dollars. Changes in the exchange rates for such currencies into U.S. dollars can affect our revenues, earnings, and the carrying value of our assets and liabilities in our Consolidated Balance Sheets, either positively or negatively. Sales made in currencies other than U.S. dollars accounted for 21%, 28%, and 23% of total sales for the years ended 2018, 2017, and 2016, respectively. As a result of foreign currency risk, we may experience economic loss and a negative impact on earnings and equity with respect to our holdings solely as a result of foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations. Our primary exposure to foreign currency risk is the Euro due to the percentage of our U.S. dollar revenue that is derived from countries where the Euro is the functional currency and the Russian Ruble due to DynaEnergetics' manufacturing and sales operations in Tyumen, Siberia.
We use foreign currency forward contracts to offset foreign exchange rate fluctuation on foreign currency denominated asset and liability positions. Foreign currency forward contracts are sensitive to changes in foreign currency exchange rates. Consistent with the use of these contracts to neutralize the effect of exchange rate fluctuations, such unrealized losses or gains would be offset by corresponding gains or losses, respectively, in the remeasurement of the asset and liability positions being hedged. As such, these forward currency contracts and the offsetting underlying asset and liability positions do not create material market risk. The notional amount of the foreign exchange contracts at December 31, 2018 and 2017 was $7,008 and $20,291, respectively.
Interest Rate Risk
The company's interest expense, in part, is sensitive to the general level of interest rates in North America and Europe. At December 31, 2018, all of the company's debt was subject to variable interest rates. A one percentage point change in average interest rates would cause interest expense, net in 2018 to increase by $351. This was determined by considering the impact of a hypothetical interest rate on the company's average outstanding variable debt. This analysis does not consider the effect of the level of overall economic activity that could exist. In the event of a change in the level of economic activity, which may adversely impact interest rates, the company could likely take actions to further mitigate any potential negative exposure to the change. However, due to the uncertainty of the specific actions that might be taken and their possible effects, the sensitivity analysis assumes no changes in the company's financial structure.
ITEM 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
DMC GLOBAL INC.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
As of December 31, 2018 and 2017 and for Each of the Three Years Ended
December 31, 2018, 2017 and 2016
|
| |
| Page |
| |
Financial Statements: | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
The consolidated financial statement schedules required by Regulation S-X are filed under Item 15 “Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules”.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of DMC Global Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of DMC Global Inc. (the Company) as of December 31, 2018 and 2017, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), stockholders' equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2018, and the related notes and financial statement schedules listed in the Index at Item 15(a) (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2018 and 2017, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2018, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2018, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated February 21, 2019 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
|
| |
| /s/ Ernst & Young LLP |
| |
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2002. | |
| |
Denver, Colorado |
February 21, 2019 |
DMC GLOBAL INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(Amounts in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data)
|
| | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2018 | | 2017 |
ASSETS | |
| | |
|
Current assets: | |
| | |
|
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 13,375 |
| | $ | 8,983 |
|
Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $513 and $1,088, respectively | 59,709 |
| | 49,468 |
|
Inventories | 51,074 |
| | 35,742 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other | 8,058 |
| | 5,763 |
|
Total current assets | 132,216 |
| | 99,956 |
|
Property, plant and equipment | 160,725 |
| | 121,339 |
|
Less - accumulated depreciation | (65,585 | ) | | (61,467 | ) |
Property, plant and equipment, net | 95,140 |
| | 59,872 |
|
Purchased intangible assets, net | 8,589 |
| | 12,861 |
|
Deferred tax assets | 4,001 |
| | 98 |
|
Other assets | 472 |
| | 296 |
|
Total assets | $ | 240,418 |
| | $ | 173,083 |
|
| | | |
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | |
Accounts payable | $ | 24,243 |
| | $ | 19,826 |
|
Accrued expenses | 8,967 |
| | 6,884 |
|
Accrued anti-dumping duties and penalties | 8,000 |
| | 3,609 |
|
Dividend payable | 295 |
| | 295 |
|
Accrued income taxes | 9,545 |
| | 2,939 |
|
Accrued employee compensation and benefits | 9,250 |
| | 6,186 |
|
Contract liabilities | 1,140 |
| | 5,888 |
|
Current portion of long-term debt | 3,125 |
| | — |
|
Total current liabilities | 64,565 |
| | 45,627 |
|
Long-term debt | 38,230 |
| | 17,984 |
|
Deferred tax liabilities | 379 |
| | 573 |
|
Other long-term liabilities | 2,958 |
| | 3,119 |
|
Total liabilities | 106,132 |
| | 67,303 |
|
Commitments and Contingencies (Note 8) |
|
| |
|
|
Stockholders' Equity: | | | |
Preferred stock, $0.05 par value; 4,000,000 shares authorized; no issued and outstanding shares | — |
| | — |
|
Common stock, $0.05 par value; 25,000,000 shares authorized; 14,905,776 and 14,782,018 shares outstanding, respectively | 749 |
| | 741 |
|
Additional paid-in capital | 80,077 |
| | 76,146 |
|
Retained earnings | 89,291 |
| | 60,074 |
|
Other cumulative comprehensive loss | (35,014 | ) | | (30,819 | ) |
Treasury stock, at cost; 82,186 and 39,783 shares, respectively | (817 | ) | | (362 | ) |
Total stockholders' equity | 134,286 |
| | 105,780 |
|
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | 240,418 |
| | 173,083 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
DMC GLOBAL INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(Amounts in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Net sales | $ | 326,429 |
| | $ | 192,803 |
| | $ | 158,575 |
|
Cost of products sold | 215,734 |
| | 133,412 |
| | 119,895 |
|
Gross profit | 110,695 |
| | 59,391 |
| | 38,680 |
|
Costs and expenses: | |
| | |
| | |
General and administrative expenses | 38,452 |
| | 27,135 |
| | 22,115 |
|
Selling and distribution expenses | 22,761 |
| | 18,589 |
| | 16,626 |
|
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | 2,944 |
| | 4,060 |
| | 4,011 |
|
Restructuring expenses | 1,114 |
| | 4,283 |
| | 1,202 |
|
Anti-dumping duty penalties | 8,000 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Goodwill impairment charge | — |
| | 17,584 |
| | — |
|
Total costs and expenses | 73,271 |
| | 71,651 |
| | 43,954 |
|
Operating income (loss) | 37,424 |
| | (12,260 | ) | | (5,274 | ) |
Other income (expense): | |
| | |
| | |
Other income (expense), net | (1,202 | ) | | (1,376 | ) | | 633 |
|
Interest expense, net | (1,615 | ) | | (1,648 | ) | | (1,067 | ) |
Income (loss) before income taxes | 34,607 |
| | (15,284 | ) | | (5,708 | ) |
Income tax provision | 4,134 |
| | 3,569 |
| | 797 |
|
Net income (loss) | 30,473 |
| | (18,853 | ) | | (6,505 | ) |
| | | | | |
Net income (loss) per share: | |
| | |
| | |
Basic | $ | 2.05 |
| | $ | (1.31 | ) | | $ | (0.46 | ) |
Diluted | $ | 2.04 |
| | $ | (1.31 | ) | | $ | (0.46 | ) |
Weighted-average shares outstanding: | |
| | |
| | |
Basic | 14,529,745 |
| | 14,346,851 |
| | 14,126,108 |
|
Diluted | 14,620,635 |
| | 14,346,851 |
| | 14,126,108 |
|
| | | | | |
Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.08 |
| | $ | 0.08 |
| | $ | 0.08 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
DMC GLOBAL INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
(Amounts in Thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Net income (loss) | $ | 30,473 |
| | $ | (18,853 | ) | | $ | (6,505 | ) |
| | | | | |
Change in cumulative foreign currency translation adjustment | (4,195 | ) | | 10,695 |
| | (1,049 | ) |
| | | | | |
Total comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 26,278 |
| | $ | (8,158 | ) | | $ | (7,554 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
DMC GLOBAL INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(Amounts in Thousands, Except Share Data)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Other | | | | | | |
| | | | | Additional | | | | Cumulative | | | | | | |
| Common Stock | | Paid-In | | Retained | | Comprehensive | | Treasury Stock | | |
| Shares | | Amount | | Capital | | Earnings | | Loss | | Shares | | Amount | | Total |
Balances, December 31, 2015 | 14,212,115 |
| | $ | 711 |
| | $ | 70,408 |
| | $ | 87,767 |
| | $ | (40,465 | ) | | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 118,421 |
|
Net loss | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (6,505 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (6,505 | ) |
Change in cumulative foreign currency translation adjustment | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,049 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (1,049 | ) |
Shares issued in connection with stock compensation plans | 286,622 |
| | 14 |
| | 308 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 322 |
|
Stock-based compensation | — |
| | — |
| | 2,400 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 2,400 |
|
Dividends declared | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,155 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,155 | ) |
Treasury stock purchases | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,378 | ) | | (25 | ) | | (25 | ) |
Balances, December 31, 2016 | 14,498,737 |
| | $ | 725 |
| | $ | 73,116 |
| | $ | 80,107 |
| | $ | (41,514 | ) | | (2,378 | ) | | $ | (25 | ) | | $ | 112,409 |
|
Net loss | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (18,853 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (18,853 | ) |
Change in cumulative foreign currency translation adjustment | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 10,695 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 10,695 |
|
Shares issued in connection with stock compensation plans | 323,064 |
| | 16 |
| | 280 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 296 |
|
Stock-based compensation | — |
| | — |
| | 2,750 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 2,750 |
|
Dividends declared | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,180 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,180 | ) |
Treasury stock purchases | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (37,405 | ) | | (337 | ) | | (337 | ) |
Balances, December 31, 2017 | 14,821,801 |
| | $ | 741 |
| | $ | 76,146 |
| | $ | 60,074 |
| | $ | (30,819 | ) | | (39,783 | ) | | $ | (362 | ) | | $ | 105,780 |
|
Net income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 30,473 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 30,473 |
|
Change in cumulative foreign currency translation adjustment | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (4,195 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (4,195 | ) |
Shares issued in connection with stock compensation plans | 166,161 |
| | 8 |
| | 434 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 442 |
|
Adjustment for cumulative effect from change in accounting principle (ASU 2016-16) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (65 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (65 | ) |
Stock-based compensation | — |
| | — |
| | 3,497 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3,497 |
|
Dividends declared | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,191 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,191 | ) |
Treasury stock purchases | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (42,403 | ) | | (455 | ) | | (455 | ) |
Balances, December 31, 2018 | 14,987,962 |
| | $ | 749 |
| | $ | 80,077 |
| | $ | 89,291 |
| | $ | (35,014 | ) | | (82,186 | ) | | $ | (817 | ) | | $ | 134,286 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
DMC GLOBAL INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Amounts in Thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Cash flows from operating activities: | |
| | |
| | |
Net income (loss) | $ | 30,473 |
| | $ | (18,853 | ) | | $ | (6,505 | ) |
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: | |
| | |
| |
|
|
Depreciation (including capital lease amortization) | 6,576 |
| | 6,506 |
| | 6,756 |
|
Amortization of purchased intangible assets | 2,944 |
| | 4,060 |
| | 4,011 |
|
Amortization and write-off of deferred debt issuance costs | 314 |
| | 390 |
| | 156 |
|
Stock-based compensation | 3,580 |
| | 2,975 |
| | 2,326 |
|
Deferred income tax benefit | (3,653 | ) | | (556 | ) | | (284 | ) |
Loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment | 78 |
| | 125 |
| | 455 |
|
Restructuring and asset impairment expenses | 1,114 |
| | 4,283 |
| | 1,202 |
|
Goodwill impairment charge | — |
| | 17,584 |
| | — |
|
Transition tax liability | (679 | ) | | 946 |
| | — |
|
Change in: | |
| | |
| | |
Accounts receivable, net | (11,409 | ) | | (14,425 | ) | | 2,679 |
|
Inventory | (16,610 | ) | | (5,294 | ) | | 6,829 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other | 491 |
| | (440 | ) | | 1,002 |
|
Accounts payable | 2,197 |
| | 5,216 |
| | (1,338 | ) |
Customer advances | (4,721 | ) | | 3,207 |
| | 223 |
|
Accrued anti-dumping duties and penalties | 4,391 |
| | (2,941 | ) | | 176 |
|
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | 12,552 |
| | 3,964 |
| | 510 |
|
Net cash provided by operating activities | 27,638 |
| | 6,747 |
| | 18,198 |
|
Cash flows used in investing activities: | |
| | |
| | |
Acquisition of property, plant and equipment | (45,095 | ) | | (6,186 | ) | | (5,719 | ) |
Other investing activities | — |
| | 2 |
| | 17 |
|
Net cash used in investing activities | (45,095 | ) | | (6,184 | ) | | (5,702 | ) |
Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | |
Borrowings (payments) on revolving loans, net | (1,628 | ) | | 2,000 |
| | (11,250 | ) |
Borrowings on capital expenditure facility | 25,000 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Payment on capital lease obligations | — |
| | — |
| | (4 | ) |
Payment of dividends | (1,189 | ) | | (1,174 | ) | | (1,150 | ) |
Payment of deferred debt issuance costs | (314 | ) | | (138 | ) | | — |
|
Net proceeds from issuance of common stock to employees and directors | 442 |
| | 296 |
| | 322 |
|
Treasury stock purchases | (453 | ) | | (337 | ) | | (25 | ) |
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 21,858 |
| | 647 |
| | (12,107 | ) |
| | | | | |
Effects of exchange rates on cash | (9 | ) | | 1,354 |
| | (261 | ) |
| | | | | |
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | 4,392 |
| | 2,564 |
| | 128 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of the period | 8,983 |
| | 6,419 |
| | 6,291 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of the period | 13,375 |
| | 8,983 |
| | 6,419 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | | | | | |
Cash paid during the period for - | | | | | |
Interest | $ | 1,383 |
| | $ | 1,150 |
| | $ | 575 |
|
Income taxes, net | $ | 1,284 |
| | $ | 124 |
| | $ | 354 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
DMC GLOBAL INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2018
(Amounts in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data)
1. ORGANIZATION AND BUSINESS
DMC Global Inc. (“DMC”, "we", "us", "our", or the "Company") was incorporated in the state of Colorado in 1971 and reincorporated in the state of Delaware in 1997. DMC is headquartered in Boulder, Colorado and has manufacturing facilities in the United States, Germany, and Russia. Customers are located throughout the world. DMC currently operates two business segments: NobelClad and DynaEnergetics. NobelClad metallurgically joins or alters metals by using explosives. DynaEnergetics manufactures, markets, and sells downhole perforating equipment and explosives to the oilfield services sector.
Restructuring
Throughout 2016, 2017, and 2018 we restructured operations within NobelClad and DynaEnergetics and eliminated positions within our corporate office. See Note 9 "Restructuring" for additional disclosures regarding these restructuring charges.
2. SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of Consolidation
The Company's consolidated financial statements ("Consolidated Financial Statements") include the accounts of DMC and its controlled subsidiaries. Only subsidiaries in which controlling interests are maintained are consolidated. All significant intercompany accounts, profits, and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (U.S. GAAP) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
Foreign Operations and Foreign Exchange Rate Risk
The functional currency of our foreign operations is the applicable local currency for each affiliate company. Assets and liabilities of foreign subsidiaries for which the functional currency is the local currency are translated at exchange rates in effect at period-end, and the Statements of Operations are translated at the average exchange rates during the period. Exchange rate fluctuations on translating foreign currency financial statements into U.S. dollars are referred to as translation adjustments. Translation adjustments are recorded as a separate component of stockholders’ equity and are included in other cumulative comprehensive loss. Transactions denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are recorded based on exchange rates at the time such transactions arise. Subsequent changes in exchange rates result in transaction gains and losses, which are reflected in other income (expense) as unrealized, based on period-end exchange rates, or realized, upon settlement of the transaction. Cash flows from our operations in foreign countries are translated at actual exchange rates when known, or at the average rate for the period. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows will not agree to changes in the corresponding balances in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The effects of exchange rate changes on cash balances held in foreign currencies are reported as a separate line item below cash flows from financing activities.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of the Consolidated Financial Statements, we consider highly liquid investments purchased with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable
We review our accounts receivable balance routinely to identify any specific customers with collectability issues. In circumstances where we are aware of a specific customer’s inability to meets its financial obligation to us, we record a specific
allowance for doubtful accounts (with the offsetting expense charged to selling and distribution expenses in our Consolidated Statements of Operations) against the amounts due, reducing the net recognized receivable to the amount we estimate will be collected.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out) or net realizable value. Significant cost elements included in inventory are material, labor, freight, subcontract costs, and manufacturing overhead. As necessary, we adjust inventory to its net realizable value by recording provisions for excess, slow moving and obsolete inventory. We regularly review inventory quantities on hand and values, and compare them to estimates of future product demand, market conditions, production requirements and technological developments.
Inventories consisted of the following at December 31:
|
| | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 |
Raw materials | $ | 26,544 |
| | 16,255 |
|
Work-in-process | 7,157 |
| | 6,120 |
|
Finished goods | 16,904 |
| | 13,049 |
|
Supplies | 469 |
| | 318 |
|
| $ | 51,074 |
| | $ | 35,742 |
|
Shipping and handling costs incurred by us upon shipment to customers are included in cost of products sold in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are recorded at cost, except for assets acquired in acquisitions which are recorded at fair value. Additions and improvements are capitalized. Maintenance and repairs are charged to operations as costs are incurred. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the related asset (except leasehold improvements which are depreciated over the shorter of their estimated useful life or the lease term) as follows:
|
| |
Buildings and improvements | 15-30 years |
Manufacturing equipment and tooling | 3-15 years |
Furniture, fixtures, and computer equipment | 3-10 years |
Other | 3-10 years |
Gross property, plant and equipment consist of the following at December 31:
|
| | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 |
Land | $ | 3,794 |
| | $ | 3,560 |
|
Buildings and improvements | 58,045 |
| | 46,270 |
|
Manufacturing equipment and tooling | 51,955 |
| | 46,814 |
|
Furniture, fixtures and computer equipment | 21,061 |
| | 17,266 |
|
Other | 5,762 |
| | 3,296 |
|
Construction in process | 20,108 |
| | 4,133 |
|
| $ | 160,725 |
| | $ | 121,339 |
|
The increase in gross property, plant and equipment in 2018 versus 2017 primarily related to construction of DynaEnergetics' new 74,000 square foot manufacturing assembly and administrative space on its manufacturing campus in Blum, Texas.
Asset Impairments
Finite-lived assets are tested for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying value may not be recoverable. We compare the expected undiscounted future operating cash flows associated with these finite-lived assets to their respective carrying values to determine if they are fully recoverable when indicators of impairment are present. If the expected future operating cash flows of an asset group are not sufficient to recover the related carrying value, we estimate the fair value of the asset. Impairment is recognized when the carrying amount of the asset group is not recoverable and when carrying value exceeds fair value. Long-lived assets to be disposed of, if any, are reported at the lower of carrying amount or fair value less cost to sell.
For the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2016, no impairments were recorded. For the year ended December 31, 2017, we recognized an impairment charge of approximately $1,241 (recorded in restructuring expenses) associated with restructuring our NobelClad operations in France, related to assets used in the explosion cladding process. The fair value of applicable French assets upon which an impairment charge was taken was primarily based upon the utilization of a third-party appraiser.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price in a business combination over the fair value of the net tangible and intangible assets acquired. The carrying value of goodwill is periodically reviewed for impairment (at a minimum annually) and whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the asset may not be recoverable. Examples of such events or changes in circumstances, many of which are subjective in nature, include significant negative industry or economic trends, significant changes in the manner of our use of the acquired assets or our strategy, a significant decrease in the market value of the assets, and a significant change in legal factors or in the business climate that could affect the value of the assets.
As required under Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") 350, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets”, we routinely review the carrying value of our net assets, including goodwill, to determine if any impairment has occurred. In the third quarter of 2017, activity in NobelClad’s primary end markets slowed considerably. NobelClad experienced a significant decline in its small size core maintenance bookings within the oil and gas industry. Additionally, certain large petrochemical projects previously forecasted to ship in the next twelve months were delayed, and uncertainty existed as to the ultimate timing of booking and shipping these potential orders. As a result, we determined that a potential indicator of goodwill impairment existed during the third quarter of 2017. We utilized an income approach (discounted cash flow analysis) to determine the fair value of the NobelClad reporting unit and concluded that our long-term forecasts were not materializing and needed to be revised downward. The key assumptions used in the discounted cash flow analysis included, among other measures, expected future sales, operating income, working capital and capital expenditures. The discount rate was determined using a peer-based, risk-adjusted weighted average cost of capital.
During 2017, we determined that the estimated fair value of the NobelClad reporting unit was less than its carrying value primarily due to the factors described above and their related impact on expected future cash flows. During the third quarter of 2017, we adopted FASB accounting standards update ("ASU") 2017-04, which amends and simplifies how an entity measures a goodwill impairment loss by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test. As the carrying value of the NobelClad reporting unit exceeded the fair value by more than the book value of goodwill, we recorded an impairment charge of $17,584 to fully impair all goodwill related to this reporting unit as of September 30, 2017.
No impairment of goodwill was identified in connection with our 2016 annual goodwill impairment test as our estimated fair value exceeded the carrying value.
The changes to the carrying amount of goodwill at the NobelClad segment during the periods are summarized below.
|
| | | |
| |
Balance at December 31, 2016 | $ | 16,097 |
|
Adjustment due to recognition of tax benefit of tax amortization of certain goodwill | (450 | ) |
Adjustment due to exchange rate differences | 1,937 |
|
Goodwill impairment | (17,584 | ) |
Balance at December 31, 2017 | — |
|
Purchased Intangible Assets
Our purchased intangible assets include finite-lived core technology, customer relationships and trademarks/trade names. For purchased intangible assets, we performed an assessment of recoverability in accordance with the general valuation requirements set forth under ASC 360, “Accounting for the Impairment of Long-Lived Assets.” If impairment indicators are present, estimated undiscounted future cash flows associated with applicable assets or operations are compared with their carrying value to determine if a write-down to fair value is required. During the years ended December 31, 2018, 2017, and 2016, we tested finite-lived intangibles for impairment, and found that the carrying amounts of assets at the lowest level of identifiable cash flows, in each case our reporting units, are fully recoverable.
Finite-lived intangible assets are amortized over the estimated useful life of the related assets which have a weighted average amortization period of 12 years in total. The weighted average amortization periods of the intangible assets by asset category are as follows:
|
| |
Core technology | 20 years |
Customer relationships | 9 years |
Trademarks / Trade names | 9 years |
Our purchased intangible assets, other than goodwill, consisted of the following as of December 31, 2018:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net |
Core technology | $ | 18,916 |
| | $ | (10,866 | ) | | $ | 8,050 |
|
Customer relationships | 37,122 |
| | (36,583 | ) | | 539 |
|
Trademarks / Trade names | 2,031 |
| | (2,031 | ) | | — |
|
Total intangible assets | $ | 58,069 |
| | $ | (49,480 | ) | | $ | 8,589 |
|
Our purchased intangible assets, other than goodwill, consisted of the following as of December 31, 2017:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net |
Core technology | $ | 20,027 |
| | $ | (10,333 | ) | | $ | 9,694 |
|
Customer relationships | 39,244 |
| | (36,077 | ) | | 3,167 |
|
Trademarks / Trade names | 2,149 |
| | (2,149 | ) | | — |
|
Total intangible assets | $ | 61,420 |
| | $ | (48,559 | ) | | $ | 12,861 |
|
The change in the gross value of our purchased intangible assets from December 31, 2017 to December 31, 2018 was due to foreign currency translation and an adjustment due to recognition of tax benefit of tax amortization previously applied to certain goodwill related to the NobelClad and DynaEnergetics reporting units. After the goodwill was written off at September 30, 2017 and December 31, 2015, respectively, the tax amortization reduces other intangible assets related to the historical acquisition.
Expected future amortization of intangible assets is as follows:
|
| | | |
For the years ended December 31 - | |
|
2019 | $ | 1,396 |
|
2020 | 1,396 |
|
2021 | 1,050 |
|
2022 | 823 |
|
2023 | 823 |
|
Thereafter | 3,101 |
|
| $ | 8,589 |
|
Contract Liabilities
On occasion, we require customers to make advance payments prior to the shipment of their orders in order to help finance our inventory investment on large orders or to keep customers’ credit limits at acceptable levels. Contract liabilities (previously known as customer advances) were as follows at December 31:
|
| | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 |
NobelClad | $ | 922 |
| | $ | 5,804 |
|
DynaEnergetics | 218 |
| | 84 |
|
Total | $ | 1,140 |
| | $ | 5,888 |
|
We expect to recognize the revenue associated with contract liabilities over a time period no longer than one year. All of the $5,888 recorded as contract liabilities at December 31, 2017, was recorded to net sales during the year ended December 31, 2018.
Revenue Recognition
On January 1, 2018, the Company adopted a new accounting standard, as amended, regarding revenue from contracts with customers using the modified retrospective approach, which was applied to all contracts with customers. Under the new standard, an entity is required to recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods.
There was no cumulative financial statement effect of initially applying the new revenue standard because an analysis of our contracts supported the recognition of revenue consistent with our historical approach. In accordance with the modified retrospective approach, the comparative information has not been restated and continues to be reported under the accounting standards in effect for those periods.
The Company’s revenues are primarily derived from consideration paid by customers for tangible goods. The Company analyzes its different goods by segment to determine the appropriate basis for revenue recognition, as described below. Revenue is not generated from sources other than contracts with customers and revenue is recognized net of any taxes collected from customers, which are subsequently remitted to governmental authorities. There are no material upfront costs for operations that are incurred from contracts with customers.
Our rights to payments for goods transferred to customers arise when control is transferred at a point in time and not on any other criteria. Payment terms and conditions vary by contract, although terms generally include a requirement of payment within 30 to 60 days. In instances when we require customers to make advance payments prior to the shipment of their orders, we record a contract liability. We have determined that our contract liabilities do not include a significant financing component given the short duration between order initiation and order fulfillment within each of our segments. Refer to Note 6 “Business Segments” for disaggregated revenue disclosures.
For the years ended December 31, 2018, 2017 and 2016, we recorded $282, $306, and $873 of bad debt expense, respectively.
NobelClad
Customers agree to terms and conditions at the time of initiating an order. The significant majority of transactions contain a single performance obligation - the delivery of a clad metal product. In instances where multiple products are included within an order, each product represents a separate performance obligation given that: (1) the customer can benefit from each product on a standalone basis and (2) each product is distinct within the context of the contract.
The transaction price is readily determinable and fixed at the time the transaction is entered into with the customer. NobelClad is entitled to each product’s transaction price upon the customer obtaining control of the item. Such control occurs as of a point in time, which is generally based upon relevant International Commercial Terms (“Incoterms”) as it relates to product ownership and legal title being transferred. Upon fulfillment of applicable Incoterms, NobelClad has performed its contractual requirements such that it has a present right to payment, and the customer from that point forward bears all risks and rewards of ownership. In addition, at this date, the customer has the ability to direct the use of, or restrict access to, the asset. No payment discounts, rebates, refunds, or any other forms of variable consideration are included within NobelClad contracts. NobelClad also does not provide service-type warranties either via written agreement or customary business practice, nor does it allow customer returns.
For contracts that contain only one performance obligation, the total transaction price is allocated to the sole performance obligation. For less frequent contracts which contain multiple distinct performance obligations, judgment is required to determine the standalone selling price (“SSP”) for each performance obligation. NobelClad uses the expected cost plus margin approach in order to estimate SSP, whereby an entity forecasts its expected costs of satisfying a performance obligation and then adds an appropriate margin for that good. The required judgment described herein largely is mitigated given the short duration between order initiation and complete order fulfillment.
DynaEnergetics
Customers agree to terms and conditions at the time of initiating an order. Transactions contain standard products, which may include perforating system components, such as detonating cord, or systems and associated hardware, including factory-assembled DynaStage® perforating systems and DynaSelect® detonators. In instances where multiple products are included within an order, each product represents a separate performance obligation given that: (1) the customer can benefit from each product on a standalone basis and (2) each product is distinct within the context of the contract.
The transaction price is readily determinable and fixed at the time the transaction is entered into with the customer. DynaEnergetics is entitled to each product’s transaction price upon the customer obtaining control of the item. Such control occurs as of a point in time, which is generally based upon relevant Incoterms as it relates to product ownership and legal title being transferred. Upon fulfillment of applicable Incoterms, DynaEnergetics has performed its contractual requirements such that it has a present right to payment, and the customer from that point forward bears all risks and rewards of ownership. In addition, at this date, the customer has the ability to direct the use of, or restrict access to, the asset. No payment discounts, rebates, refunds, or any other forms of variable consideration are included within contracts. DynaEnergetics also does not provide service-type warranties either via written agreement or customary business practice, nor does it allow customer returns without its prior approval.
For orders that contain only one performance obligation, the total transaction price is allocated to the sole performance obligation. For orders that contain multiple products being purchased by the customer, judgment is required to determine SSP for each distinct performance obligation. However, such judgment largely is mitigated given that products purchased are generally shipped at the same time. In instances where products purchased are not shipped at the same time, DynaEnergetics uses the contractually stated price to determine SSP as this price approximates the price of each good as sold separately.
Research and Development
Research and development costs include expenses associated with developing new products and processes as well as improvements to current manufacturing processes. Research and development costs are included in our cost of products sold and were as follows for the years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
DynaEnergetics research and development costs | $ | 5,932 |
| | $ | 4,335 |
| | $ | 3,990 |
|
NobelClad research and development costs | 1,278 |
| | 833 |
| | 609 |
|
Total research and development costs | $ | 7,210 |
| | $ | 5,168 |
| | $ | 4,599 |
|
Earnings Per Share
The Company computes earnings per share (“EPS”) using a two-class method, which is an earnings allocation formula that determines EPS for (i) each class of common stock (the Company has a single class of common stock), and (ii) participating securities according to dividends declared and participation rights in undistributed earnings. Restricted stock awards are considered participating securities as they receive non-forfeitable rights to dividends as common stock.
Basic EPS is then calculated by dividing net income (loss) available to common shareholders of the Company by the weighted‑average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted EPS adjusts basic EPS for the effects of restricted stock awards, performance share units and other potentially dilutive financial instruments (dilutive securities), only in the periods in which such effect is dilutive. The effect of the dilutive securities is reflected in diluted EPS by application of the more dilutive of (1) the treasury stock method or (2) the two-class method assuming nonvested shares are not converted into common shares. For the periods presented, diluted EPS using the treasury stock method was less dilutive than the two-class method; as such, only the two-class method has been included below.
EPS was calculated as follows for the years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Net income (loss) as reported | $ | 30,473 |
| | $ | (18,853 | ) | | $ | (6,505 | ) |
Less: Distributed net income available to participating securities | (27 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
Less: Undistributed net income available to participating securities | (666 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
Numerator for basic net income per share: | 29,780 |
| | (18,853 | ) | | (6,505 | ) |
Add: Undistributed net income allocated to participating securities | 666 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Less: Undistributed net income reallocated to participating securities | (662 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
Numerator for diluted net income per share: | 29,784 |
| | (18,853 | ) | | (6,505 | ) |
Denominator: | | | | | |
Weighted average shares outstanding for basic net income per share | 14,529,745 |
| | 14,346,851 |
| | 14,126,108 |
|
Effect of dilutive securities | 90,890 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Weighted average shares outstanding for diluted net income per share | 14,620,635 |
| | 14,346,851 |
| | 14,126,108 |
|
Net income (loss) per share: | | | | | |
Basic | $ | 2.05 |
| | $ | (1.31 | ) | | $ | (0.46 | ) |
Diluted | $ | 2.04 |
| | $ | (1.31 | ) | | $ | (0.46 | ) |
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. We are required to use an established hierarchy for fair value measurements based upon the inputs to the valuation and the degree to which they are observable or not observable in the market. The three levels in the hierarchy are as follows:
•Level 1 — Inputs to the valuation based upon quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets that are accessible as of the measurement date.
•Level 2 — Inputs to the valuation include quoted prices in either markets that are not active, or in active markets for similar assets or liabilities, inputs other than quoted prices that are observable, and inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data.
•Level 3 — Inputs to the valuation that are unobservable inputs for the asset or liability.
The highest priority is assigned to Level 1 inputs and the lowest priority to Level 3 inputs.
The carrying value of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable and payable, accrued expenses, revolving loans under our credit facility and borrowings under our capital expenditure facility approximate their fair value, and these are considered Level 1 assets and liabilities. Our foreign currency forward contracts are valued using quoted market prices or are determined using a yield curve model based on current market rates. As a result, we classify these investments as Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy.
We did not hold any Level 3 assets or liabilities as of December 31, 2018 or December 31, 2017. The goodwill impairment charge recorded in the third quarter of 2017 was calculated using Level 3 inputs.
Income Taxes
We recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future income tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities. Any effects of changes in income tax rates or tax laws are included in the provision for income taxes in the period of enactment. The deferred income tax impact of tax credits are recognized as an immediate adjustment to income tax expense. We recognize deferred tax assets for the expected future effects of all deductible temporary differences to the extent we believe these assets will more likely than not be realized. We record a valuation allowance when, based on current circumstances, it is more likely than not that all or a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. In making such determination, we consider all available positive and negative
evidence, including future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies, recent financial operations and their associated valuation allowances, if any.
We recognize the tax benefits from uncertain tax positions only when it is more likely than not, based on the technical merits of the position, that the tax position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of any related appeals or litigation. The tax benefits recognized in the Consolidated Financial Statements from such a position are measured as the largest benefit that is more likely than not to be realized upon ultimate resolution. We recognize interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions in operating expense.
See Note 5 "Income Taxes" for more information on our income taxes, including discussion of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017.
Concentration of Credit Risk and Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
Financial instruments, which potentially subject us to a concentration of credit risk, consist primarily of cash, cash equivalents, and accounts receivable. Generally, we do not require collateral to secure receivables. At December 31, 2018, we had no financial instruments with off-balance sheet risk of accounting losses.
Other Cumulative Comprehensive Loss
Other cumulative comprehensive loss as of December 31, 2018, 2017, and 2016 consisted entirely of currency translation adjustments including those in intra-entity foreign currency transactions that are classified as long-term investments.
Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
On January 1, 2018, the Company adopted a new accounting standard, as amended, regarding revenue from contracts with customers using the modified retrospective approach. This standard provides guidance on recognizing revenue, including a five-step model to determine when revenue recognition is appropriate. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations. Refer to Note 6 "Business Segments" for the related additional disclosures.
In October 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-16 which removes the prohibition against the immediate recognition of the current and deferred income tax effects of intra-entity transfers of assets other than inventory. This ASU is effective for public business entities in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years, and the Company adopted this ASU in the first quarter of 2018. The adoption of this ASU resulted in a reduction to January 1, 2018 “Retained earnings” in the Consolidated Balance Sheet of $65 and eliminated a $65 prepaid income tax balance.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2016, the FASB issued a new accounting pronouncement that requires lessees to record assets and liabilities on the balance sheet for lease-related rights and obligations and disclose key information about certain leasing arrangements. This new standard establishes a right-of-use (“ROU”) model that requires a lessee to recognize a ROU asset and lease liability on the balance sheet for all leases with a term longer than 12 months.
Leases will be classified as financing or operating, with classification affecting the pattern of expense recognition in the Statement of Operations. The Company will adopt the new standard, including the related amendments, effective January 1,
2019 using the modified retrospective approach, applying the provisions of the new standard on its effective date.
Management has substantially completed its analysis and determined that the significant majority of its leasing arrangements will be classified as operating. Additionally, management has implemented new systems to facilitate the requirements of the new standard and estimates the ROU asset to be less than 5% of total assets on January 1, 2019.
In June 2016, the FASB issued a new accounting pronouncement regarding credit losses for financial instruments. The new standard requires entities to measure expected credit losses for certain financial assets held at the reporting date using a current expected credit loss model, which is based on historical experience, adjusted for current conditions and reasonable and supportable forecasts. The Company is required to adopt the new standard on January 1, 2020. Management is currently evaluating the potential impact that the adoption of this standard will have on the Company's financial position, results of operations, and related disclosures.
3. DEBT
Outstanding borrowings consisted of the following at December 31:
|
| | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 |
Syndicated credit agreement: | |
| | |
|
U.S. Dollar revolving loan | $ | 17,128 |
| | $ | 18,250 |
|
Alternative currency revolving loan | — |
| | — |
|
Capital expenditure facility | 25,000 |
| | — |
|
Commerzbank line of credit | — |
| | — |
|
Outstanding borrowings | 42,128 |
| | 18,250 |
|
Less: debt issuance costs | (773 | ) | | (266 | ) |
Total debt | 41,355 |
| | 17,984 |
|
Less: current portion of long-term debt | (3,125 | ) | | — |
|
Long-term debt | $ | 38,230 |
| | $ | 17,984 |
|
Syndicated Credit Agreement
On March 8, 2018, we entered into a five-year $75,000 syndicated credit agreement (“credit facility”) which replaced in its entirety our prior syndicated credit facility entered into on February 23, 2015. The new credit facility allows for revolving loans of up to $50,000 with a $20,000 US dollar equivalent sublimit for alternative currency loans. In addition, the new agreement provides for a $25,000 Capital Expenditure Facility (“Capex Facility”) which has been used to assist in financing our DynaEnergetics manufacturing expansion project in Blum, Texas. The Capex Facility allowed for advances to fund capital expenditures of the Blum expansion project during year one of the credit facility. At the end of year one, the Capex Facility will convert to a term loan which will be amortizable at 12.5% of principal per year with a balloon payment for the outstanding balance upon the credit facility maturity date in year five. The credit facility has a $100,000 accordion feature to increase the commitments under the revolving loan class and/or by adding a term loan subject to approval by applicable lenders. We entered into the credit facility with a syndicate of three banks, with KeyBank, N.A. acting as administrative agent. The syndicated credit facility is secured by the assets of DMC including accounts receivable, inventory, and fixed assets, as well as guarantees and share pledges by DMC and its subsidiaries.
Borrowings under the $50,000 revolving loan limit can be in the form of one, two, three, or six month London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) loans. Additionally, US dollar borrowings on the revolving loan can be in the form of Base Rate loans (Base Rate borrowings are based on the greater of the administrative agent’s Prime rate, an adjusted Federal Funds rate or an adjusted LIBOR rate). LIBOR loans bear interest at the applicable LIBOR rate plus an applicable margin (varying from 1.50% to 3.00%). Base Rate loans bear interest at the defined Base rate plus an applicable margin (varying from 0.50% to 2.00%). All revolving loan borrowings and repayments have been in the form of one month loans and are reported on a net basis in our Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
Borrowings under the $20,000 alternate currency sublimit can be in euros, Canadian dollars, pounds sterling, and in any other currency acceptable to the administrative agent. Alternative currency borrowings denominated in euros, pounds sterling, and any other currency that is dealt with on the London Interbank Deposit Market shall be comprised of LIBOR loans and bear interest at the LIBOR rate plus an applicable margin (varying from 1.50% to 3.00%). We did not make any borrowings during 2018 under the alternative currency sublimit.
The credit facility includes various covenants and restrictions, certain of which relate to the payment of dividends or other distributions to stockholders; redemption of capital stock; incurrence of additional indebtedness; mortgaging, pledging or disposition of major assets; and maintenance of specified ratios. As of December 31, 2018, we were in compliance with all financial covenants and other provisions of our debt agreements.
As of December 31, 2017, we had a $35,000 syndicated credit agreement that allowed for revolving loans of $30,000 in U.S. dollars and $5,000 in alternative currencies as well as a $25,000 accordion feature to increase the commitments in any of the loan classes subject to approval by applicable lenders.
Line of Credit with German Bank
We maintain a line of credit with a German bank for our NobelClad and DynaEnergetics operations in Europe. This line of credit provides a borrowing capacity of €4,000 and is also used to issue bank guarantees to customers to secure advance payments made by them. As of December 31, 2018, we had no outstanding borrowings under this line of credit and bank guarantees of $2,370 secured by the line of credit. The line of credit bears interest at a EURIBOR-based variable rate which at December 31, 2018 was 3.33%. The line of credit has open-ended terms and can be canceled by the bank at any time.
Debt Issuance Costs
Included in long-term debt are deferred debt issuance costs of $773 and $266 as of December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Upon entering into the credit facility on March 8, 2018, we wrote off $159 of previously deferred debt issuance costs and incurred $821 of additional costs. Debt issuance costs of $507 were paid directly by the administrative agent and increased outstanding amounts under U.S. dollar revolving loans, and debt issuance costs of $314 were paid by the Company. Deferred debt issuance costs are being amortized over the remaining term of the credit facility, which expires on March 8, 2023.
4. STOCK OWNERSHIP AND BENEFIT PLANS
Our stock-based compensation expense results from restricted stock awards ("RSAs"), restricted stock units ("RSUs"), performance share units ("PSUs"), and stock issued under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan. The following table sets forth the total stock-based compensation expense included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Cost of products sold | | $ | 342 |
| | $ | 282 |
| | $ | 235 |
|
General and administrative expenses | | 2,862 |
| | 2,337 |
| | 1,755 |
|
Selling and distribution expenses | | 376 |
| | 356 |
| | 336 |
|
Restructuring expense | | — |
| | — |
| | 74 |
|
Stock-based compensation expense, net of income taxes | | 3,580 |
| | 2,975 |
| | 2,400 |
|
| | | | | | |
Earnings per share impact | | |
| | |
| | |
|
Basic | | $ | 0.25 |
| | $ | 0.21 |
| | $ | 0.17 |
|
Diluted | | $ | 0.24 |
| | $ | 0.21 |
| | $ | 0.17 |
|
On November 4, 2016, our stockholders approved the 2016 Omnibus Incentive Plan (“2016 Plan”). The 2016 Plan provides for the granting of various types of equity-based incentives, including stock options, RSAs, RSUs, stock appreciation rights, performance shares, performance units, other stock-based awards, and cash-based awards. Our stockholders approved a total of 5,000,000 shares available for grant under the 2016 Plan, less the number of awards outstanding under the 2006 Stock Incentive Plan ("2006 Plan") on September 21, 2016, which was the expiration date of the 2006 Plan. As of September 21, 2016, we had granted RSAs and RSUs representing an aggregate of 1,639,881 shares of stock under the 2006 Plan, leaving 3,360,119 shares available for grant under the 2016 Plan. As of December 31, 2018, we have granted RSAs and RSUs representing an aggregate of 550,275 shares of stock under the 2016 Plan, and 2,809,844 shares are available for future grant.
RSAs and RSUs are granted to employees and non-employee directors based on time-vesting. For RSAs or RSUs granted to employees, vesting occurs in one-third increments on the first, second, and third anniversary of the grant date. For RSAs or RSUs granted to non-employee directors, vesting occurs on the first anniversary of the grant date. Each RSA represents a restricted share that has voting and dividend rights and becomes fully unrestricted upon vesting. Each RSU represents the right to receive one share of stock upon vesting.
The fair value of RSAs and RSUs granted to employees and non-employee directors is based on the fair value of DMC’s stock on the grant date. RSAs and RSUs granted to employees and non-employee directors are amortized to compensation expense over the vesting period on a straight-line basis. Our policy is to recognize forfeitures of RSAs and RSUs as they occur.
PSUs are granted to employees with vesting based on performance and market conditions. Each PSU represents the right to receive one share of stock upon the achievement of two separate, equally-weighted performance conditions - the
achievement of a targeted Adjusted EBITDA goal and total shareholder return ("TSR") performance relative to a disclosed peer group. A target number of PSUs is awarded on the grant date, and the recipient is eligible to earn shares of common stock between 0% and 200% of the number of targeted PSUs awarded. The PSUs earned, if any, cliff vest at the end of the third year following the year of grant based on the degree of satisfaction of the PSUs performance and market conditions.
The fair value of PSUs with target Adjusted EBITDA performance conditions is based on the fair value of DMC’s stock on the grant date, and the value is amortized to compensation expense over the vesting period based on the relative satisfaction of the performance condition to date. The fair value of PSUs with TSR performance conditions is based on a third-party valuation simulating a range of possible TSR outcomes over the performance period, and the resulting fair value is amortized to compensation expense over the vesting period based on a straight-line basis. Our policy is to recognize forfeitures of PSUs as they occur.
A summary of the activity of our nonvested shares of RSAs issued under the 2016 Plan is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
Balance at December 31, 2016 | | — |
| | $ | — |
|
Granted | | 260,095 |
| | 15.27 |
|
Vested | | (4,027 | ) | | 13.05 |
|
Forfeited | | — |
| | — |
|
Balance at December 31, 2017 | | 256,068 |
| | $ | 15.31 |
|
Granted | | 102,817 |
| | 25.11 |
|
Vested | | (63,288 | ) | | 14.89 |
|
Forfeited | | (5,666 | ) | | 19.26 |
|
Balance at December 31, 2018 | | 289,931 |
| | $ | 18.81 |
|
A summary of the activity of our nonvested shares of RSAs issued under the 2006 Plan is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
Balance at December 31, 2015 | | 241,687 |
| | $ | 19.55 |
|
Granted | | 228,532 |
| | 8.07 |
|
Vested | | (144,008 | ) | | 15.08 |
|
Forfeited | | (42,634 | ) | | 10.82 |
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 | | 283,577 |
| | $ | 13.88 |
|
Granted | | — |
| | — |
|
Vested | | (130,547 | ) | | 12.41 |
|
Forfeited | | — |
| | — |
|
Balance at December 31, 2017 | | 153,030 |
| | $ | 15.14 |
|
Granted | | — |
| | — |
|
Vested | | (71,223 | ) | | 10.03 |
|
Forfeited | | (18,772 | ) | | 8.40 |
|
Balance at December 31, 2018 | | 63,035 |
| | $ | 22.91 |
|
A summary of the activity of our nonvested RSUs issued under the 2016 Plan is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
Balance at December 31, 2016 | | — |
| | $ | — |
|
Granted | | 73,000 |
| | 15.62 |
|
Vested | | — |
| | — |
|
Forfeited | | (500 | ) | | 15.60 |
|
Balance at December 31, 2017 | | 72,500 |
| | $ | 15.62 |
|
Granted | | 36,000 |
| | 21.88 |
|
Vested | | (13,175 | ) | | 15.61 |
|
Forfeited | | — |
| | — |
|
Balance at December 31, 2018 | | 95,325 |
| | $ | 17.99 |
|
A summary of the activity of our nonvested RSUs issued under the 2006 Plan is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Share Units | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
Balance at December 31, 2015 | | 87,162 |
| | $ | 18.33 |
|
Granted | | 48,855 |
| | 6.88 |
|
Vested | | (40,836 | ) | | 16.24 |
|
Forfeited | | — |
| | — |
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 | | 95,181 |
| | $ | 13.35 |
|
Granted | | — |
| | — |
|
Vested | | (36,450 | ) | | 13.30 |
|
Forfeited | | (333 | ) | | 6.22 |
|
Balance at December 31, 2017 | | 58,398 |
| | $ | 13.42 |
|
Granted | | — |
| | — |
|
Vested | | (32,069 | ) | | 10.74 |
|
Forfeited | | — |
| | — |
|
Balance at December 31, 2018 | | 26,329 |
| | $ | 16.69 |
|
A summary of the activity of our nonvested PSUs issued under the 2016 Plan is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
Balance at December 31, 2016 | | — |
| | $ | — |
|
Granted | | 23,000 |
| | 18.18 |
|
Vested | | — |
| | — |
|
Forfeited | | — |
| | — |
|
Balance at December 31, 2017 | | 23,000 |
| | $ | 18.18 |
|
Granted | | 23,000 |
| | 26.47 |
|
Vested | | — |
| | — |
|
Forfeited | | — |
| | — |
|
Balance at December 31, 2018 | | 46,000 |
| | $ | 22.32 |
|
As of December 31, 2018, total unrecognized stock-based compensation related to unvested awards was as follows:
|
| | | | | | |
| | Unrecognized stock compensation | | Weighted-average recognition period |
Unvested RSAs | | $ | 3,659 |
| | 2.1 years |
Unvested RSUs | | 1,009 |
| | 1.8 years |
Unvested PSUs | | 853 |
| | 1.6 years |
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
We have an Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”) pursuant to which we are authorized to issue up to 850,000 shares of DMC common stock of which 241,365 shares remain available for future purchase as of December 31, 2018. The offerings begin on the first day following each previous offering (“Offering Date”) and end six months from the Offering Date (“Purchase Date”). The ESPP provides that full time employees may authorize DMC to withhold up to 15% of their earnings, subject to certain limitations, to be used to purchase stock at the lesser of 85% of the fair market value of the stock on the Offering Date or the Purchase Date. In connection with the ESPP, 18,100, 26,519, and 45,888 shares of our stock were purchased during the years ended December 31, 2018, 2017, and 2016, respectively. Our total stock-based compensation expense for 2018, 2017, and 2016 includes $121, $92, and $54 respectively, in compensation expense associated with the ESPP.
401(k) Plan
We offer a contributory 401(k) plan to our employees. We make matching contributions equal to 100% of each employee’s contribution up to 3% of qualified compensation and 50% of the next 2% of qualified compensation contributed by each employee. Total DMC contributions were $828, $511, and $455 for the years ended December 31, 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Defined Benefit Plans
We have defined benefit pension plans at certain foreign subsidiaries for which we have recorded an unfunded pension obligation of $1,708 and $1,374 as of December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively, which is included in other long-term liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. All necessary adjustments to the obligation are based upon actuarial calculations and are recorded directly to the Consolidated Statements of Operations. We recognized expense of $406, $10 and $235 (recorded in general and administrative expenses) for the years ended December 31, 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
5. INCOME TAXES
The domestic and foreign components of income (loss) before taxes for our operations consist of the following for the years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Domestic | | $ | 9,399 |
| | $ | (5,942 | ) | | $ | (4,346 | ) |
Foreign | | 25,208 |
| | (9,342 | ) | | (1,362 | ) |
| | | | | | |
Total income (loss) before income taxes | | $ | 34,607 |
| | $ | (15,284 | ) | | $ | (5,708 | ) |
The components of the provision (benefit) for income taxes consist of the following for the years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Current – Federal | | $ | 444 |
| | $ | 946 |
| | $ | (888 | ) |
Current – State | | 371 |
| | 91 |
| | 55 |
|
Current – Foreign | | 6,972 |
| | 3,088 |
| | 1,914 |
|
| | | | | | |
Current income tax expense | | 7,787 |
| | 4,125 |
| | 1,081 |
|
| | | | | | |
Deferred – Federal | | 98 |
| | (393 | ) | | — |
|
Deferred – State | | — |
| | (5 | ) | | — |
|
Deferred -– Foreign | | (3,751 | ) | | (158 | ) | | (284 | ) |
| | | | | | |
Deferred income tax benefit | | (3,653 | ) | | (556 | ) | | (284 | ) |
| | | | | | |
Income tax provision | | $ | 4,134 |
| | $ | 3,569 |
| | $ | 797 |
|
Our deferred tax assets and liabilities consist of the following at December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 |
Deferred tax assets: | | |
| | |
|
Net operating loss carryforward | | $ | 8,843 |
| | $ | 10,144 |
|
Inventory differences | | 695 |
| | 570 |
|
Equity compensation | | 952 |
| | 591 |
|
Investment in subsidiaries | | 2,861 |
| | 3,514 |
|
Restructuring | | 12 |
| | 1,389 |
|
Purchased goodwill | | 2,516 |
| | 3,331 |
|
Accrued employee compensation and benefits | | 1,459 |
| | 979 |
|
Other, net | | 57 |
| | 144 |
|
Gross deferred tax assets | | 17,395 |
| | 20,662 |
|
Less valuation allowances | | (9,143 | ) | | (18,063 | ) |
Total deferred tax assets | | 8,252 |
| | 2,599 |
|
| | | | |
Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | |
Purchased intangible assets and goodwill | | (1,566 | ) | | (2,644 | ) |
Depreciation and amortization | | (2,783 | ) | | (267 | ) |
Other, net | | (281 | ) | | (163 | ) |
Total deferred tax liabilities | | (4,630 | ) | | (3,074 | ) |
| | | | |
Net deferred tax assets (liabilities) | | $ | 3,622 |
| | $ | (475 | ) |
As of December 31, 2018, we had loss carryforwards for tax purposes totaling approximately $55,062, comprised of $51,477 foreign and $3,585 domestic state loss carryforwards, which will be available to offset future taxable income in certain jurisdictions. Certain losses can be carried forward indefinitely, while the remainder generally have carryforward periods of 5 to 20 years, depending on jurisdiction. We have analyzed the net operating losses and placed valuation allowances on those where we have determined the realization is not more likely than not to occur.
We assess the available positive and negative evidence to estimate if sufficient future taxable income will be generated to use existing deferred tax assets. Additionally, a three-year cumulative loss at a Consolidated Financial Statement level may be viewed as negative evidence impacting a jurisdiction that by itself is not in a three-year cumulative loss position. At December 31, 2017, the Company was in a consolidated three-year cumulative loss position. Accordingly, we evaluated the impact on all jurisdictions and have recorded a valuation allowance against the corresponding net deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2017. At December 31, 2018, the Company was no longer in a consolidated three-year cumulative loss position. Accordingly,
we have evaluated deferred tax assets at the jurisdictional level and have released valuation allowances of $5,818 in jurisdictions where we believe sufficient future taxable income will be generated to use existing deferred tax assets. We continue to record valuation allowances against deferred tax assets where we do not believe sufficient future taxable income will be generated to use existing deferred tax assets. The amount of the deferred tax assets considered realizable, however, could be adjusted in future periods if positive evidence such as current and expected future taxable income outweighs negative evidence.
A reconciliation of our income tax provision computed by applying the Federal statutory income tax rate of 21% in 2018 and 35% in 2017 and 2016 to income before taxes is as follows for the years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Statutory U.S. federal income tax | | $ | 7,268 |
| | $ | (5,350 | ) | | $ | (1,998 | ) |
U.S. state income tax, net of federal benefit | | 430 |
| | 305 |
| | (158 | ) |
U.S. TCJA - net impact | | (604 | ) | | 4,435 |
| | — |
|
Foreign rate differential | | 3,054 |
| | (1,728 | ) | | 164 |
|
Tax audit adjustments | | (11 | ) | | 426 |
| | — |
|
Equity compensation | | (156 | ) | | (52 | ) | | 339 |
|
Deemed repatriation of foreign earnings | | 281 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Impairment of goodwill | | — |
| | 239 |
| | — |
|
Non-deductible penalties | | 1,686 |
| | 1 |
| | — |
|
Other | | 1,046 |
| | (95 | ) | | 97 |
|
Change in valuation allowances | | (8,860 | ) | | 5,388 |
| | 2,353 |
|
| | | | | | |
Provision for income taxes | | $ | 4,134 |
| | $ | 3,569 |
| | $ | 797 |
|
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (“TCJA”) was enacted in December 2017. Among other things, the TCJA reduced the U.S. federal corporate tax rate from 35% to 21% beginning in 2018, required companies to pay a one-time transition tax on unremitted earnings of non-U.S. subsidiaries that were previously tax deferred, and created new taxes on certain foreign sourced earnings. The SEC staff issued Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) 118, which provided guidance on accounting for enactment effects of the TCJA. SAB 118 provided a measurement period of up to one year from the TCJA’s enactment date for companies to complete their accounting under ASC 740. In accordance with SAB 118, we have completed our accounting for the tax effects of enactment of the Act as further described below.
The transition tax is a tax on previously untaxed accumulated and current earnings and profits ("E&P") of certain of the Company’s non-U.S. subsidiaries. To determine the amount of the transition tax, we determined, in addition to other factors, the amount of post-1986 E&P of the relevant subsidiaries, as well as the amount of non-U.S. income taxes paid on such earnings. E&P is similar to retained earnings of the subsidiary, but requires other adjustments to conform to U.S. tax rules. Further, the transition tax is based in part on the amount of those earnings held in cash and other specified assets. We were able to make a reasonable estimate of the transition tax and recorded a provisional obligation and additional income tax expense of $946 in the fourth quarter of 2017, which was reduced to $678 in the first quarter of 2018 in response to additional guidance received from the Internal Revenue Service ("IRS") and to $343 in the third quarter of 2018 upon completion of certain E&P calculations. There were no additional changes in the fourth quarter of 2018 to the amount previously calculated. The Company has elected to pay this liability over eight years. A payment of $76 was made during the second quarter of 2018. As of December 31, 2018, we reflected $267 in other long term liabilities.
In 2017, we performed a one-time remeasurement of certain deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the rates at which they were expected to reverse, generally 21% under the TCJA. As our U.S. deferred tax assets were fully offset by a valuation allowance, there was no net additional tax impact related to deferred tax assets and liabilities recognized in the fourth quarter of 2017.
Current year expense related to global intangible low-taxed income (“GILTI”) is included in Federal tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2018. Proposed regulations related to GILTI and the related foreign tax credits were released in 2018, and more guidance is expected to be released in 2019. We have calculated 2018 GILTI expense of $179 based on our interpretation of the statute with the information currently available. This amount may change when final guidance is issued by the IRS. We have elected to account for GILTI as period costs if and when incurred.
DMC files income tax returns in the U.S. federal jurisdiction, as well as various U.S. state and foreign jurisdictions. In the U.S., tax audits for the years 2012 through 2015 were closed during the second quarter of 2017, and no adjustments to the Company's tax provisions were proposed. In the spring of 2016, German tax authorities commenced an examination of the tax returns of our German subsidiaries for the 2011 through 2014 tax years. During 2017, German tax authorities proposed and we agreed to a settlement, with related assessments paid in 2018. The key provisions of the settlement resulted in increases to income related to various transfer pricing matters. We recorded an additional $251 in income tax expense and $41 of interest in 2017 to reflect these adjustments and the impact of these adjustments. German tax authorities have announced that an examination of the tax returns of our German subsidiaries for the 2015 through 2017 tax years will commence in 2019.
Most of DMC’s state tax returns remain open to examination for the tax years 2014 onward. DMC’s foreign tax returns generally remain open to examination for the tax years 2014 onward, depending on jurisdiction.
At December 31, 2018 and 2017, the balance of unrecognized tax benefits was zero. We recognize interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions in operating expense. As of December 31, 2018 and 2017, our accrual for interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions was zero.
The TCJA also provides that the repatriation to the U.S. of foreign earnings can be done without federal tax consequence. We have reassessed the assertion that cumulative earnings by our foreign subsidiaries are indefinitely reinvested. We continue to permanently reinvest the earnings of our international subsidiaries and therefore we do not provide for U.S. income taxes or withholding taxes that could result from the distribution of those earnings to the U.S. parent. If any such earnings were ultimately distributed to the U.S. in the form of dividends or otherwise, or if the shares of our international subsidiaries were sold or transferred, we could be subject to additional U.S. state income taxes. Due to the multiple avenues in which earnings can be repatriated, and because a large portion of these earnings are not liquid, it is not practical to estimate the amount of additional taxes that might be payable on these amounts of undistributed foreign income.
6. BUSINESS SEGMENTS
Our business is organized in the following two segments: NobelClad and DynaEnergetics. NobelClad is a global leader in the production of explosion-welded clad metal plates for use in the construction of corrosion resistant industrial processing equipment and specialized transition joints. DynaEnergetics designs, manufactures and distributes products utilized by the global oil and gas industry principally for the perforation of oil and gas wells.
The accounting policies of both segments are the same as those described in the summary of significant accounting policies. Our reportable segments are separately managed strategic business units that offer different products and services. Each segment’s products are marketed to different customer types and require different manufacturing processes and technologies.
Segment information is as follows as of and for the years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2018 |
| 2017 |
| 2016 |
Net sales: |
|
|
|
|
|
DynaEnergetics | $ | 237,448 |
| | $ | 121,253 |
| | $ | 67,290 |
|
NobelClad | $ | 88,981 |
| | $ | 71,550 |
| | $ | 91,285 |
|
Net sales | $ | 326,429 |
|
| $ | 192,803 |
|
| $ | 158,575 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Operating income (loss): |
|
|
|
|
|
DynaEnergetics | 44,476 |
| | 15,470 |
| | (5,381 | ) |
NobelClad | $ | 6,499 |
| | $ | (17,360 | ) | | $ | 8,878 |
|
Segment operating income (loss) | 50,975 |
|
| (1,890 | ) |
| 3,497 |
|
| | | | | |
Unallocated corporate expenses | (9,971 | ) | | (7,395 | ) | | (6,371 | ) |
Stock-based compensation | (3,580 | ) | | (2,975 | ) | | (2,400 | ) |
Other income (expense), net | (1,202 | ) | | (1,376 | ) | | 633 |
|
Interest expense | (1,620 | ) | | (1,651 | ) | | (1,070 | ) |
Interest income | 5 |
| | 3 |
| | 3 |
|
Income (loss) before income taxes | $ | 34,607 |
|
| $ | (15,284 | ) |
| $ | (5,708 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Depreciation and Amortization: |
|
|
|
|
|
DynaEnergetics | 6,308 |
| | 6,879 |
| | 6,768 |
|
NobelClad | $ | 3,212 |
| | $ | 3,687 |
| | $ | 3,999 |
|
Segment depreciation and amortization | $ | 9,520 |
|
| $ | 10,566 |
|
| $ | 10,767 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Acquisition of property, plant and equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
DynaEnergetics | 41,041 |
| | 4,025 |
| | 4,448 |
|
NobelClad | $ | 2,281 |
| | $ | 1,584 |
| | $ | 1,217 |
|
Segment acquisition of property, plant and equipment | 43,322 |
|
| 5,609 |
|
| 5,665 |
|
Corporate and other | 1,773 |
|
| 577 |
|
| 54 |
|
Consolidated acquisition of property, plant and equipment | $ | 45,095 |
|
| $ | 6,186 |
|
| $ | 5,719 |
|
|
| | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 |
Assets: | | | |
DynaEnergetics | 151,001 |
| | 98,640 |
|
NobelClad | $ | 59,831 |
| | $ | 57,906 |
|
Segment assets | 210,832 |
| | 156,546 |
|
| | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | 13,375 |
| | 8,983 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other assets | 8,530 |
| | 6,058 |
|
Deferred tax assets | 4,001 |
| | 98 |
|
Corporate property, plant and equipment | 3,680 |
| | 1,398 |
|
Consolidated assets | $ | 240,418 |
| | $ | 173,083 |
|
The geographic location of our property, plant and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation, is as follows at December 31:
|
| | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | 2017 |
United States | $ | 59,862 |
| | $ | 23,620 |
|
Germany | 27,442 |
| | 25,876 |
|
Russia | 7,256 |
| | 9,323 |
|
France | 377 |
| | 837 |
|
Kazakhstan | — |
| | 15 |
|
Canada | 198 |
| | 193 |
|
Rest of the world | 5 |
| | 8 |
|
Total | $ | 95,140 |
| | $ | 59,872 |
|
All of our sales are from products shipped from our manufacturing facilities and distribution centers located in the United States, Germany, Canada, and Russia. The following represents our net sales based on the geographic location of the customer for years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the years ended December 31, |
| 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
United States | $ | 221,847 |
| | $ | 116,083 |
| | $ | 78,999 |
|
Canada | 30,126 |
| | 23,377 |
| | 16,021 |
|
United Arab Emirates | 4,093 |
| | 1,768 |
| | 7,449 |
|
France | 4,581 |
| | 3,032 |
| | 3,744 |
|
South Korea | 2,263 |
| | 1,173 |
| | 1,690 |
|
Germany | 4,067 |
| | 5,397 |
| | 5,979 |
|
Russia | 4,117 |
| | 4,504 |
| | 3,731 |
|
India | 4,291 |
| | 2,927 |
| | 5,066 |
|
Egypt | 2,419 |
| | 2,721 |
| | 1,942 |
|
Spain | 1,083 |
| | 1,126 |
| | 1,500 |
|
Iraq | 314 |
| | 77 |
| | 13 |
|
China | 12,503 |
| | 3,673 |
| | 7,012 |
|
Italy | 1,730 |
| | 1,582 |
| | 2,577 |
|
Hong Kong | 496 |
| | 255 |
| | 699 |
|
Sweden | 2,339 |
| | 2,009 |
| | 2,124 |
|
Rest of the world | 30,160 |
| | 23,099 |
| | 20,029 |
|
Total | $ | 326,429 |
| | $ | 192,803 |
| | $ | 158,575 |
|
During the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2016, no single customer accounted for more than 10% of total net sales. During the year ended December 31, 2017, one customer in our DynaEnergetics segment was responsible for approximately 10% of total net sales.
7. DERIVATIVES
We are exposed to foreign currency exchange risk resulting from fluctuations in exchange rates, primarily the U.S. dollar to the euro, the U.S. dollar to the Canadian dollar, the euro to the Russian ruble, and, to a lesser extent, other currencies, arising from inter-company and third party transactions entered into by our subsidiaries that are denominated in currencies other than their functional currency. Changes in exchange rates with respect to these transactions result in unrealized gains or losses if such transactions are unsettled at the end of the reporting period or realized gains or losses at settlement of the transaction. During the third quarter of 2017, we began using foreign currency forward contracts to offset foreign exchange rate fluctuations on foreign currency denominated asset and liability positions. None of these contracts are designated as accounting hedges, and all changes in the fair value of the forward contracts are recognized in "Other income (expense), net" within our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
We execute derivatives with a specialized foreign exchange brokerage firm. The primary credit risk inherent in derivative agreements represents the possibility that a loss may occur from the nonperformance of a counterparty to the agreements, and thus we perform a review of the credit risk of our counterparties at the inception of the contract and on an ongoing basis. We anticipate that our counterparties will be able to fully satisfy their obligations under the agreements but will take action if doubt arises regarding the counterparties' ability to perform.
As of December 31, 2018 and 2017, the notional amounts of the forward currency contracts the Company held were $7,008 and $20,291, respectively. At December 31, 2018 and 2017, the fair values of outstanding foreign currency forward contracts were $0 and $79, respectively, and were recorded in accrued expenses.
The gain or loss recognized on derivatives is as follows for the years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Derivative type | | Income Statement Location | | 2018 | | 2017 | | 2016 |
Foreign currency contracts | | Other income (expense), net | | $ | (77 | ) | | $ | (157 | ) | | $ | — |
|
8. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Contingent Liabilities
The Company records an accrual for contingent liabilities when a loss is both probable and reasonably estimable. If some amount within a range of loss appears to be a better estimate than any other amount within the range, that amount is accrued. When no amount within a range of loss appears to be a better estimate than any other amount, the lowest amount in the range is accrued.
Anti-dumping and Countervailing Duties
In June 2015, U.S. Customs and Border Protection (“U.S. Customs”) sent us a Notice of Action that proposed to classify certain of our imports as subject to anti-dumping duties pursuant to a 2010 anti-dumping duty (“AD”) order on Oil Country Tubular Goods (“OCTG”) from China. A companion countervailing duty (“CVD”) order on the same product is in effect as well. The Notice of Action covered one entry of certain raw material steel mechanical tubing made in China and imported into the U.S. from Canada by our DynaEnergetics segment during 2015 for use in manufacturing perforating guns.
In July 2015, we sent a response to U.S. Customs outlining the reasons for our position that our mechanical tubing imports do not fall within the scope of the AD order on OCTG from China and should not be subject to anti-dumping duties. U.S. Customs proposed to take similar action with respect to other entries of this product and requested an approximately $1,100 cash deposit or bond for AD/CVD duties.
In August 2015, we posted bonds of approximately $1,100 to U.S. Customs. Subsequently, U.S. Customs declined to conclude that the mechanical tubing the Company had been importing was not within the scope of the AD order on OCTG from China. As a result, on September 25, 2015 the Company filed a request for a scope ruling with the U.S. Department of Commerce ("Commerce Department").
On February 15, 2016, the Company received the Commerce Department’s scope ruling, which determined certain imports, primarily used for gun carrier tubing, are included in the scope of the AD/CVD orders on OCTG from China and thus are subject to AD/CVD. On March 11, 2016, the Company filed an appeal with the U.S. Court of International Trade (“CIT”) related to the Commerce Department’s scope ruling. On February 7, 2017, the CIT remanded the scope ruling to the Commerce Department to reconsider its determination. The Commerce Department filed its remand determination with the CIT on June 7, 2017, continuing to find that the Company’s imports at issue are within the scope of the AD/CVD orders on OCTG from China. On March 16, 2018,
the CIT issued its decision on the appeal and sustained the Commerce Department’s scope ruling. The Company did not appeal this ruling, and during the quarter ended September 30, 2018, the Company paid the remaining accrued AD/CVD and interest of $3,461 to U.S. Customs.
On December 27, 2016, we received notice from U.S. Customs that it may pursue penalties against us related to the AD/CVD issue and demanding tender of alleged loss of AD/CVD in an amount of $3,049, which had previously been accrued for in our financial statements. We filed a response to the notice on February 6, 2017. On February 16, 2017, we received notice that U.S. Customs was seeking penalties in the amount of $14,783. U.S. Customs also reasserted its demand for tender of alleged loss of AD/CVD in the amount of $3,049. We tendered $3,049 in AD amounts on March 6, 2017 into a suspense account pending ultimate resolution of the AD/CVD case. We submitted a petition for relief and mitigation of penalties on May 17, 2017.
On March 27, 2018, we received notice from U.S. Customs Headquarters that it intended to move forward with its pursuit of penalties. The Company engaged in discussions with U.S. Customs Headquarters regarding the scope of penalties asserted and the arguments set forth in the Company’s petition for relief and mitigation of penalties. Based on these discussions and the Company’s assessment of the probable ultimate penalty rate, the Company accrued $3,103 in the first quarter of 2018.
On October 11, 2018, we received a decision from U.S. Customs Headquarters in which a mitigated amount of $8,000 in penalties was asserted. In its financial statements for the quarter ended September 30, 2018, the Company accrued an additional $4,897 of penalties. On December 7, 2018, we submitted a supplemental petition requesting a waiver of the penalty under the Small Business Regulatory Enforcement Act in lieu of tendering the penalty amount. We expect to receive a response to this waiver request by the end of the first quarter of 2019.
Patent and Trademark Infringement
On April 28, 2017, GEODynamics, Inc., a US-based oil and gas perforating equipment manufacturer based in Fort Worth, Texas (“GEODynamics”) filed a patent infringement action against DynaEnergetics US, Inc. (“DynaEnergetics”) in the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Texas (“District Court”) alleging infringement of U.S. Patent No. 8,220,394 (the “394 patent”), based on DynaEnergetics’ U.S. sales of its DPEX® and HaloFrac® shaped charges. The 394 patent case went to trial in early October 2018, and on October 10, 2018, the jury found in favor of DynaEnergetics on all counts.
On August 21, 2017, GEODynamics filed a patent infringement action against DynaEnergetics and DynaEnergetics Beteiligungs GmbH, both wholly owned subsidiaries of DMC (collectively, “DynaEnergetics EU”), in the Regional Court of Düsseldorf, Germany, alleging infringement of the German part DE 60 2004 033 297 of European patent EP 1 671 013 B1 granted on June 29, 2011, a patent related to the 394 patent (the “EP 013 patent”). DynaEnergetics EU filed its defense at the Regional Court of Düsseldorf and a nullity action against EP 013 at the German Federal Patent Court on February 14, 2018.
On September 27, 2017, DynaEnergetics filed a revocation action in the Patents Court, Shorter Trials Scheme in the UK against GEODynamics, asserting that the EP 013 patent, as maintained in the UK, is invalid. GEODynamics filed its defense in November 2017.
On November 9, 2018, DynaEnergetics entered into a global settlement agreement with GEODynamics, which resolves all outstanding claims and legal disputes between the parties concerning reactive shaped charge technology. All actions in the UK and Germany and other related actions have been dismissed. The settlement had no negative financial impact on DynaEnergetics.
Operating Leases and License Agreements
We lease certain office space, equipment, storage space, vehicles and other equipment under various non-cancelable lease agreements. Additionally, during 2008, we entered into a license agreement and a risk allocation agreement related to our U.S. NobelClad business. These agreements, which were amended in 2018, provide us with the ability to perform our explosive shooting process at a second shooting site in Pennsylvania.
Future minimum commitments under are as follows:
|
| | | | | | | |
For the years ended December 31 - | Operating Leases | | License and Risk Allocation Agreements |
2019 | $ | 2,234 |
| | $ | 300 |
|
2020 | 1,724 |
| | 300 |
|
2021 | 969 |
| | 300 |
|
2022 | 685 |
| | 300 |
|
2023 | 214 |
| | 300 |
|
Thereafter | 210 |
| | 1,275 |
|
Total minimum payments | $ | 6,036 |
| | $ | 2,775 |
|
Total rental expense included in continuing operations was $2,840, $2,988, and $2,510 for the years ended December 31, 2018, 2017, and 2016, respectively.
9. RESTRUCTURING
NobelClad
During the fourth quarter of 2017, NobelClad announced plans to consolidate its European production facilities by closing manufacturing operations in France. During the third quarter of 2018, final approval of the proposed measures was granted by the local workers council, in accordance with applicable French law. NobelClad completed the closure of the Rivesaltes production facility in the fourth quarter of 2018, but will maintain its sales and administrative office in France. NobelClad has entered into a sales agreement with a buyer for the manufacturing plant, and the sale is expected to close during the first quarter of 2019. Except for the sale of the manufacturing plant, the restructuring activities, including severance, equipment moving, legal fees and contract termination were completed as of December 31, 2018.
DynaEnergetics
In 2017, DynaEnergetics announced the closure of its operations in Kazakhstan after legislative changes increased our costs to do business while the overall sales in Kazakhstan were not significant to our results. In conjunction with the announcement, we recorded severance expense, wrote off remaining receivables, prepaid assets, and inventory, recorded an asset impairment to reduce the fixed assets to their salable value, and recorded within the Consolidated Statements of Operations foreign exchange losses that had previously been recorded within the Consolidated Balance Sheets through currency translation adjustments, due to the substantial liquidation of the entity.
In 2016, DynaEnergetics reduced headcount in Troisdorf, Germany and Austin, Texas, consolidated administrative offices to Houston, Texas and wrote-off certain assets after relocating perforating gun manufacturing operations from the previous leased facility in Troisdorf, Germany to the new facility in Liebenscheid, Germany.
Corporate Restructuring
In conjunction with the cost reductions announced in 2016, we eliminated certain positions and incurred restructuring charges associated with the accelerated vesting of stock awards.
Total restructuring charges incurred for these programs are as follows and are reported in the Restructuring expenses line item in our Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2018 |
| Severance | | Contract Termination Costs | | Equipment Moving Costs | | Other Exit Costs | | Total |
NobelClad | $ | 637 |
| | $ | 43 |
| | $ | 249 |
| | $ | 185 |
| | $ | 1,114 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2017 |
| Severance | | Asset Impairment | | Other Exit Costs | | Total |
NobelClad | $ | 2,513 |
| | $ | 1,241 |
| | $ | 71 |
| | $ | 3,825 |
|
DynaEnergetics | $ | 20 |
| | $ | 143 |
| | $ | 295 |
| | $ | 458 |
|
Total | $ | 2,533 |
| | $ | 1,384 |
| | $ | 366 |
| | $ | 4,283 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2016 |
| Severance | | Contract Termination Costs | | Equipment Moving Costs | | Other Exit Costs | | Total |
DynaEnergetics | 684 |
| | 386 |
| | 15 |
| | 43 |
| | 1,128 |
|
Corporate | 74 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 74 |
|
Total | $ | 758 |
| | $ | 386 |
| | $ | 15 |
| | $ | 43 |
| | $ | 1,202 |
|
The changes to the restructuring liability within accrued expenses associated with these programs is summarized below:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2017 | | Expense | | Payments | | Currency and Other Adjustments | | December 31, 2018 |
Severance | $ | 2,568 |
| | $ | 637 |
| | $ | (1,980 | ) | | $ | (120 | ) | | $ | 1,105 |
|
Contract termination costs | — |
| | 43 |
| | (43 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
Equipment moving costs | — |
| | 249 |
| | (241 | ) | | — |
| | 8 |
|
Other exit costs | 10 |
| | 185 |
| | (153 | ) | | — |
| | 42 |
|
Total | $ | 2,578 |
| | $ | 1,114 |
| | $ | (2,417 | ) | | $ | (120 | ) | | $ | 1,155 |
|
10. SELECTED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (UNAUDITED)
Selected unaudited quarterly financial data were as follows for the years ended December 31:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2018 |
| | Quarter ended March 31, | | Quarter ended June 30, | | Quarter ended September 30, | | Quarter ended December 31, |
Net sales | | $ | 67,313 |
| | $ | 80,915 |
| | $ | 87,883 |
| | $ | 90,318 |
|
Gross profit | | $ | 22,753 |
| | $ | 26,775 |
| | $ | 29,728 |
| | $ | 31,439 |
|
Net income | | $ | 3,920 |
| | $ | 6,372 |
| | $ | 4,910 |
| | $ | 15,271 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Net income per share | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 0.26 |
| | $ | 0.43 |
| | $ | 0.33 |
| | $ | 1.02 |
|
Diluted | | $ | 0.26 |
| | $ | 0.43 |
| | $ | 0.33 |
| | $ | 1.02 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2017 |
| | Quarter ended March 31, | | Quarter ended June 30, | | Quarter ended September 30, | | Quarter ended December 31, |
Net sales | | $ | 38,962 |
| | $ | 47,190 |
| | $ | 52,161 |
| | $ | 54,490 |
|
Gross profit | | $ | 10,366 |
| | $ | 14,018 |
| | $ | 17,162 |
| | $ | 17,845 |
|
Net income (loss) | | $ | (3,020 | ) | | $ | 189 |
| | $ | (14,064 | ) | | $ | (1,958 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net income (loss) per share | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | (0.21 | ) | | $ | 0.01 |
| | $ | (0.98 | ) | | $ | (0.13 | ) |
Diluted | | $ | (0.21 | ) | | $ | 0.01 |
| | $ | (0.98 | ) | | $ | (0.13 | ) |
ITEM 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
There are no changes in or disagreements with accountants on accounting and financial disclosure for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2018.
ITEM 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934). Based on that evaluation, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2018. Our management’s annual report on internal control over financial reporting is set forth below.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
The management of DMC Global Inc. (“DMC”) is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f).
Under the supervision and with the participation of DMC’s management, including its Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of DMC’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2018 based on the 2013 framework in "Internal Control - Integrated Framework" issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. In designing and evaluating the internal control over financial reporting, management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Based upon this evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that, as of December 31, 2018, our internal controls over financial reporting were effective.
DMC’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2018 has also been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their attestation report which expressed an unqualified opinion and is included elsewhere herein.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There has been no change in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) promulgated under the Exchange Act) during the fourth quarter of 2018, that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
|
| |
| /s/ Kevin Longe |
| Kevin Longe |
| President and Chief Executive Officer |
| February 21, 2019 |
| |
| /s/ Michael Kuta |
| Michael Kuta |
| Chief Financial Officer |
| February 21, 2019 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of DMC Global Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited DMC Global Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2018, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, DMC Global Inc. (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2018, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2018 and 2017, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), stockholders' equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2018, and the related notes and financial statement schedules listed in the Index at Item 15(a) and our report dated February 21, 2019 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
|
| |
| /s/ Ernst & Young LLP |
Denver, Colorado |
February 21, 2019 |
ITEM 9B. Other Information
Not applicable.
PART III
ITEM 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
Item 10 incorporates information by reference to our Proxy Statement for the 2019 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which is expected to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the close of fiscal year 2018.
ITEM 11. Executive Compensation
Item 11 incorporates information by reference to our Proxy Statement for the 2019 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which is expected to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the close of fiscal year 2018.
ITEM 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
Item 12 incorporates information by reference to our Proxy Statement for the 2019 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which is expected to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the close of fiscal year 2018.
For information regarding securities authorized for issuance under our equity compensation plans see the Proxy Statement for our 2019 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
Item 13 incorporates information by reference to our Proxy Statement for the 2019 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which is expected to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the close of fiscal year 2018.
ITEM 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
Item 14 incorporates information by reference to our Proxy Statement for the 2019 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which is expected to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the close of fiscal year 2018.
PART IV
ITEM 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a)(1) Financial Statements
See Index to Financial Statements in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, which is incorporated herein by reference.
(a)(2) Financial Statement Schedules
See Schedule II beginning on page 93 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
(a)(3) Exhibits
|
| | |
Exhibit Number | | Description |
3.1 | | |
3.2 | | |
10.1 | | |
10.6 | | |
|
| | |
Exhibit Number | | Description |
10.7 | | |
10.8 | | |
10.9 | | |
10.10 | | |
10.11 | | |
10.12 | | |
10.13 | | |
10.14 | | |
10.15 | | |
10.16 | | |
10.17 | | |
10.18 | | |
10.19 | | |
10.20 | | |
10.21 | | |
10.22 | | |
10.23 | | |
10.24 | | |
10.25 | | |
10.26 | | |
10.27 | | |
10.28 | | |
10.29 | | |
|
| | |
Exhibit Number | | Description |
10.30 | | |
21.1 | | |
23.1 | | |
31.1 | | |
31.2 | | |
32.1 | | |
32.2 | | |
101 | | The following materials from the Annual Report on Form 10-K of DMC Global Inc. For the year ended December 31, 2015, formatted in XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language): (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income, (iv) the Consolidated Statement of Stockholders’ Equity, (v) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, and (vi) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.** |
* Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
** Pursuant to Rule 406T of Regulation S-T, the Interactive Data Files on Exhibit 101 hereto are deemed not filed or part of a registration statement or prospectus for purposes of Sections 11 or 12 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, are deemed not filed for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and otherwise are not subject to liability under those sections.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Company has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
| | |
| DMC Global Inc. |
| |
| | |
February 21, 2019 | By: | /s/ Michael Kuta |
| | Michael Kuta |
| | Chief Financial Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Company and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
| | | | |
SIGNATURE | | TITLE | | DATE |
| | | | |
/s/ Kevin T. Longe | | President and Chief Executive Officer and Director | | February 21, 2019 |
Kevin T. Longe | | (Principal Executive Officer) | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Michael Kuta | | Chief Financial Officer | | February 21, 2019 |
Michael Kuta | | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | | |
| | | | |
/s/ David C. Aldous | | Chairman and Director | | February 21, 2019 |
David C. Aldous | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Yvon Pierre Cariou | | Director | | February 21, 2019 |
Yvon Pierre Cariou | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Robert A. Cohen | | Director | | February 21, 2019 |
Robert A. Cohen | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ James J. Ferris | | Director | | February 21, 2019 |
James J. Ferris | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Richard P. Graff | | Director | | February 21, 2019 |
Richard P. Graff | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Clifton Peter Rose | | Director | | February 21, 2019 |
Clifton Peter Rose | | | | |
DMC GLOBAL INC.
INDEX TO SCHEDULE II
AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2018
DMC GLOBAL INC.
SCHEDULE II(a) - VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS AND RESERVES
ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Balance at beginning of period | | Additions charged to income | | Accounts receivable written off | | Currency and Other Adjustments | | Balance at end of period |
Year ended - | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2016 | | $ | 974 |
| | $ | 873 |
| | $ | (351 | ) | | $ | (350 | ) | | $ | 1,146 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2017 | | $ | 1,146 |
| | $ | 306 |
| | $ | (174 | ) | | $ | (190 | ) | | $ | 1,088 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2018 | | $ | 1,088 |
| | $ | 282 |
| | $ | (742 | ) | | $ | (115 | ) | | $ | 513 |
|
DMC GLOBAL INC.
SCHEDULE II(b) - VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS AND RESERVES
WARRANTY RESERVE
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Balance at beginning of period | | Additions charged to income | | Repairs allowed | | Currency and Other
Adjustments | | Balance at end of period |
Year ended - | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2016 | | $ | 130 |
| | $ | 535 |
| | $ | (140 | ) | | $ | — |
| | $ | 525 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2017 | | $ | 525 |
| | $ | 218 |
| | $ | (466 | ) | | $ | 74 |
| | $ | 351 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2018 | | $ | 351 |
| | $ | 65 |
| | $ | (13 | ) | | $ | (9 | ) | | $ | 394 |
|